Advanced Network Management
Water utilities today face many challenges in improving asset management, coordinating daily operations, and responding to customer service requests and emergencies. To help address these challenges, Esri has developed next generation data structures and tools delivered via ArcGIS Utility Network. Utility Network enables utilities to not only store the location and associated information of assets, but also model internal configurations of complex assemblies such as pump houses, meter pits, and valve assemblies. Network connectivity of assets within complex assemblies is maintained, yet assets within assemblies can be hidden from view to keep maps from becoming cluttered.
With ArcGIS software and Utility Network, asset information and analysis capabilities are delivered to staff in the office and the field via desktop, web, and mobile apps. Analytical tools give staff actionable information for planning projects, operational oversight, and responding to emergencies. This enables more informed, confident decision-making. Water utilities are implementing Utility Network to enhance asset data quality, improve modeling and analytics capabilities, optimize operations workflows, and increase overall efficiency in their organizations.
Taking Modern Network Management to the Field
ArcGIS Field Maps is an all-in-one mobile application that combines many of the map viewing, data editing, and location sharing capabilities of the ArcGIS system. Field Maps is currently being used by many water organizations to help staff streamline their mobile workflows.
Having access to system and asset information in the field is critical for mobile workers at water organizations. With the map viewing capabilities of Field Maps, mobile workers can access detailed information about their system from their mobile devices, both online and offline. When workers are assigned to perform maintenance on an asset, they can use the Field Maps mobile application to check information, like the location, material type, and diameter of a pipe, to ensure they have the proper resources and equipment to complete their assigned tasks. Field Maps supports real-time access to your organization’s maps and system data. As information is updated from the office or by other mobile workers, it will be made immediately available across the organization.
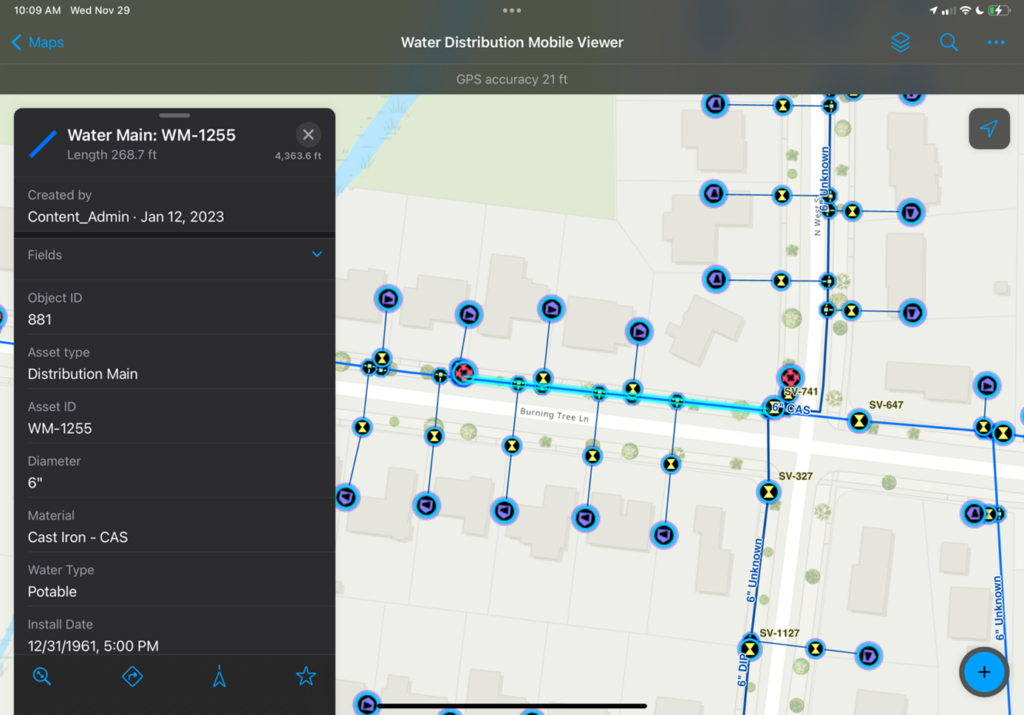
Image of water distribution map with water main feature popup in ArcGIS Field Maps.
Mobile staff at water organizations also need to be able to report their observations to those back in the office. Field Maps supports many common data collection workflows, making it easier than ever for mobile workers to collect new assets into their system, update existing data, and perform form-based workflows like asset inspections. In addition, the smart form capabilities of Field Maps easily allow organizations to digitize and modernize their paper-based workflows. While collecting, updating, and sharing data in an offline environment, once back online, edits made from mobile devices will automatically sync back to the office, and data will be updated on the mobile application based on changes from other sources.
Video demonstrating hydrant inspection data collection and smart form capabilities in ArcGIS Field Maps.
The location sharing and geofencing capabilities of Field Maps can be used to improve efficiency and safety for mobile workers. With location sharing, organizations can quickly locate the crews closest to work orders and emergencies in their systems, ultimately saving time when responding to these tasks and issues. Geofences in our maps allow users to define point, line, and polygon boundaries that will trigger alerts or enable location sharing when a mobile user enters or exits the area. Water organizations can use these geofences to track and alert workers of various hazards in the field. For example, notifying a mobile worker when they are entering a restricted area in the system, or automatically turning on location sharing when mobile staff enter a work zone.
Video demonstrating the location sharing and alert geofencing capabilities in ArcGIS Field Maps. Location sharing begins when the user enters the construction zone and ends when the user exits the area marked by the blue line. The user is also alerted of a hazardous area as they approach the blue polygon Excavation Site.
Utility Network Capabilities in the Palm of Your Hand
Field Maps is Utility Network aware! As water organizations adopt Utility Network, it’s important that they can take advantage of its advanced capabilities in the field. Field Maps currently supports the advanced viewing capabilities of Utility Network, with the ability to view connectivity associations, structural attachments, and containment of assets. Tracing analysis is also available within the Field Maps application, allowing mobile workers to quickly gain a better understanding of their system.
With support of connectivity associations, mobile workers can understand how complex assets are assembled and connected. With containment, mobile workers can access detailed representations of their buildings and facilities to understand where individual assets are located within larger and more detailed areas of their system. For example, with these modeling capabilities, a water engineer could open Field Maps on their mobile device and enter a meter vault, allowing them to immediately identify the individual meters, valves, tees, and pipes within. Then, with associations, they could understand which meters are connected to which buildings or individual units that the meter vault supports.
Video demonstrating connectivity associations and containment associations in ArcGIS Field Maps. Connectivity associations are used here to connect the customer meters to the service connection features. Containment is used to hide and display assets within the pump station boundary.
The tracing analysis capabilities of Utility Network can play a key role in how water organizations better understand their system. Named trace configurations can be set up in ArcGIS Pro and made accessible through the Field Maps application to support the workflows of mobile staff. Depending on an organization’s system and data schema, there are many ways to take advantage of tracing analysis. A valve isolation trace of a water distribution system allows mobile workers to quickly identify the closest valves to shut off water in the event of a main break or planned maintenance. An illicit discharge trace of a sewer or stormwater system makes it easy to identify upstream inlets and catch basins from a location where contaminants or pollutants are identified. Check out Esri’s documentation on Utility Network trace types to better understand what trace types are best for your organization and workflows.
Video demonstrating the network tracing capabilities in ArcGIS Field Maps. The user defines a point on the line that they want to isolate, and the trace returns all of the features that will be affected by this isolation, including which valves to close in order to isolate.
ArcGIS Utility Network is the next generation tool for water organizations to manage their asset system of record. The detailed data model and database tools of Utility Network ensure that asset information is both accurate and a more detailed reflection of the real world. With ArcGIS Field Maps’ support of Utility Network, those in the field are now able to access more accurate representations of their systems and gain a better understanding of how to accomplish their work during day-to-day activities. As the ArcGIS Field Maps application continues to implement the advanced capabilities of Utility Network, we know that these tools will play a key role in how organizations and mobile workers operate.
Stay Connected with Esri’s Water Team
ArcGIS is an extensive information system that enables modernization of workflows with easy-to-use applications for the field and office. Strengthen your organization with smart water solutions that will increase efficiency and provide insight for decision-makers. Visit the Esri Water Utilities web site for more information.
Join the Water Utilities Community
Follow #EsriWater on social media: Twitter | LinkedIn
Subscribe to the Water Industry newsletter “Esri News for Water Utilities and Water Resources“