Imagery can add valuable information and context to a wide array of GIS projects. For example, you can detect impervious surfaces for storm water management, map and manage riparian corridors, or track what’s changing in your county. Sometimes, though, incorporating imagery into your GIS can feel overwhelming—how can your system handle that much data?
Enter raster analytics, a distributed processing, storage, and sharing system designed to quickly process large collections of aerial, drone, or satellite imagery, then extract and share meaningful information for critical decision support. Raster analytics can be run locally, but you can also pair it with distributed cloud computing to maximize efficiency. Image processing and analysis jobs that used to take days or weeks can be completed in minutes or hours, bringing imagery projects that were impossibly large or daunting within reach.
Raster analytics leverages ArcGIS Enterprise, expanded with ArcGIS Image Server configured for distributed raster analysis, to integrate the components of the raster analytics system to support scalable, real-world workflows.
What can raster analytics do?
By leveraging ArcGIS Enterprise with ArcGIS Image Server, raster analytics enables you to:
- Quickly process massive imagery or raster datasets in a scalable environment
- Execute advanced, customized raster analysis
- Share results with individuals, departments, and organizations within or outside your enterprise
The scalable environment of raster analytics empowers you to perform computationally intensive image processing that would otherwise be out of reach or cost-prohibitive. When implemented on-site, raster analytics uses distributed processing to improve efficiency. You can also maximize efficiency by exploiting cloud platforms such as Amazon Web Services or Microsoft Azure, which allow you to dynamically increase or reduce your capacity based on the size and urgency of your projects. Either implementation can save you time, money, and resources.
Raster analytics uses all the advanced image processing and analysis capabilities of ArcGIS Pro to maximum advantage. Built-in raster functions cover preprocessing, orthorectification and mosaicking, remote sensing analysis, and an extensive range of math and trigonometry operators, while your custom functions can extend the platform’s analytical capabilities even further.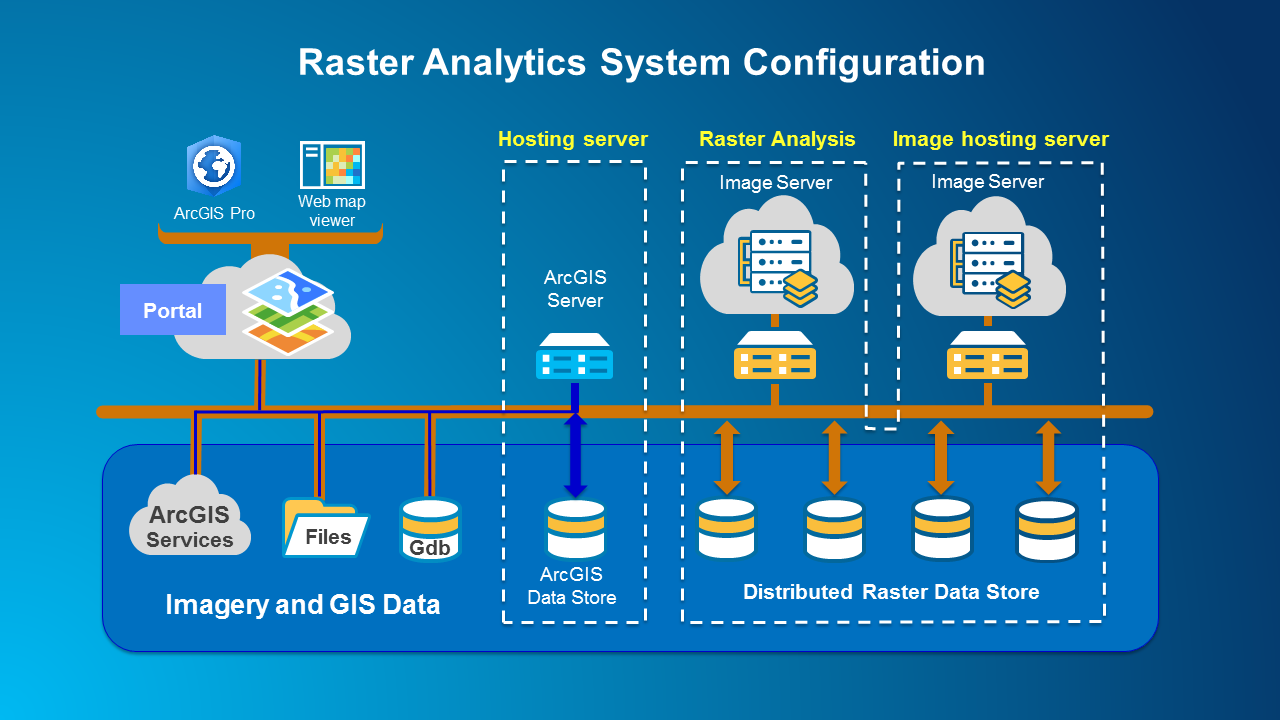
Raster analytics is also designed to streamline collaboration and sharing. Users across your enterprise can contribute data, processing models, and expertise to your imagery project, then share results with individuals, departments, and organizations in your enterprise.
Finally, raster analytics integrates your image processing and analysis with the world’s leading GIS platform, and allows users to seamlessly draw on Living Atlas of the World, the world’s largest collection of online digital maps and imagery.
How is raster analytics used today?
The Chesapeake Conservancy, working with the University of Vermont and WorldView Solutions, was tasked by the Chesapeake Bay Program to produce one-meter-resolution land cover maps covering 100,000 square miles of the Chesapeake Bay watershed. These high-resolution land cover maps, which classify natural and man-made landscape features, are crucial for supporting watershed and storm water management, conservation, and for reducing pollution into the bay.
To produce this essential dataset, the Chesapeake Conservancy needed to process over 20 terabytes of raster data and categorize it into twelve land cover types. This project took a daunting 18 months to complete using their local machine resources. As a result, Chesapeake Conservancy is now working with raster analytics in the cloud to make this timeline more efficient and cost-effective going forward.
As a proof of concept, they used raster analytics to produce a persistent one-meter land cover dataset of Kent County, Delaware (798 square miles). The Kent County project—comprised of more than 30GB and 3.8 billion pixels of raster data—ran on a ten-machine cluster, each with twenty cores, and completed in less than 5 minutes. This same job took days to to process on their local machines.
The Chesapeake Conservancy is now engaged in reprocessing the entire Chesapeake watershed to benchmark time and cost savings using raster analytics for the project. Using raster analytics for projects in the future will mean that the Chesapeake Conservancy can accomplish ambitious projects in a timely and cost-effective manner, without having to spend resources to acquire, configure, and maintain a large computing and storage infrastructure.
To see how raster analytics is being used, check out the Plenary presentation at the 2017 Esri User Conference in San Diego to hear about Chesapeake Conservancy’s experience processing and sharing the entire Chesapeake watershed using raster analytics.
More Information
To learn more about raster analytics using ArcGIS Enterprise and ArcGIS Image Server, check out the following video:
Explore these help topics to get started with raster analytics:
- Get Started with Raster Analytics
- Raster analysis on Portal for ArcGIS
- Configure the portal to perform raster analysis

Commenting is not enabled for this article.