While I was at the user conference earlier this year I was getting a lot of questions about migrating to the geodatabase from other data formats. I talked it over with Derek Law and he thought he’d make a podcast about it (we’ll link to that podcast when it hits the net). After seeing the script for his podcast I decided that some introductory style posts would also be a good way to get the info out to our users.
So this is the first in a series of posts that will be addressing how to migrate to the geodatabase. We’ll discuss migration strategies for five common GIS data formats:
- Shapefiles
- Coverages
- CAD
- Tables
- Imagery
ArcCatalog is the ArcGIS Desktop application that allows you to manage and access GIS data. Within ArcCatalog, there are two general workflows to migrate GIS data into the geodatabase:
- Import data into the geodatabase
- Export data into the geodatabase
Importing data into the geodatabase – in the Catalog tree, select the geodatabase you want to place your GIS data into, right-click and select Import from the context menu, then choose the appropriate data import tool.
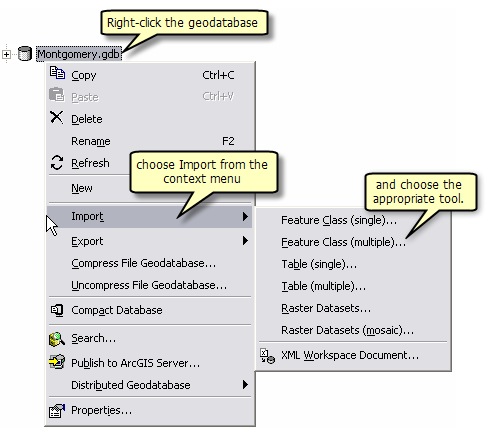
Exporting data into the geodatabase – In the Catalog tree, browse to and select the GIS dataset that you want to put into the geodatabase, right-click and select export from the context menu, then choose the appropriate data export tool
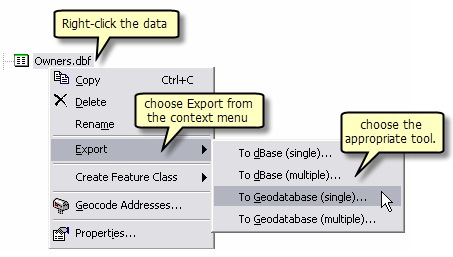
Both approaches use the same geoprocessing (GP) tools that are readily available directly within ArcToolbox, specifically in the Conversion Tools toolbox, in the To Geodatabase toolset.
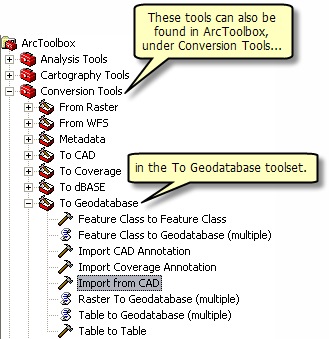
Since the To Geodatabase toolset migration tools are GP tools, you can leverage them within the ArcGIS geoprocessing framework.
This means that you can execute the migration tools in several different ways:
- As a regular tool dialog by activating the tool in ArcToolbox
- As part of a model in ModelBuilder
- Within a Python script
- Via the ArcGIS Desktop command line interface
For more detailed information on the different ways to execute a GP tool in ArcGIS, look in the Geoprocessing help book, in the ArcGIS Desktop help.
Migrating Shapefiles into a Geodatabase
So first, let’s look at migrating shapefiles into the geodatabase. A shapefile is the native data format for ArcView GIS 3.x technology. It is a type of feature class and therefore directly maps to the geodatabase as a single feature class when you migrate it to the geodatabase.
There are two key GP tools for migrating your shapefiles into the geodatabase:
- Feature Class to Feature Class
- Feature Class to Geodatabase
The Feature Class to Feature Class tool works on a single shapefile.
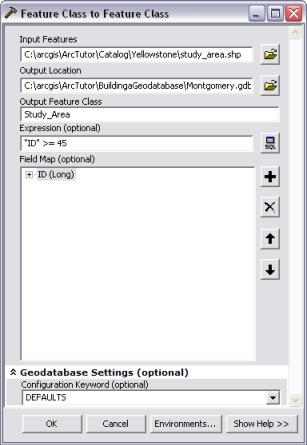
You will need to specify the following:
- Input Features – you can browse to a shapefile or drag and drop one into the input box.
- Output location – this can be the geodatabase or a feature dataset within the geodatabase. Again you can browse to a location or drag and drop one into the input box
- Output Feature Class – the name of the output feature class that will be created.
There are also 3 optional input parameters:
- Expression – enables you to define a SQL expression to select a subset of the rows in the input table to migrate.
- Field Map – provides options to add, rename, or delete fields when the input shapefile is converted to the output feature class.
- Configuration Keyword – this is used to specify storage parameters in ArcSDE geodatabases and File geodatabases.
For the Field Map parameter, we recommended that you drop the FID, shape_length, and shape_area attribute fields, because these will be replaced by new fields when the shapefile becomes a feature class in the geodatabase.
The Feature Class to Geodatabase tool works on multiple shapefiles. Idealy you would use this tool over the Feature Class to Feature Class tool if you had many shape files to migrate to a Geodatabase. To use this tool you specify one or more shapefiles to convert and the output geodatabase location. By default, the shapefiles will have the same names as the original shapefiles when they are migrated into the geodatabase.
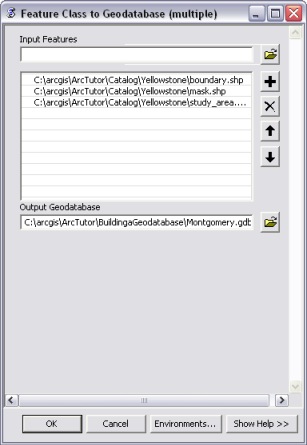
Using GP tools makes the task of migrating shapefile data into a geodatabase quick and painless. As mentioned before, GP tools can be used in a number of different ways including initiating the tools through ArcCatalog, using them directly from the toolbox, or scripting the tool execution in python.

Commenting is not enabled for this article.