With the release of ArcGIS Pro 2.7 on December 16th 2020, the Spatial Statistics team is excited to share with you the new capabilities we’ve added in ArcGIS Pro 2.7, ranging from out of the box Data Engineering tools to sophisticated statistical methods for analysis. Let’s explore each of the new capabilities and tools in more detail!
New Data Engineering Tools
Data Engineering is an integral and often the most time-consuming part of an analysis. The following new tools available in ArcGIS Pro 2.7 can help make your data ready for subsequent analysis!
- Dimension Reduction: This new tool in Spatial Statistics toolbox (Utilities toolset) reduces the number of dimensions of a set of continuous variables into fewer components using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) or Reduced-Rank Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA).
Dimension reduction is commonly used to explore multivariate relationships between variables, reduce the computational cost of machine learning algorithms, and provide comparable (or better) results while consuming fewer computational resources. - Transform Field: This new tool in Data Management toolbox (Fields toolset) transforms continuous values by applying mathematical functions (such log, square root, Box-Cox, multiplicative inverse, square, exponential, and inverse Box-Cox) and changes the shape of the distribution.
A transformation can be applied to reduce skewness in the distribution and make it follow a normal (Gaussian) distribution. - Standardize Field: This new tool in Data Management toolbox (Fields toolset) standardizes continuous values by converting them to values that follow a specified scale. Standardization methods include z-score, minimum-maximum, absolute maximum, and robust standardization.
- Encode Field: This new tool in Data Management toolbox (Fields toolset) converts categorical values (string, integer, or date) into multiple numerical fields, each representing a category. The encoded numerical fields can be used in most data science and statistical workflows, including regression models.
- Reclassify Field: This new tool, also in Data Management toolbox (Fields toolset), reclassifies values in a numerical or text field into classes based on bounds defined manually or using a reclassification method.
New Spatial Statistics Tools
- Spatial Outlier Detection—This new tool in Spatial Statistics toolbox (Mapping Clusters toolset) identifies spatial outliers in point features by calculating the local outlier factor (LOF) of each feature. The LOF is a measurement that describes how isolated a location is from its local neighbors.
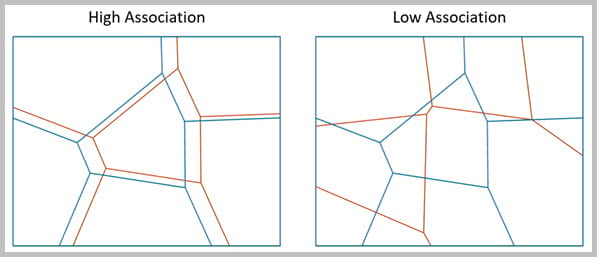
- Spatial Association Between Zones— This new tool in Spatial Statistics toolbox (Modeling Spatial Relationships toolset) measures the degree of spatial association between two regionalizations of the same study area in which each regionalization is composed of a set of categories, called zones. For example, this tool can be used to measure the association between forest type and soil class of the same study area.
- Neighborhood Summary Statistics— This new tool in Spatial Statistics toolbox (Measuring Geographic Distributions toolset) calculates local summary statistics of one or more numeric fields of point or polygon features using neighborhoods. The local statistics include mean (average), median, standard deviation, interquartile range, skewness, and quantile imbalance.
New Space Time Pattern Mining Tools
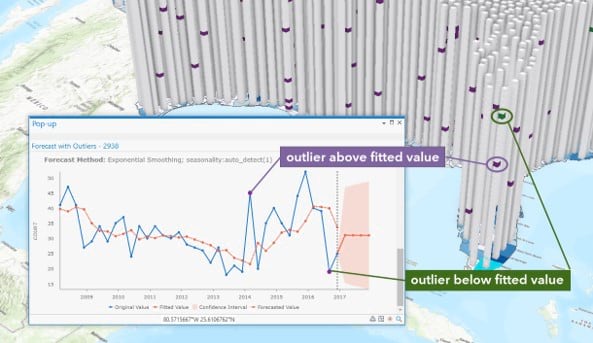
- Curve Fit Forecast, Exponential Smoothing Forecast, and Forest-based Forecast—Three new parameters detect and identify outliers in the time series at each location of a space-time cube. Identified outliers can be viewed using interactive pop-up charts on the output features.
- The Visualize Space Time Cube in 2D and Visualize Space Time Cube in 3D tools include a new display theme to visualize and explore the time series outliers of a space-time cube.
- Updated outlier display theme in Space Time Cube Explorer Add-in for ArcGIS Pro 2.7.
For a complete list of all the new capabilities in ArcGIS Pro 2.7, see What’s new in ArcGIS Pro 2.7.
Message from Spatial Statistics Team
In 2020 so many things have changed; the way we work, interact and collaborate. However, this pandemic has also showed us that somethings never change like the dedication of the GIS community to make this world a better place and our team’s commitment to continue providing the tools our users need to be successful. We can’t wait to see how you leverage these new tools and capabilities in your analysis workflows.


Commenting is not enabled for this article.