Finding the best site with GeoPlanner
Spero Vineyards is a small winery in Temecula, California, with a special mission. It teaches adults with developmental disabilities to work in the viticulture industry. The winery wants to expand its viticulture education program, so it needs to identify land that is suitable for growing wine grapes. In this exercise, you will learn how to use GeoPlanner for ArcGIS, a new web-based premium app hosted on ArcGIS Online, to find areas that will allow Spero Vineyards to enlarge its operations.
Focused on land-based planning and design activities, GeoPlanner helps you create, analyze, and report on planning alternatives. All data and reclassification functionality is available within the application. This makes the common GIS task of modeling suitability using weighted overlay easy by including data and tools you can learn to use quickly in a web application. [See the accompanying article “Understanding Weighted Overlay.”]
The New Weighted Overlay Model tool in GeoPlanner uses 24 Esri-curated landscape layers. These layers represent the physical structure of the United States, including hydrography, soil characteristics, geologic units, and land surface forms. These data layers are maintained and updated by Esri so your analyses execute against current data.
Powerful server-side processing frees up local computing resources so you can use GeoPlanner from nearly any device at any time. By providing the data, analytical tools, and a hosted environment, GeoPlanner gives you access to sophisticated analysis without requiring a high level of expertise or investments in time and money to acquire and maintain data.
Processing the weighted overlay is done by ArcGIS Online. The resultant suitability model is a new hosted image layer that can be viewed at any scale for the continental United States. Because the output image layer is stored in the ArcGIS cloud, it can be accessed from many connected devices.
Establishing Criteria
By identifying and rating areas based on criteria that you have determined will reveal opportunities, risks, and constraints, suitability models help answer questions such as, Where are the greatest fire risks? or Where are optimal locations for a new housing development? The answers generated depend on the data you use and criteria you define.
Spero Vineyards has defined four criteria to identify land suitable for additional vineyards.
- To receive the correct amount of sun, the aspect of the land should be east or west.
- For ideal growing conditions, the elevation should be approximately 1,400 to 1,600 feet.
- To enable circulation of colder air, land should be on a 5 to 10 percent slope.
- In addition, Native American lands, areas of open water, and areas of residential development should be excluded from consideration.
Accessing GeoPlanner
With the criteria for analysis chosen, the next step is accessing GeoPlanner. If you have an ArcGIS organizational subscription, you can sign up for a trial of the GeoPlanner app and add it to your ArcGIS organizational subscription.
- Sign in to ArcGIS.com with administrator credentials.
- Click Groups at the top of the site.
- Click Create A Group. Name it GeoPlanner App. Add information about this group under Summary and Description. Add a tag and set status to Organization. Optionally, add to this group some ArcGIS Online members to whom you want to give access to the GeoPlanner app.
- Go to ArcGIS Marketplace and search for GeoPlanner. Click the item listing. Click Try it Now and enter your ArcGIS Online administrator credentials. Fill out the form, agree to terms and conditions, and click Submit.
- In the Thank you page, click the link to your console.
- In the My Console page, click View Item and share it with the group you created in step 3. Click OK.
- Click Open and choose View Application from the drop-down menu.
- GeoPlanner is now ready to use for you and the members of the group created in step 3. Sign in to GeoPlanner using your ArcGIS Online credentials.

Getting Started with a Template
To perform weighted overlay analysis in GeoPlanner, you will choose a template when you create a new project and then open the New Weighted Overlay Model widget
- In the Getting started screen, choose Create a New Project.
- In the template gallery, click the Select button for the GeoPlanner Template for Land Use Planning.
- In the Create Project dialog box, type “Spero Vineyards” for Title. Add a summary, description, and a tag and click Create.
- When the project opens, click the Find tool in the button bar and type “Temecula CA” to zoom the map extent into the area of interest.
- Click the big blue action button in the upper left corner labeled Project and choose Assess from the drop-down.
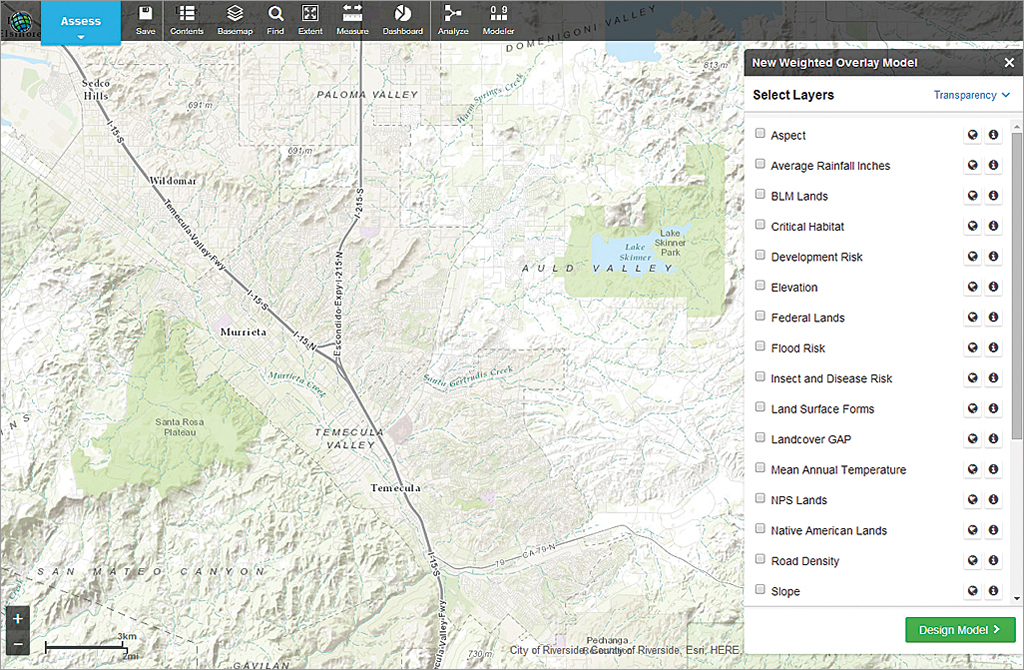
- Click the Modeler button on the far right of the button bar. The New Weighted Overlay Model widget appears on the right side of the browser containing a list of layers.
Performing Suitability Analysis
Next let’s choose the layers, set the weights, and reclassify raster values to a common suitability scale using the criteria previously determined.
Check the boxes beside the Aspect, Elevation, Landcover GAP, Native American Lands, and Slope layers to turn them on. Click the Design Model button.
Click Color Ramp and set the color ramp to Low (Red) to High (Green).
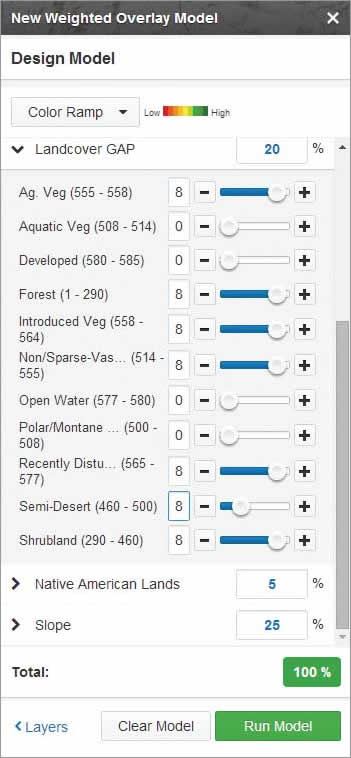
For Elevation, assign a weight of 25. Click the > symbol. The values in the widget are given in meters, rather than feet. The ideal elevation of 1400–1600 feet is 426–487 meters and falls into the 300–800 range, so set Medium (300–800) to 8 either by moving the slider or typing in the value. Set all other elevation values to 1. Setting these values represents the reclassification of the input raster cell values to a common suitability scale. (Read the accompanying article “Understanding Weighted Overlay” for more information.)
For Aspect, assign a weight of 25. Click the > symbol and set NE, E, W, and NW to 8 and all other Aspect values to 1.
For Landcover GAP, type “20” in the % text box and set Aquatic Veg, Developed, Open Water, and Polar/Montane to 0 and set the other parameters to 9. This will remove lakes, residential development, and other unsuitable land uses from the analysis.
For Native American Lands, type “5” in the % text box. Click the > symbol next to Native American Lands and set Native American lands to 0 and Non-Native American lands to 8.
For Slope, type “25” in the % text box. This assigns a value of 25 percent for the weight of Slope in the weighted overlay analysis. Click the > symbol next to Slope. Set the Slope value for Low (3–8) as 8 and all others to 1. This will map all values of 0–2, and 9–82 to a suitability value of 1. Values of 3–8 will be reclassified to a value of 8.
Click the Run Model button. In the Save Model dialog box, name the model Spero Vineyards Potential Sites and click Save.
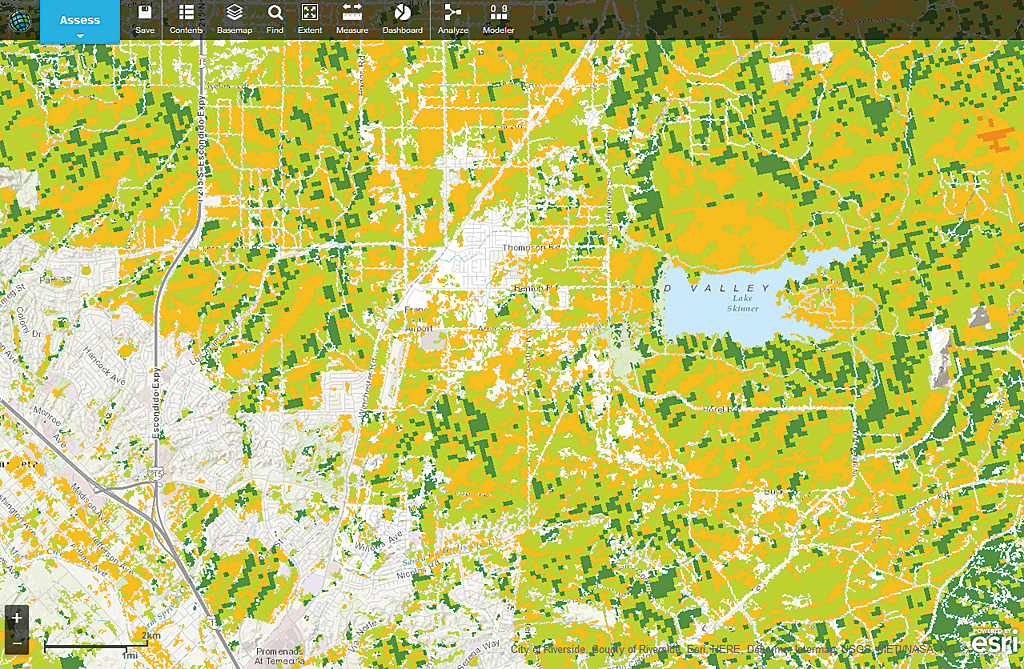
Looking at the Results
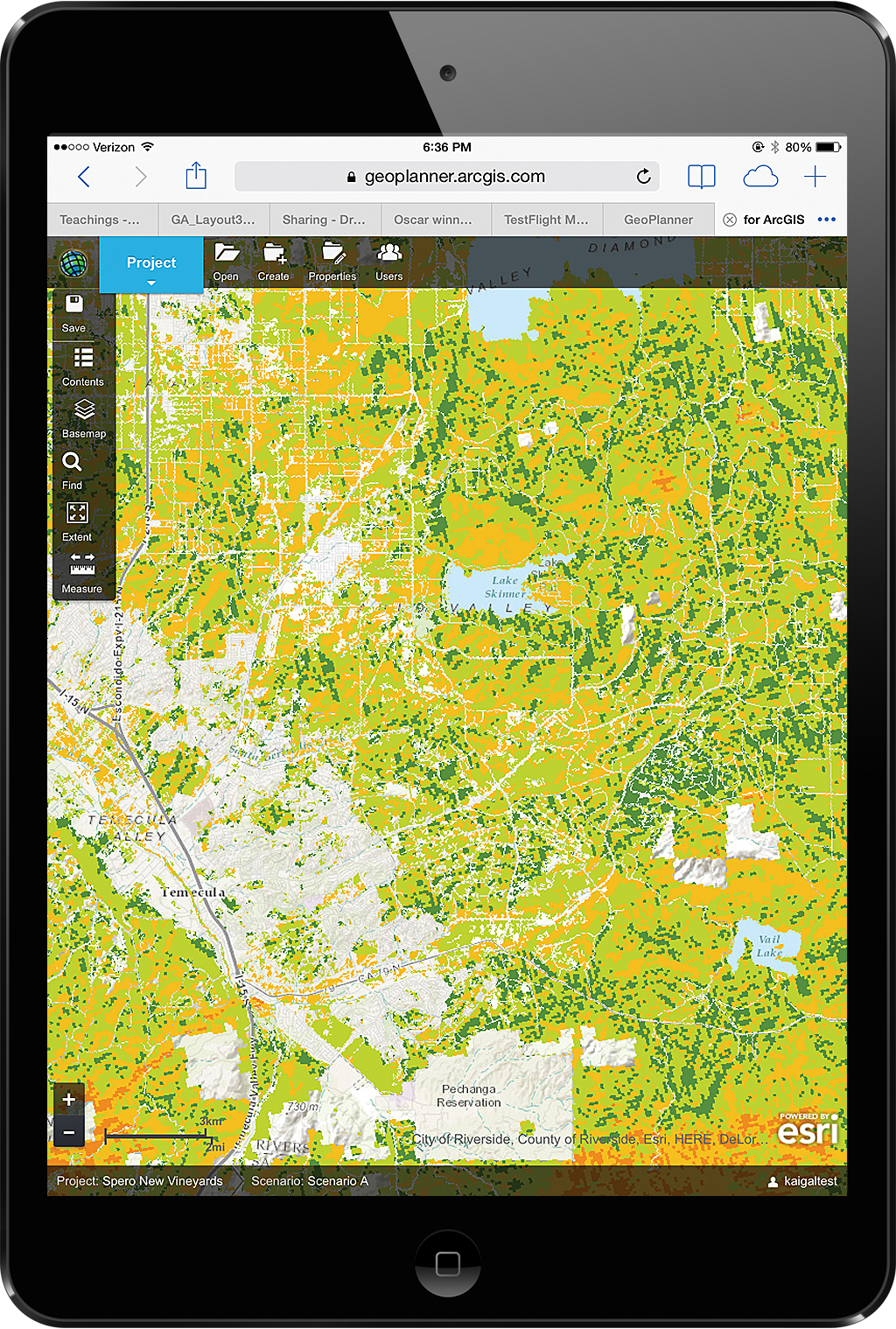
When you click Save, the information you just entered is submitted to ArcGIS Online. The suitability values are computed for overlaying raster cells and written to a new output image layer. This layer is added to the GeoPlanner project as a suitability map. On this suitability map, you’ll see a few areas of red, more areas of orange, and areas with several shades of green. Dark green cells denote the areas most suitable for wine production based on the input criteria. Areas without shading were those excluded from the analysis. Based on this analysis, the area southeast of Lake Skinner looks like a promising area for Spero to expand its operations.
Using GeoPlanner
GeoPlanner was originally designed as a planning tool that incorporates many geodesign concepts and includes online data, spatial analysis tools, GeoEnrichment services, raster geospatial landscape variables, and sketching tools. This tutorial showed how it can be used for agriculture, but it can also be applied to problems in utilities (route planning and facilities siting), the oil and gas industry, emergency response planning, and other uses that require GIS information integration and evaluation. GeoPlanner is a touch-enabled web application that runs on desktop and tablet browsers without the need for additional software or plug-ins.

