This is a continuation of another blog post where I described how to compute aggregated results such as totals and averages from a time series table and show them at the point locations where those values were measured. These results are helpful in many analyses. But there are cases where it is required to visualize them using polygon features. For example, if you are an emergency management professional, you may want to know which counties have the most rainfall; whereas if you’re a scientist, you may want to see the same result but aggregated into watershed boundaries/catchment areas instead.
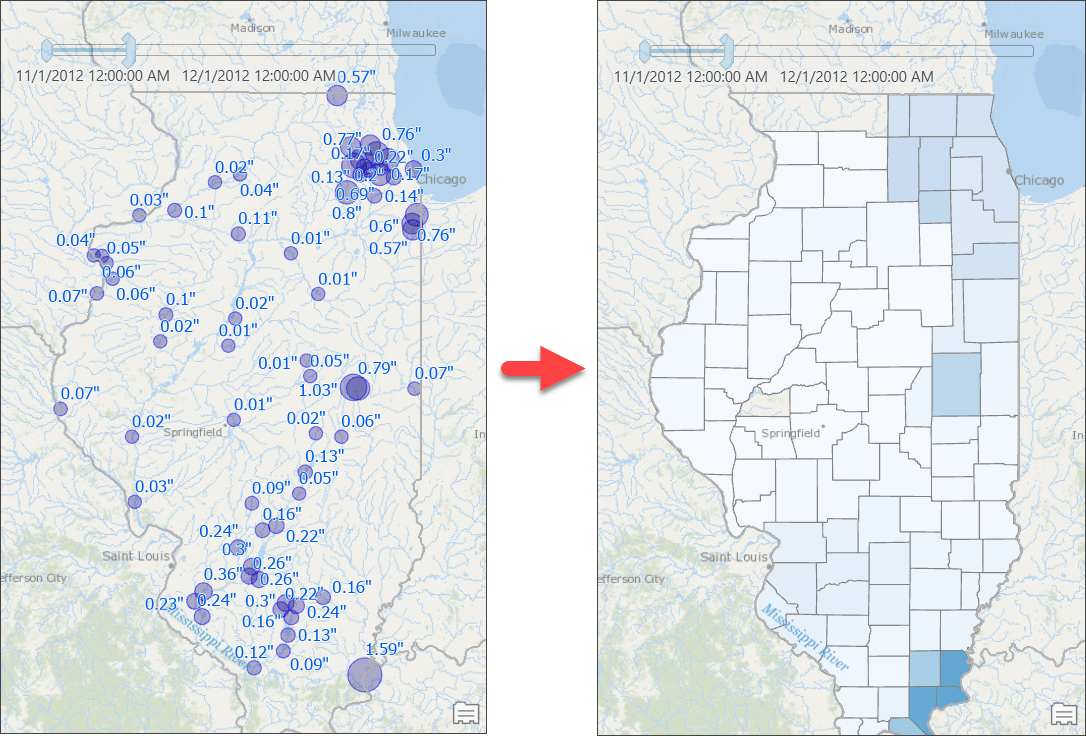
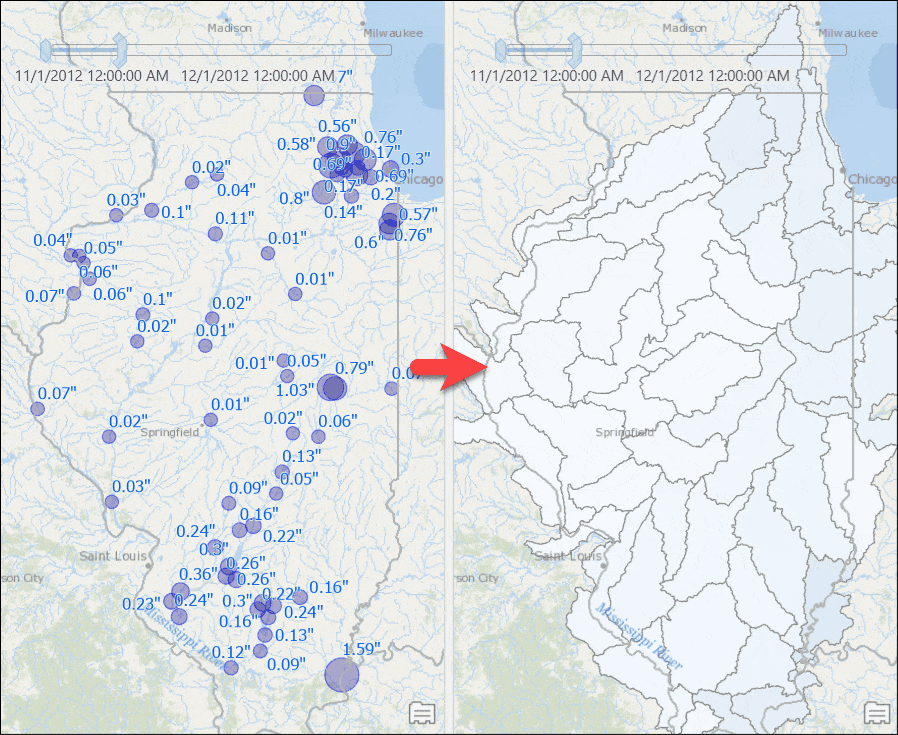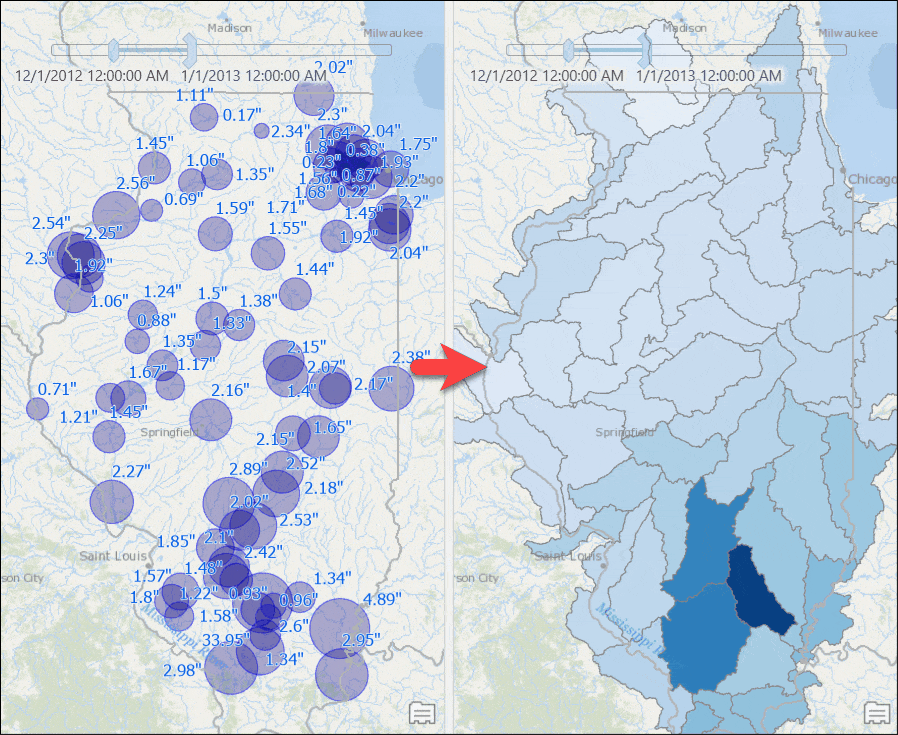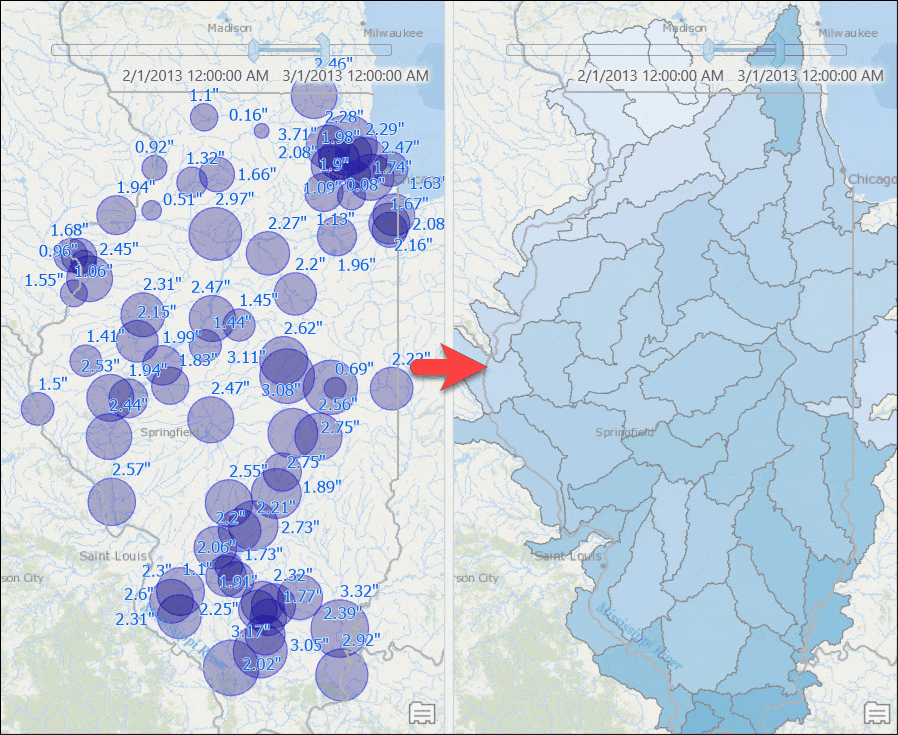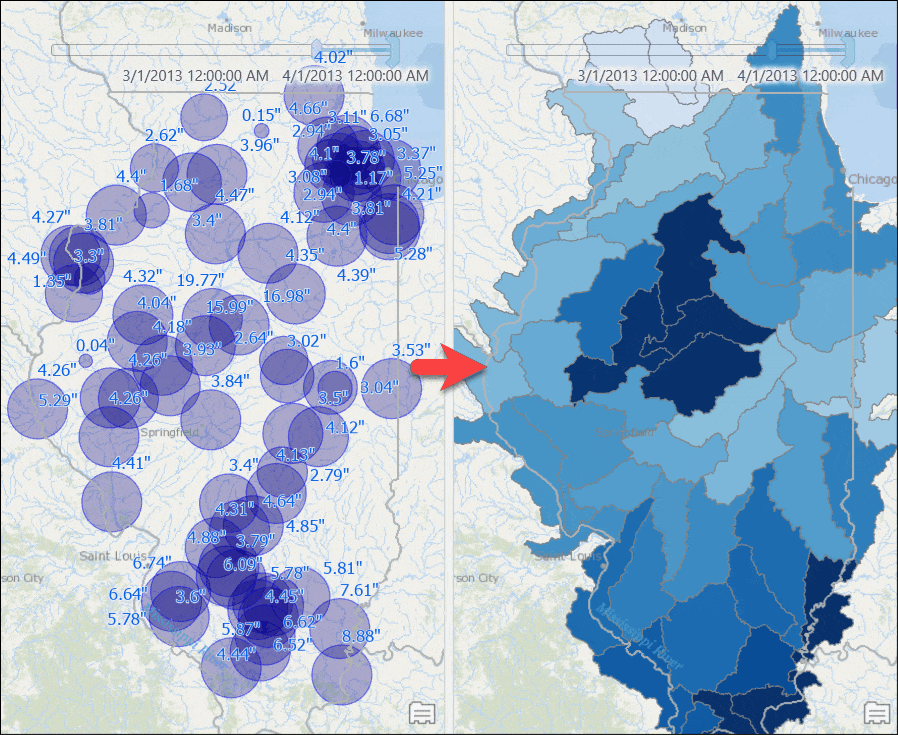
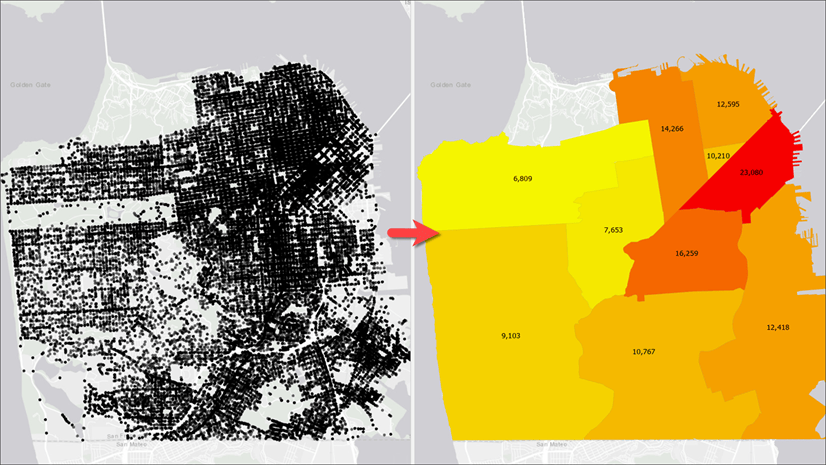
When it comes to transforming results from points to polygons, naturally we think of a simple spatial operation—such as a Contains or a Within operation—to (a) find all points that fall within a polygon feature and (b) use those features to compute the result. This simple approach works well with discrete data, such as computing total sales from all point locations at the state or county level. But this does not work for analyses with sampled data such as rainfall measurements. If you were to do that, you’d get a map, like the one below, where counties with no rainfall stations are not even drawn on the map — basically the map says there were no rain in those counties! That is not true, right?
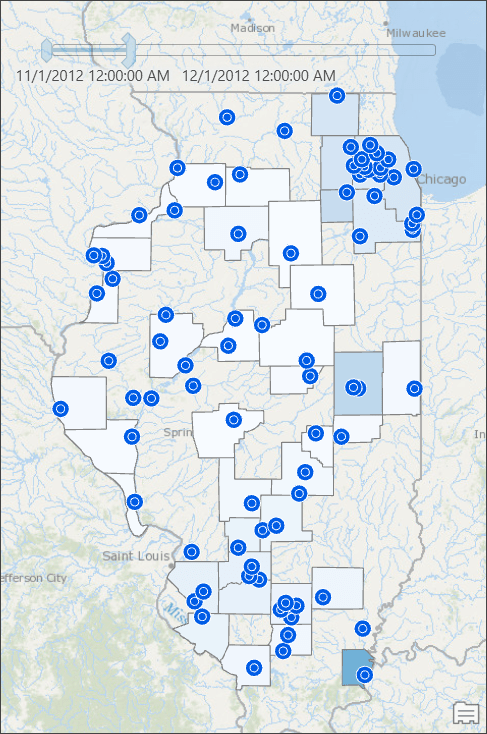
To avoid that problem and produce an accurate map, we will use Thiessen polygons to compute the rainfall distribution in our area of interest. Such result can be achievable by executing some geoprocessing tools, but that produces result only for one time slice. Every time you want to see result for a different time slice, you need to rerun those tool. This blog post provides step-by-step instructions that overcomes geoprocessing tools limitations – makes the result map reactive to time slider’s current time and still computes aggregated results, such as total rainfall dynamically from a time series table.
Prepare the Data
Let’s get started:
- Download an ArcGIS Pro package to get started with sample data.
- Double-click on the package file you downloaded to open in ArcGIS Pro.
The Rainfall Data map contains a table and a couple of layers:- The two intermediate layers, found in a group layer, are the results of overlay operation between (a) Thiessen polygons (from point features representing rainfall stations) and county boundaries, and (b) Thiessen polygons and watershed boundaries.
- Create a new database connection to your enterprise database.
- Go to the Catalog pane, then navigate to Databases\Rainfall_IL.gdb.
- Copy all feature class and tables from the file geodatabase to your enterprise database.
Visualize Weighted Total Rainfall at the County Level
Next, we’ll add a query layer:
- Click the Query Layer option from the Add Data command on the Map tab.
- Select your database connection.
- Give it a name such as Weighted Total Rainfall by County.
- Copy the following query and paste it in the Query text box:
SELECT c.objectid, c.Name, c.shape, c.POP2010, fo.Rainfall AS Weighted_Total_Rainfall
FROM COUNTIES_IL c
INNER JOIN
(
SELECT t.fips, (sum(r.rainfall_inch * t.area) / sum(t.area)) AS rainfall
FROM COUNTIES_THSN_INTSCT_IL t
INNER JOIN
(
SELECT site_no, Sum(rainfall_inch) AS rainfall_inch
FROM USGS_RAINFALL_TIMESERIES_IL
WHERE ::r:dateRange
GROUP BY site_no
) r
ON r.site_no = t.site_no
GROUP BY t.FIPS
) fo
ON c.fips = fo.fips - Click the blue pencil icon next to the ::r:dateRange parameter to bring up an inline editor to define the parameter.
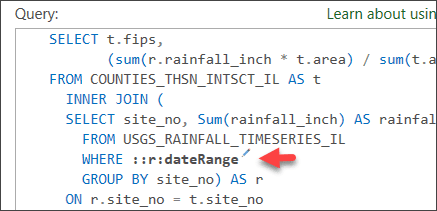
- Fill in all necessary information as seen in the following screenshot.
- Field or Expression—Type “date_time”.
- Data Type —Choose Date.
- Default value—Uncheck the check box.
- Name of the table the field belongs to—Type “USGS_RAINFALL_TIMESERIES_IL”.
- Click Done.
- Click the Validate button.
- Click the Next button if there is no error.
On the next page, Unique Identifier Field(s), Geometry Type, and Spatial Reference should get determined automatically. - Click Finish.
A query layer gets added to the map. - Symbolize the layer with unclassed symbology using the Weighted_Total_Rainfall attribute.
Since a range parameter is used in the query layer’s source SQL, the layer is automatically made time aware.
The Time Slider appears on the map. - Enable the time slider from the Time tab.
- Set the time span to 1 month.
Counties with computed rainfall for that month will appear. - Use the time slider to go to a different month, or change the time settings to view the aggregated result by week or for any other time duration.
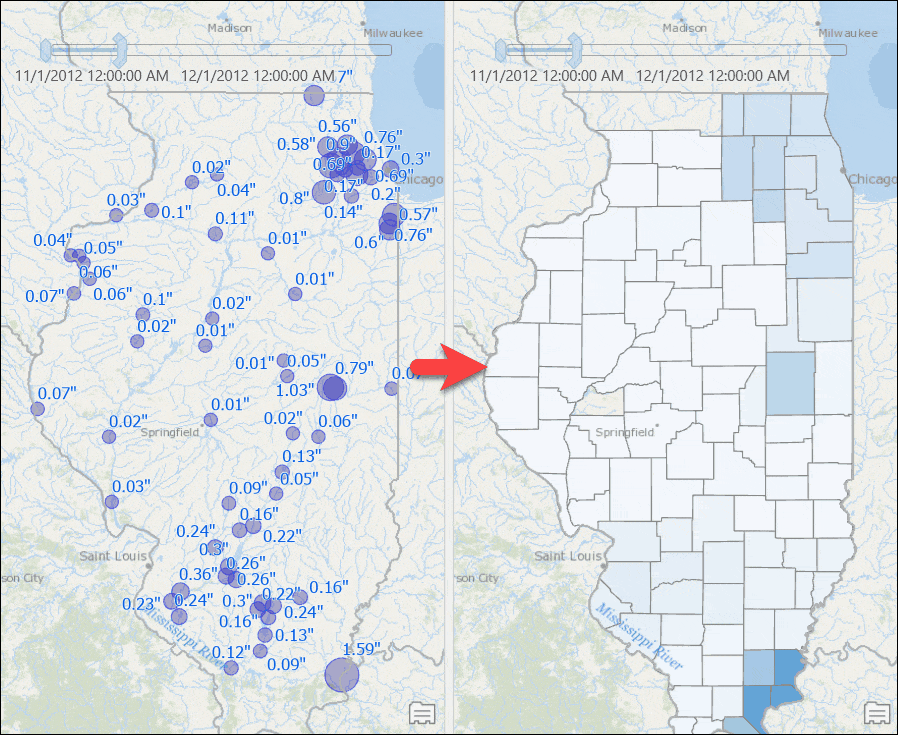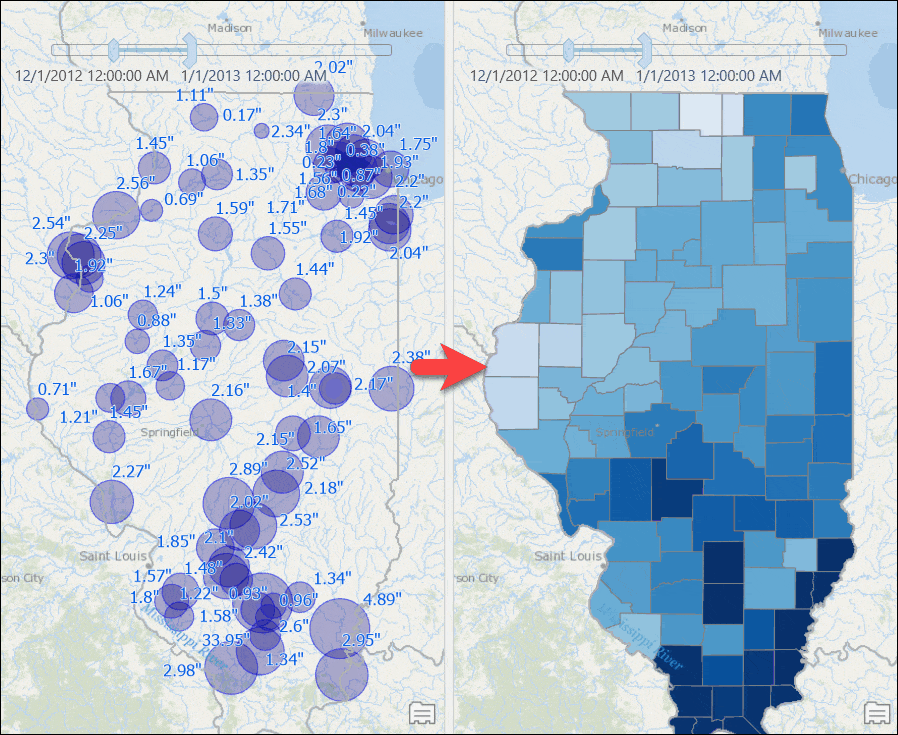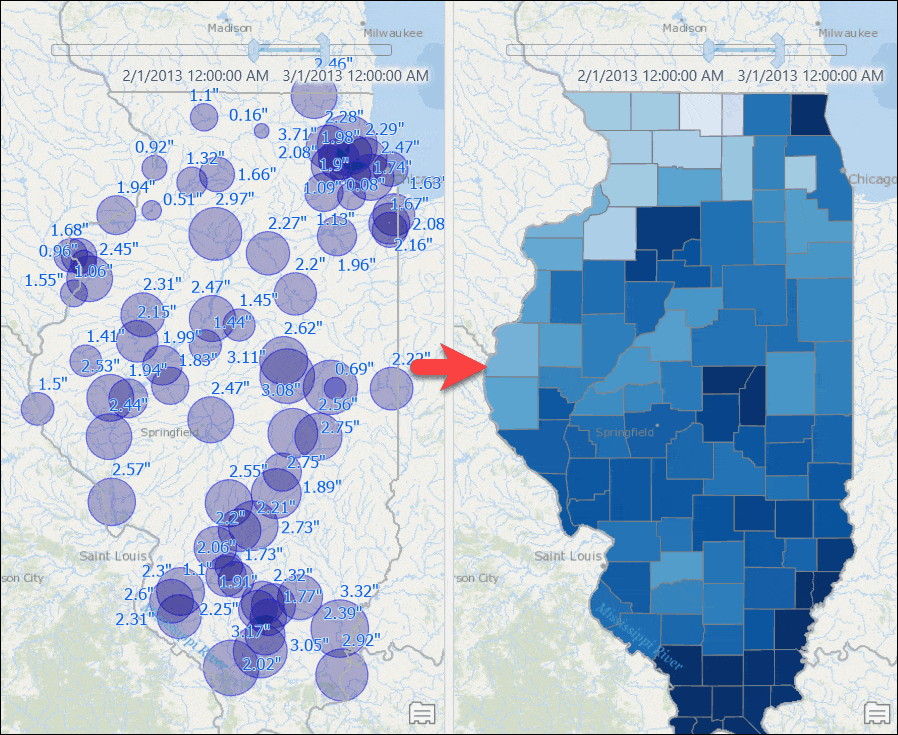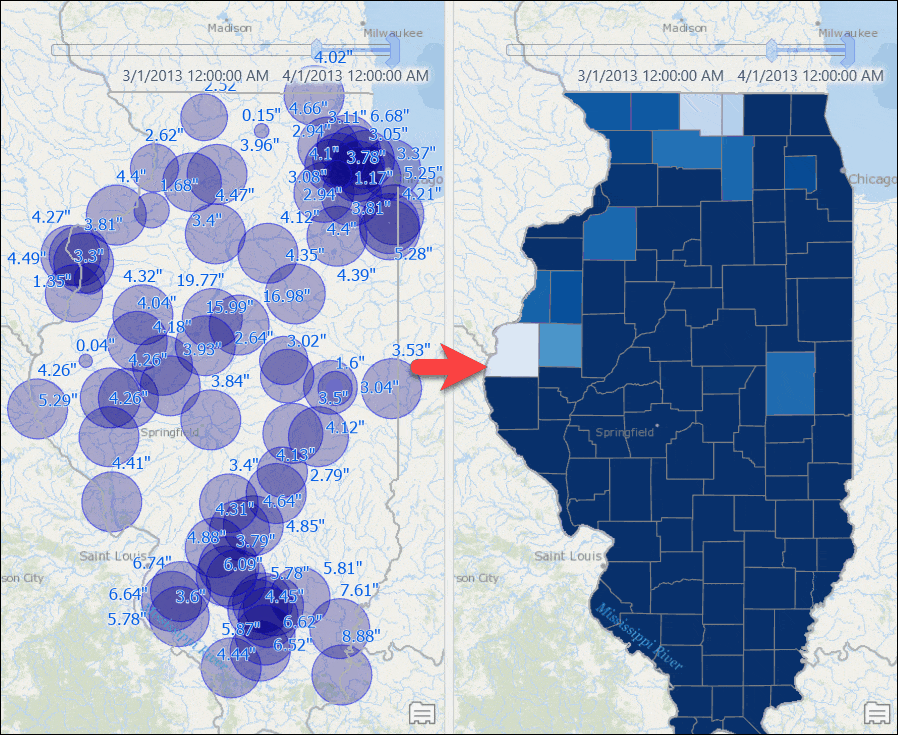
Visualize Weighted Total Rainfall for Watersheds
If you want to visualize the weighted total rainfall for watersheds instead of county boundaries, all you need to do is to repeat steps from the previous section but with a watershed layer. Let’s create another query layer with the following SQL query:
SELECT w.objectid, w.huc8, w.Shape, rh.rainfall_w AS Weighted_Total_Rainfall
FROM USGS_HUC8_WATERSHEDS_IL w
INNER JOIN
(
SELECT huc8, (sum(r.rainfall_inch * c.areasqkm) / sum(c.areasqkm)) as rainfall_w
FROM USGS_HUC8_thsn_intsct_il c
INNER JOIN
(
SELECT site_no, Sum(rainfall_inch) AS rainfall_inch
FROM USGS_RAINFALL_TIMESERIES_IL
WHERE ::r:dateRange
GROUP BY site_no
) AS r
ON r.site_no = c.site_no
GROUP BY c.huc8
) AS rh
ON w.huc8 = rh.huc8
Share and Consume Data in Web Maps
You can share the map as a map image layer (or map service).
- Consume the service on a web application such as ArcGIS Online or a portal map viewer or a Web AppBuilder for ArcGIS application.
- Use the time slider to see the same results.

Article Discussion: