ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Engine is a cloud-agnostic solution that brings Esri’s industry-leading geospatial analytics capabilities directly to your big data in a data lake or data warehouse. It equips your organization with the technology you need to spatially analyze your data in the cloud by making a comprehensive library of spatial analysis tools accessible from Apache Spark in order to augment your data science workflows with spatial insights.
With the GeoAnalytics Engine 1.2 release (July 2023), there are now over 150 tools and functions available for geospatial analysis! The highlights of this release include:
- Performance improvements for spatial joins
- New functionality to improve authentication support
- Several new spatial functions
- Improvements to the built-in tools for spatial aggregation and nearest neighbor calculations
- Ability to use file geodatabases directly in your analytics
- 64-bit integer support for feature service fields
Here is an overview of the new features!
Performance improvements for spatial joins
Faster performance is always better! Increasing the speed at which you can perform spatial analysis is highly important to us. To make joins more performant, we have updated the spatial join functionality to be more robust and less sensitive to complex polygons and dataset ordering. This has resulted in up to two orders of magnitude improvement with certain complex datasets.
Authentication support
As of the 1.2 release, GeoAnalytics Engine supports Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and OpenID authentication. Keeping your users, data, and services secure is of paramount importance in a big data environment, so we are making it easier for you to maintain the security of your analytic environments while simplifying your authentication experience.
Enhanced collection of spatial functions
The 1.2 release has numerous new spatial functions to support data processing in your analytics workflow. To support data transformation, we have introduced five new affine transformation functions (Translate, Shear, Flip, Rotate, and Scale).
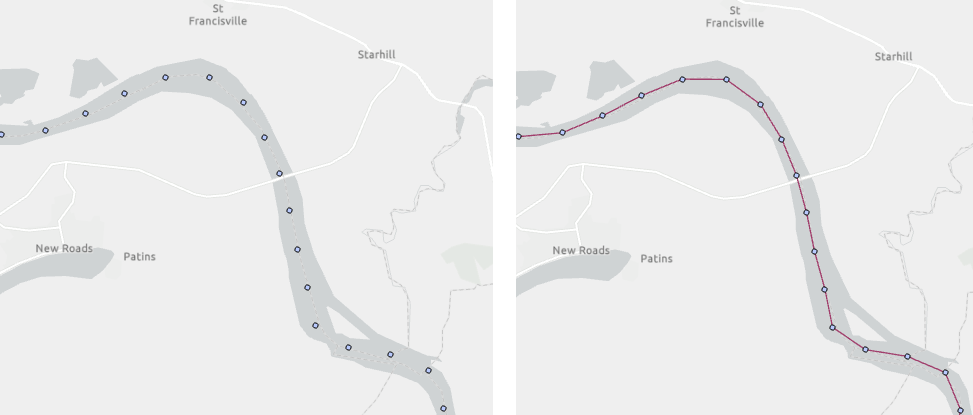
Point data doesn’t always contain timestamps to indicate the order in which points are connected into a line, so we have added a function to create linestrings from ordered lists of points without timestamps (ST_Aggr_Linestring) to make it easier to work with these data. For instance, you can easily connect points along mile markers on rivers to form continuous linestrings.
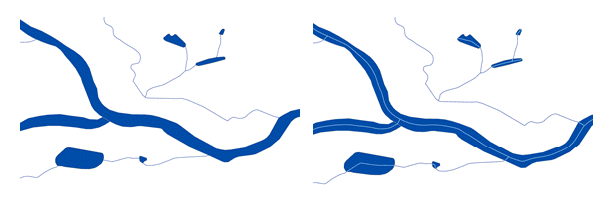
We have also added a new function (ST_Centerline) to create a centerline from narrow polygons, such as detailed hydrographic features, to aid in representing these polygon features at smaller map scales.
Improvements to analytics tools
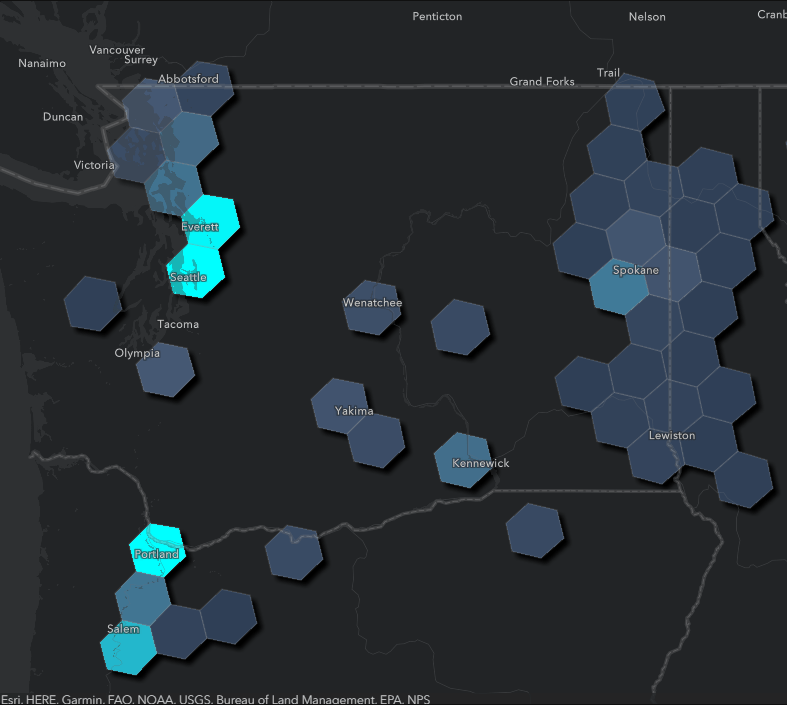
The tools in GeoAnalytics Engine provide more advanced calculations that can operate across all rows and columns in the dataset. In the 1.2 release, the Aggregate Points tool now has built-in support for H3 bins, which makes it easier to combine results with data from other sources that are indexed to the H3 grid.
Nearest Neighbors has also been updated to support geodesic distance and now supports inputs using geographic or projected coordinate systems. This provides greater flexibility in determining the set of nearest locations of interest using planar or geodesic calculations, so that you don’t need to adjust your coordinate system in order to perform accurate calculations.
ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Engine is updated two to three times each year bringing you new features to make spatial analytics a seamless part of your data science workflows. We are always looking to hear from you about the features you need to enhance your big data workflows!
For more information on the latest features, check out the product release notes or stop by the GeoAnalytics Engine Community Site for resources on getting started, tips and tricks with various tools, and much more!


Article Discussion: