Do you work with multidimensional scientific data? If so, ArcGIS Pro 3.0 has some new tools for creating Discrete Sampling Geometry output from netCDF data.
Multidimensional data represents geospatial data captured at multiple dimensionalities, such as time, depths, or heights. This type of data is commonly used in atmospheric, oceanographic, and earth sciences. ArcGIS Pro has many capabilities for creating, converting, visualizing, and performing complex analysis on this type of data. NetCDF is a specific open format for storing multidimensional scientific data (GRIB and HDF are the other main ones). For the netCDF format, the Climate and Forecast (CF) convention is a common standard for the description of attributes, names of variables, and units of multidimensional data.
The CF convention identifies several types of multidimensional Discrete Sampling Geometry (DSG) features that can be stored in netCDF files.
ArcGIS Pro 3.0 introduces new tools for creating feature class output from three types of DSG features—profiles, time series, and trajectories. Those tools are:
- NetCDF Profile To Feature Class (Discrete Sampling Geometry)
- NetCDF Time Series To Feature Class (Discrete Sampling Geometry)
- NetCDF Trajectories To Feature Class (Discrete Sampling Geometry)
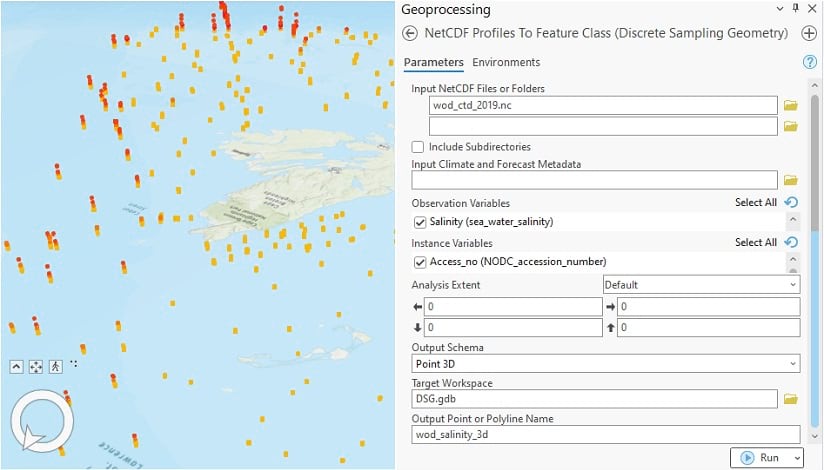
Everything you need to know about the new DSG tools, their input requirements, how they operate, and the output they produce is covered in the following help topic:
Learn more about multidimensional analysis, netCDF data, and the CF Conventions here:
- Multidimensional analysis in ArcGIS Pro
- What is netCDF data
- Climate and Forecast (CF) convention (cfconventions.org)
- Discrete Sampling Geometries (cfconventions.org)
ArcGIS Pro 3.0 was released on June 23, 2022.
Download it from here
A selection of the changes in this release can be found in the What’s New in ArcGIS Pro 3.0 blog post and video. For a more comprehensive list, see What’s New in ArcGIS Pro 3.0 in the online Help.



Article Discussion: