As the aviation industry embraces innovation, smart airports are transforming operations by leveraging cutting-edge technology to enhance airfield safety, regulatory compliance, and efficiency. For airports certified under Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Regulation 14 CFR Part 139, Certification of Airports (Part 139), this means automating inspections, optimizing maintenance workflows, and managing airside operations with real-time data insights. Esri’s suite of location-based tools enables airports to digitally manage inspections, streamline work orders, and monitor performance. From mobile data collection to integrated asset management, smart airports are revolutionizing how they function—driving safer, more efficient, and more environmentally sustainable aviation.
Streamlining Regulatory Compliance and Operational Efficiency
Airports certified under FAA Part 139 face challenges of maintaining airfield safety, ensuring compliance, and maximizing operation efficiency. Esri’s airfield operations tools streamline Part 139 airfield inspections, automate maintenance workflows, and provide real-time airside management insights. These tools, approved by the FAA, help airports meet requirements with secure, web-based dashboards that display discrepancies, real-time inspector locations, and work order status associated with issues.

Streamlined Data Collection
Leveraging configurable off-the-shelf (COTS) technology, airfield inspectors use tablets or mobile phones to conduct and log their daily Part 139 inspections. The form they use to log and report discrepancies is a simple survey that can be quickly configured to collect information about issues discovered during inspections, whether connected to the internet or offline. This survey mimics the inspector’s existing data collection format, saving significant time and effort. Additionally, owning the data collected about airside issues is valuable, as it avoids the costs and restrictions associated with third-party vendors.
The technology also links quickly to an airport’s work order/asset management system (EAM), automating the generation of work orders and notifications for needed repairs, thus reducing the time and effort required to identify and address issues.
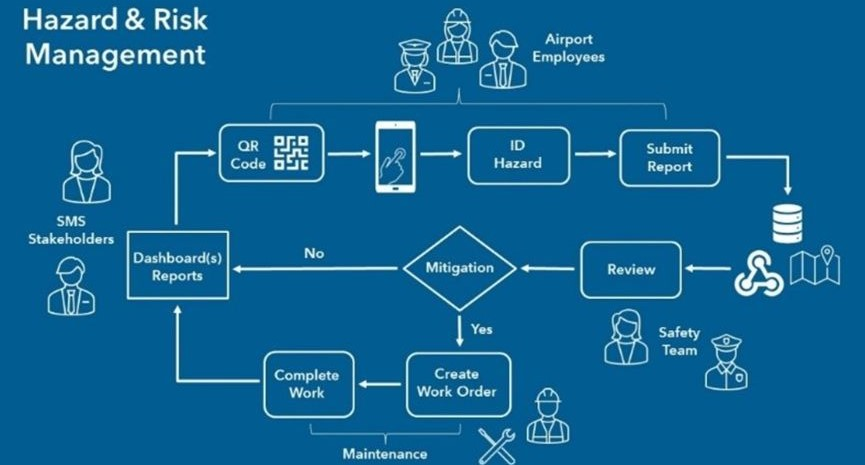
Based on the same technology, airports are using a variation of this technology to satisfy the FAA requirement to conduct daily fueling inspections, as well as a variety of other non-Part 139 safety related checks. Whether on the airside or landside, it is becoming common practice to deploy field crews equipped with mobile devices, with ready-to-use Esri apps such as ArcGIS Field Maps, ArcGIS Quick Capture, and ArcGIS Survey123 to quickly collect authoritative information that can be consumed real-time via dashboard. This information helps managers quickly make location-based, data-driven decisions.
Harnessing Indoor GIS for Efficient Facility Work Order Management
Airports must carefully monitor and control infrastructure maintenance costs. Indoor GIS empowers employees with indoor maps and apps to locate and navigate to infrastructure needing inspection or service, report issues, and track and visualize maintenance. The basis of indoor GIS is indoor mapping, enabled through ArcGIS Indoors. Indoors allows airports to visualize their indoor spaces, assets, and people on floor-aware maps, meaning they are associated to specific sites, facilities, and floor levels. Floor-aware maps help airports identify the spatial distribution of work orders and prioritize them based on proximity, asset type, specific facilities, or individual floors within a facility. This optimization of resource allocation ensures timely completion of repairs.
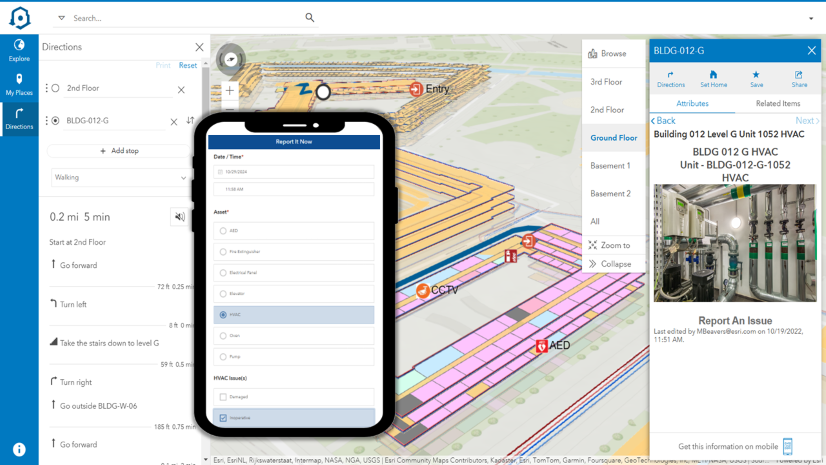
By integrating spatial data with work order management systems, GIS enables airports to efficiently track, prioritize, assign, and visualize work orders based on their locations, both indoors and outdoors. The ArcGIS Indoors web and mobile apps allow facilities managers and maintenance personnel to understand where maintenance is needed and underway. 360-degree photos provide a comprehensive view of the indoor environment and further help mobile workers understand local conditions within the facility to better prepare their maintenance work for efficient and effective services delivery.
Inside airport terminals, conveyances such as elevators, escalators, and moving walkways are crucial components of critical infrastructure. When any of these conveyances are out of service, it can lead to delays, negatively affecting on-time performance and passenger satisfaction. In larger airports like Atlanta Hartsfield, monitoring the real-time operational status of conveyances can be challenging.
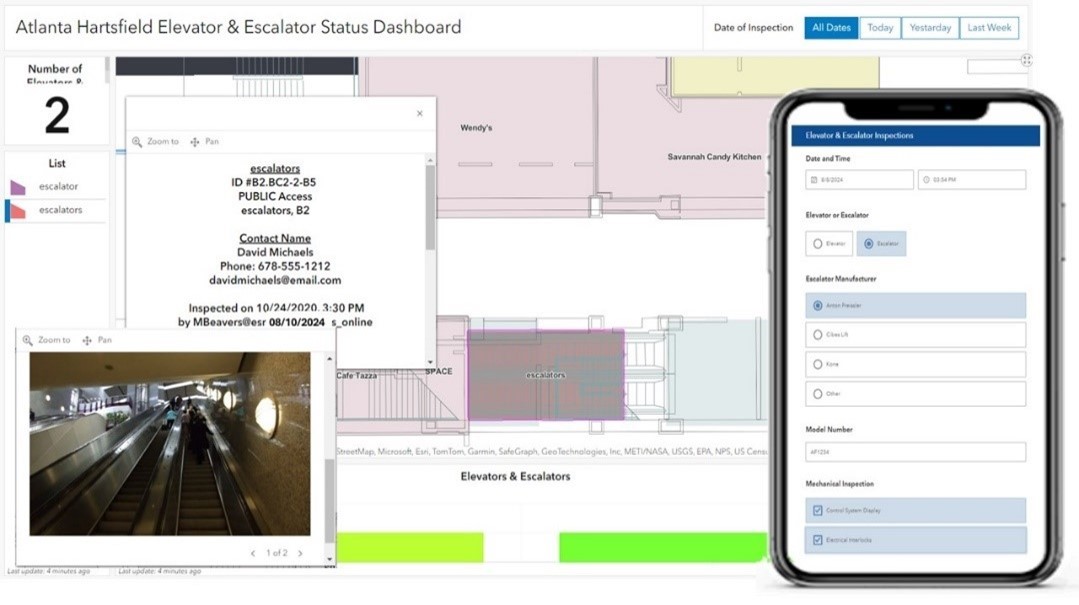
When they become inoperative, facility managers can utilize ArcGIS Dashboards to check the status and location of these assets. Additionally, using ArcGIS IPS, Esri’s indoor positioning system, helps mobile workers collecting data about the assets understand which building, floor, and area they are currently in- to identify the correct asset on the map and avoid data entry errors. Moreover, when unfamiliar with the precise location of conveyances requiring inspection, they can navigate to those assets in real-time using their mobile devices.
Watch this video to learn how organizations can streamline their facility asset management and inspections using indoor GIS.
Enhancing Coordination and Teamwork in Facilities Management
The ArcGIS Workforce application provides significant value for facilities and maintenance managers by enhancing coordination and teamwork among field workers. Dispatchers use a web app to create work assignments and send them to repair while localizing the workers in real-time. Mobile workers use an app to receive work assignments, navigate to repair sites, and complete to-do lists, while dispatchers receive progress updates. These tools also retain work activity records for FAA audits and inspections.
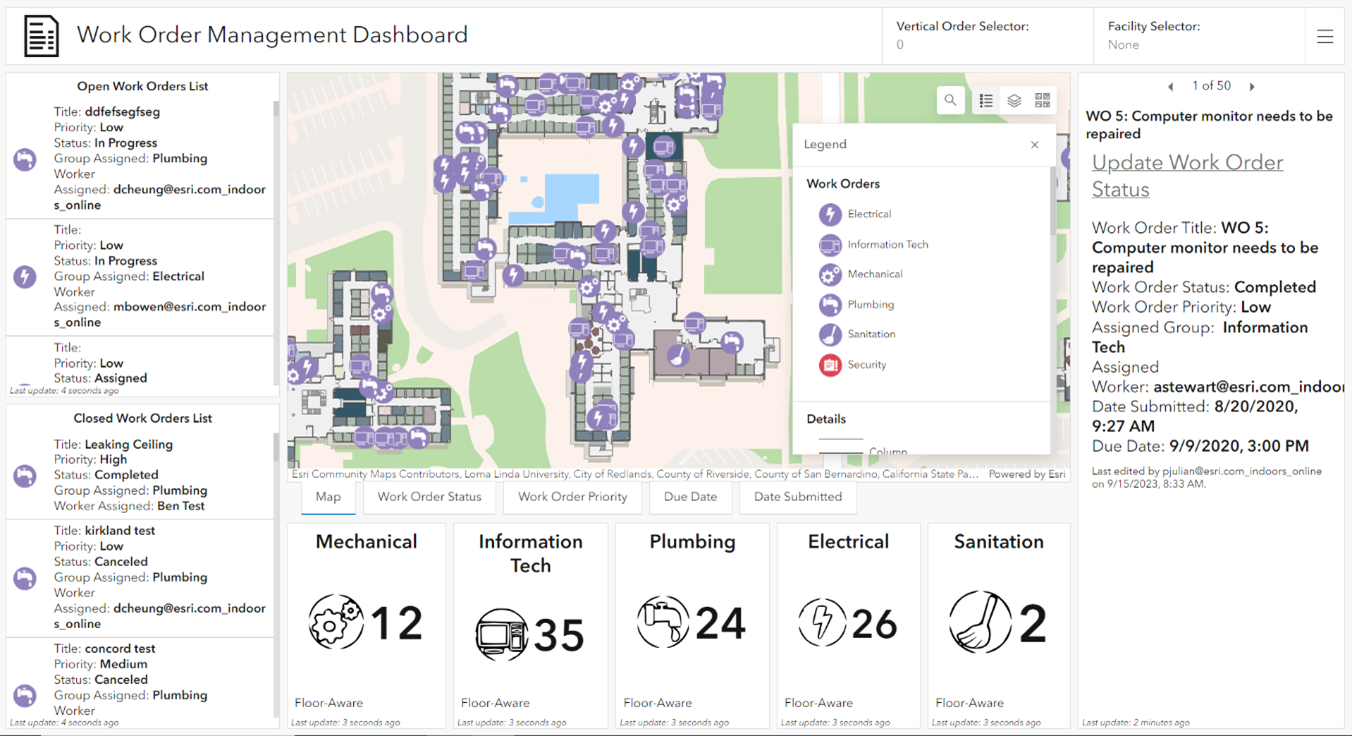
Building managers can also monitor the status, priority, and due dates of all work orders and repairs throughout each facility at the airport.
Dashboards for Live and Historic Activity Monitoring
GIS is employed to consume and visualize real-time flight locations, aircraft and ground support vehicles movements, gate utilization information, and on-time performance. By integrating air and ground traffic control systems, such as radar and smart GPS devices, with GIS, operations managers can visualize live and historic activities through dashboards. Configurable ArcGIS tools allow users to map, see, and understand movement patterns, enabling better data-based decision-making for routing and resource allocation. Understanding ground traffic movement helps planners and managers reduce inefficiencies. Additionally, ArcGIS mobile applications can be configured to collect field worker locations and track history, providing supervisors with valuable insights into the whereabouts of field crews across the air and landsides.
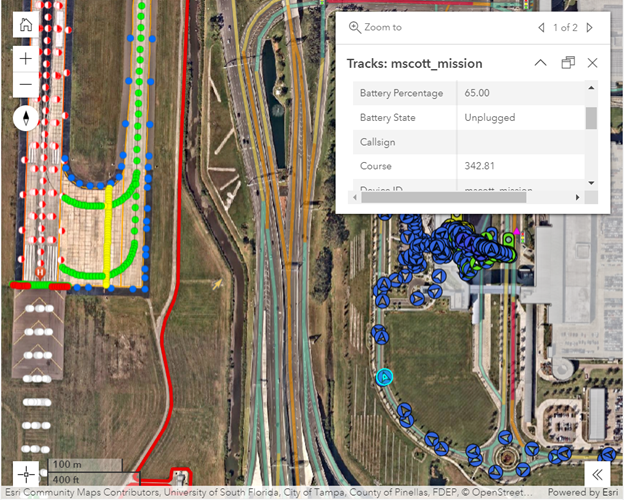
Transforming Data into Actionable Strategies
ArcGIS helps airports transform data into actionable strategies by generating insightful reports and visualizations for work order management. By analyzing historical work order data, airports can identify trends, patterns, and areas prone to repairs. This data-driven approach allows them to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and enhance overall performance.
Smart airports use GIS to continuously track energy usage and monitor building efficiency, contributing to significant cost savings over the lifespan of facilities.
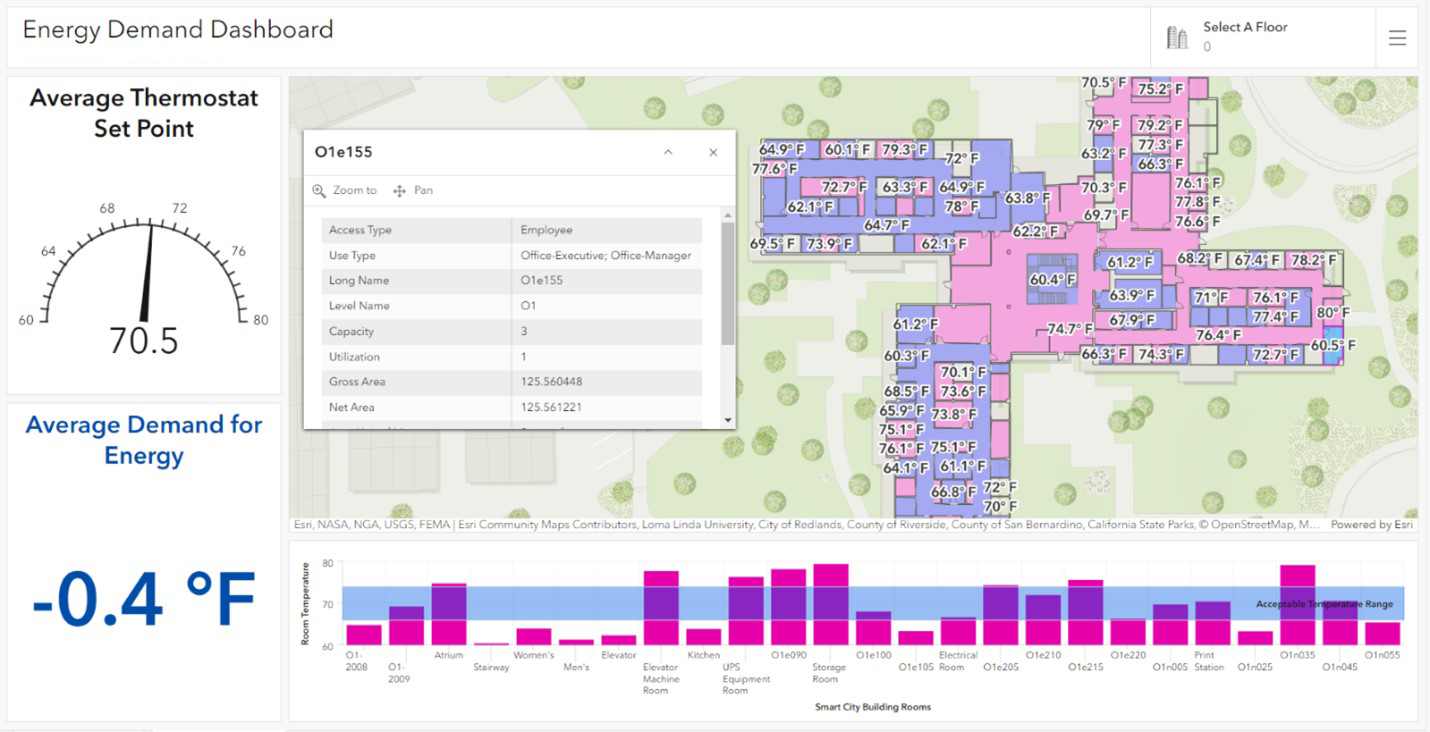
By connecting to smart sensors installed inside facilities, building officials can monitor and set temperatures in rooms and track average energy demand and usage. GIS maps and analyzes energy consumption at various scales, from individual rooms and buildings to entire campuses.
Esri’s location-based solutions empower airports to streamline safety, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency, marking a significant leap toward the smart airport of the future. By integrating GIS technology with FAA-approved workflows, airports can automate Part 139 inspections, better manage infrastructure, and enhance collaboration across teams. This real-time, data-driven approach transforms the way airports handle everything from work orders to airside operations, allowing for better decision-making and cost management. As the aviation industry continues to evolve, GIS technology is at the forefront of enabling smarter, safer, and more efficient airports.
Find more information and contact us via the following web pages:

Commenting is not enabled for this article.