Please note: This article has been updated. Please refer to these two articles, Beyond Open Data and ArcGIS Hub: A Catalyst for Creating Smart Communities for more current information.
Organizations create and manage a vast amount of data. Many organizations, such as government agencies, want to or are required to share certain data with the public. This data that’s freely available for people to obtain, use, and redistribute is called open data.
Open data is important for transparency and fostering innovation such as developing new products and services. Open data is also important for ensuring data integrity. But just being “open” often isn’t enough. Your open data also needs to be useful data—discoverable, accessible, explorable, and collaborative. But four common problems crop up:
1. People Can’t Find Your Data
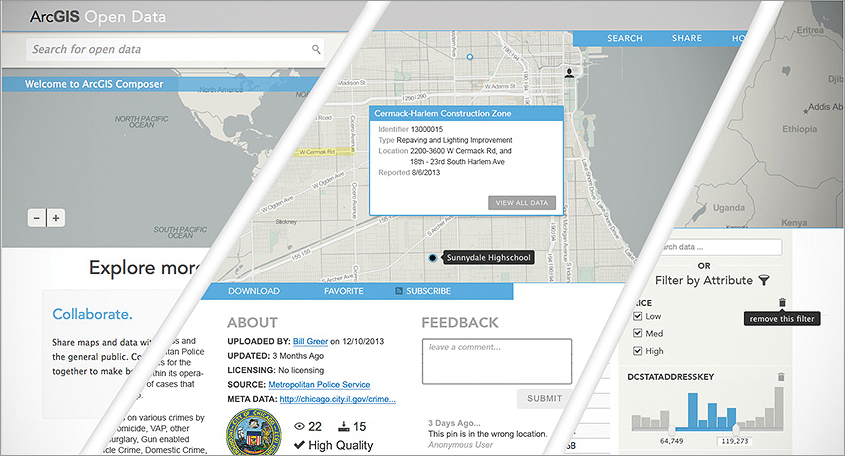
To be useful, people must first be able to find your open data. Open data available through Esri ArcGIS Online is easily discovered by the public. Not only does ArcGIS Online provide a web interface where people can search for the open data they are interested in, it also allows them to discover data through a general web search or by getting recommendations or notifications of new and relevant data.
2. People Can’t Access Your Data
People must be able to access your open data to freely reuse and integrate it into their own tools and applications.
ArcGIS Online can automatically make your data available in common formats for anyone to use. Data can be made available via a wide variety of mediums, such as APIs, web services, and common file formats. Ideally, the data is made available via multiple media that conform to open industry standards. Esri shapefile (SHP) is an open data format and industry standard. Additional open standards for geospatial data, such as KML, are managed by the Open Geospatial Consortium, Inc. The widespread comma-separated value (CSV) data format for storing tabular data is also commonly used for sharing geospatial data.
3. People Can’t Explore Your Data
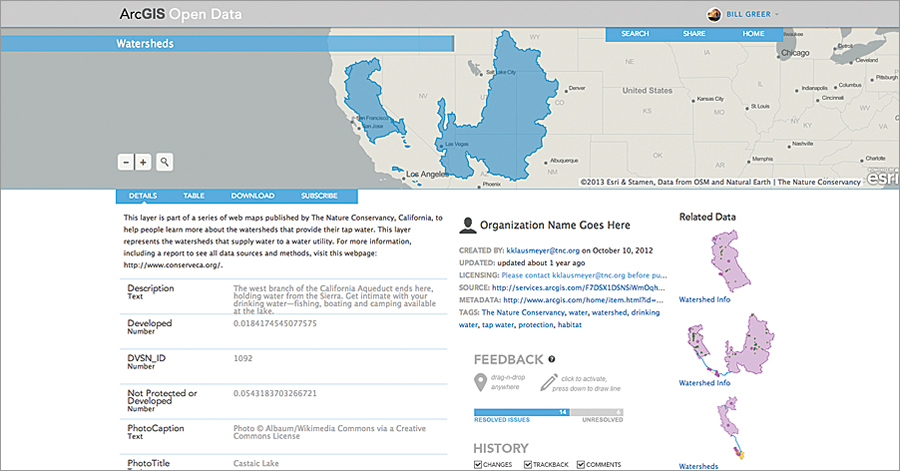
If people can’t filter, visualize, and analyze your open data, as well as combine it with other datasets, they won’t be able to use it to answer questions and make new discoveries.
Open data enhancements in ArcGIS Online are integrated into the ArcGIS platform, which allows people to combine open data with other datasets in ArcGIS Online or to bring the data into ArcGIS for Desktop for advanced geospatial analysis. By adhering to the open standards mentioned above, the data is also usable in other programs, such as spreadsheet or statistics packages, for additional analysis.
4. People Can’t Collaborate Well with Your Data
For your open data to be truly useful, people must be able to share the results of their exploration and analysis with the public and bring it back to the data provider.
The whole point of open data is to make it widely available so more people have access to it and can derive real value from it and then share it back with the community. Using ArcGIS Online, you can share and disseminate open data, for instance, by creating Web and mobile applications. The results are then open for feedback and improvements that can lead to further exploration and analysis, helping organizations and their data become an important part of the growing open data community.
Sign Up for a Free ArcGIS Online Trial
Using ArcGIS Open Data, available at no charge with an ArcGIS Online subscription, makes data discoverable, accessible, explorable, and collaborative within minutes.
Through a collaborative and social web application, data creators and publishers can share their authoritative open data with the world quickly, reliably, and seamlessly from their existing ArcGIS Online infrastructure.
If you don’t already have ArcGIS Online and want to see how easy it is to share your open data, sign up for a free 30-day trial.
For more information, visit ArcGIS Open Data.
