Being able to identify different plant species is a common task in many industries such as Agriculture, Horticultural, and Forestry. Vegetation management is essential to fight against wildfires, since being able to classify different plant species is important for identifying species that can be vulnerable to fire. Automatic recognition of plants is also useful for tasks such as species identification/reservation for management in botany gardens or farms uses plants.
Here we can use Deep Learning tools in ArcGIS Pro to identify plant species. We will also show some ArcGIS functionalities and concepts that you may not have seen previously.
Key Concepts
- For training data, we will be labeling entire images because all pixels in the images are needed for training.
- For inference, we will use a feature class with image attachments. These images are non-spatial.
Outline of the workflow
- Prepare Data for Training
- Train Model for Deep Learning
- Preparing Data for inferencing
- Use the Classify Objects for Deep Learning tool for inferencing
- Results and conclusion
Prepare Data for Training
Because we have multiple images to train our model, we will create a mosaic dataset.
Create Mosaic Dataset
We will start with the Creating a mosaic dataset using the Create Mosaic Dataset tool. We need a simple mosaic dataset so will accept all default parameters except for the output geodatabase and the name for our mosaic dataset that we need to specify.
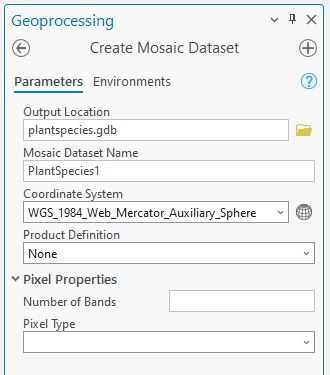
Add Images to the mosaic dataset
Next, we will use the Add Raster to Mosaic Dataset tool to add images to our mosaic dataset that we created in the last step. For the Input Data, we will select the Folder option from the drop-down and browse and add the folder that contains the images. We will accept all default parameters values (note: don’t build overviews). We will be using this mosaic dataset as an Image Collection for labeling the images in the following step.
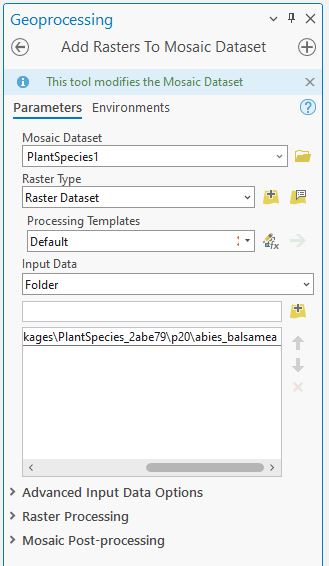
Labeling Images
Next, we will use the Label Objects for Deep Learning tool.
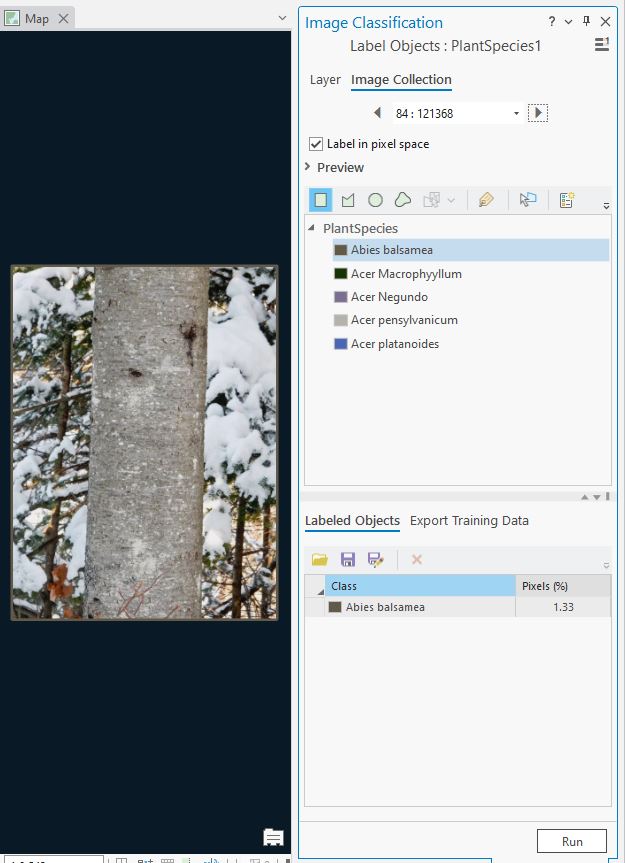
This video shows the labeling experience in ArcGIS Pro, specifically labeling multiple images.
You can refer to ArcGIS Pro: Classification Schema to learn how to create predefined labeling schema.
Export Training Data
Next, we will use the Export Training Data tab on the Label Objects for Deep Learning tool to export the data. Here we will take care of a few things. We will change the following parameters values as listed below and shown in the tool screen-capture:
- Tile Size X and Tile Size Y (these values are about average size of our images that we added in the mosaic dataset)
- Because images are non-spatial, we will select the Pixel Space in the Reference System parameter.
- for the Metadata Format, we want to select the Labeled Tiles option
- And, we will use the Bounding Box option on the Crop Mode parameter.
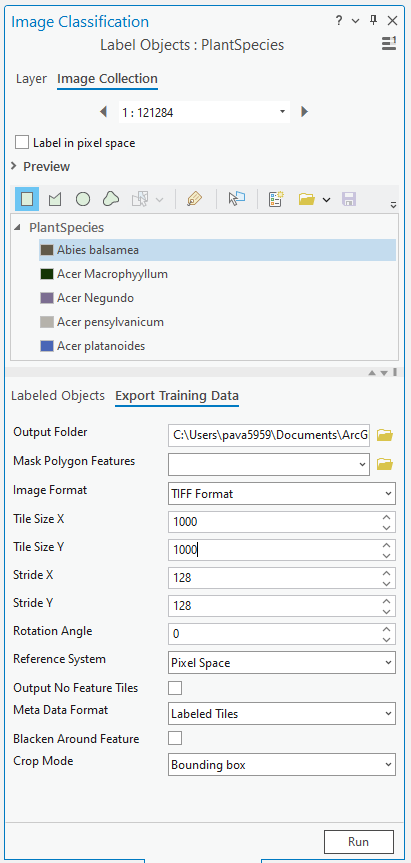
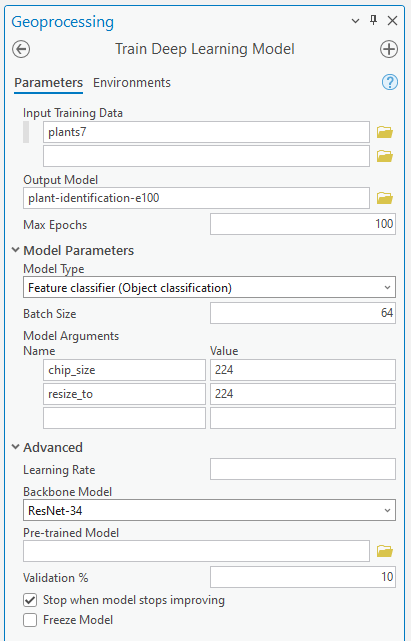
Train Deep Learning Model
Now, we will use the above exported data in the Train Deep Learning Model tool. We are going to train the model for 100 epochs but we will use the two options specifically:
1. Check the Stop when model improving checkbox so that the tool stops when it sees model cannot be further improved.
2. Uncheck the Freeze Model option so that if we find our model is not performing well, we can train it further will some more epochs.
Preparing data for inferencing
The images of various plants we want to identify species on are non-spatial. In other words, they don’t contain any spatial information. And, because we want to inference images in bulk, one way to do this is to attach the images to a feature class and use the feature class as an input in the inference tool. You can learn more about adding attachments to a feature in this video – Attaching images to a feature in ArcGIS Pro
Use the Classify Objects for Deep Learning tool for inferencing
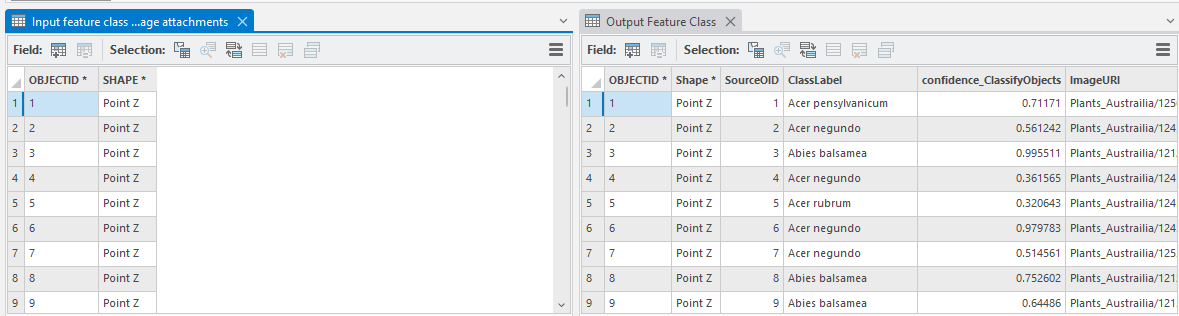
Now, we are ready to inference our images – identify plant species. To do that, we will use the Classify Objects for Deep Learning tool. For the Input Raster, we will use the Feature Class with Image Attachments that we created in the last step, and for model we will use what we created in the Train Deep Learning Model section. The output will be a feature class with the following new fields:
- Class Label (these are the identified plant species)
- Confidence_ClassifyObjects (Confidence of inferencing)
- ImageURI (location of the images)
- SourceID (can be useful when more than one images are attached in the input/output feature classes)
Note: In the output feature class the tool is not attaching images by default to avoid any potential performance delays but if it’s something you would like to see as a feature of the tool, please let us know. For now, if you want to have images attached as well, you can use the same workflow of attaching images to feature class that we discussed above.
Here are attribute tables of the input and output feature classes.
Our analysis is complete. To display the result, below we are using the Attributes pane. Here you can see image, class label, and confidence.
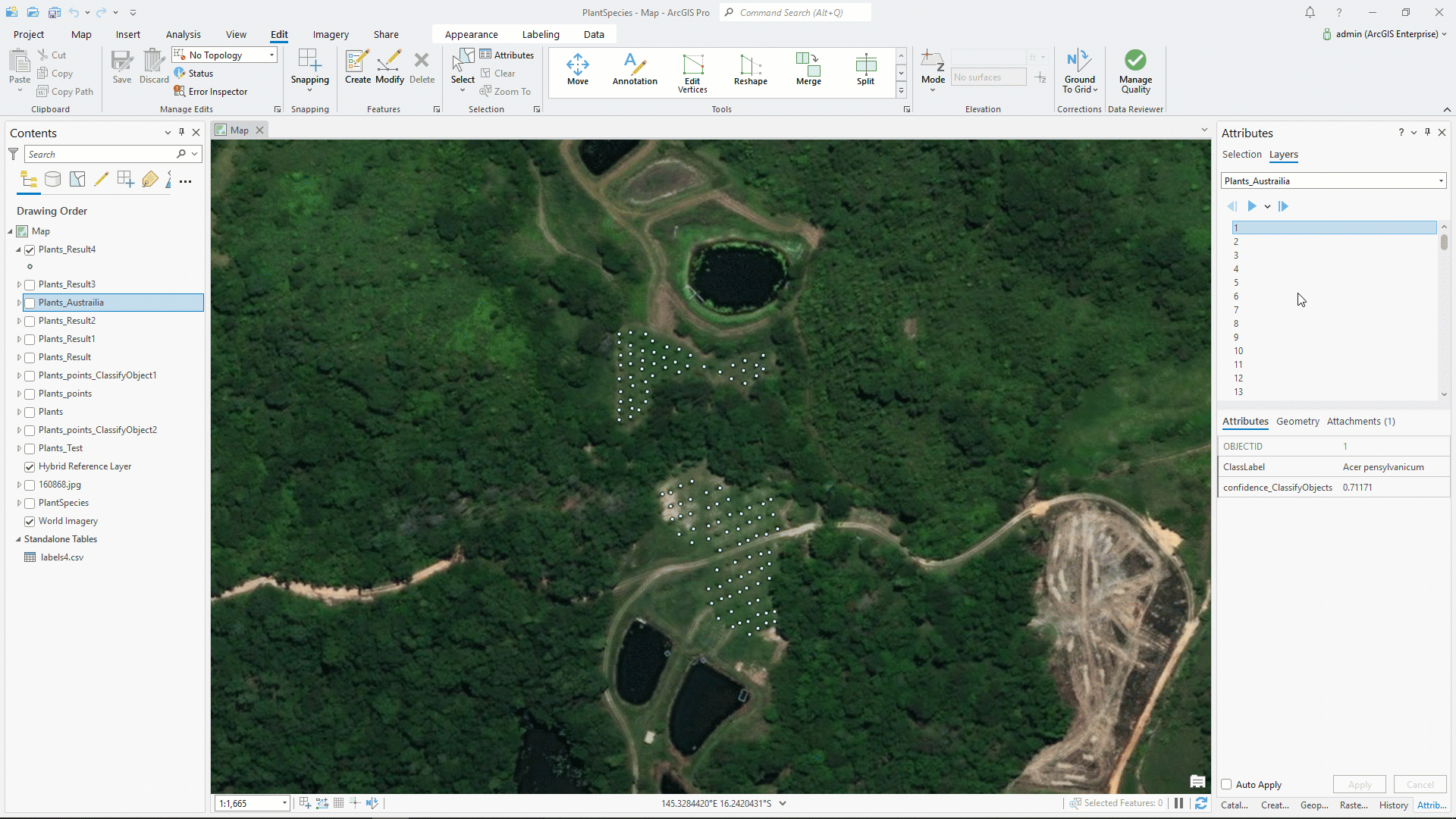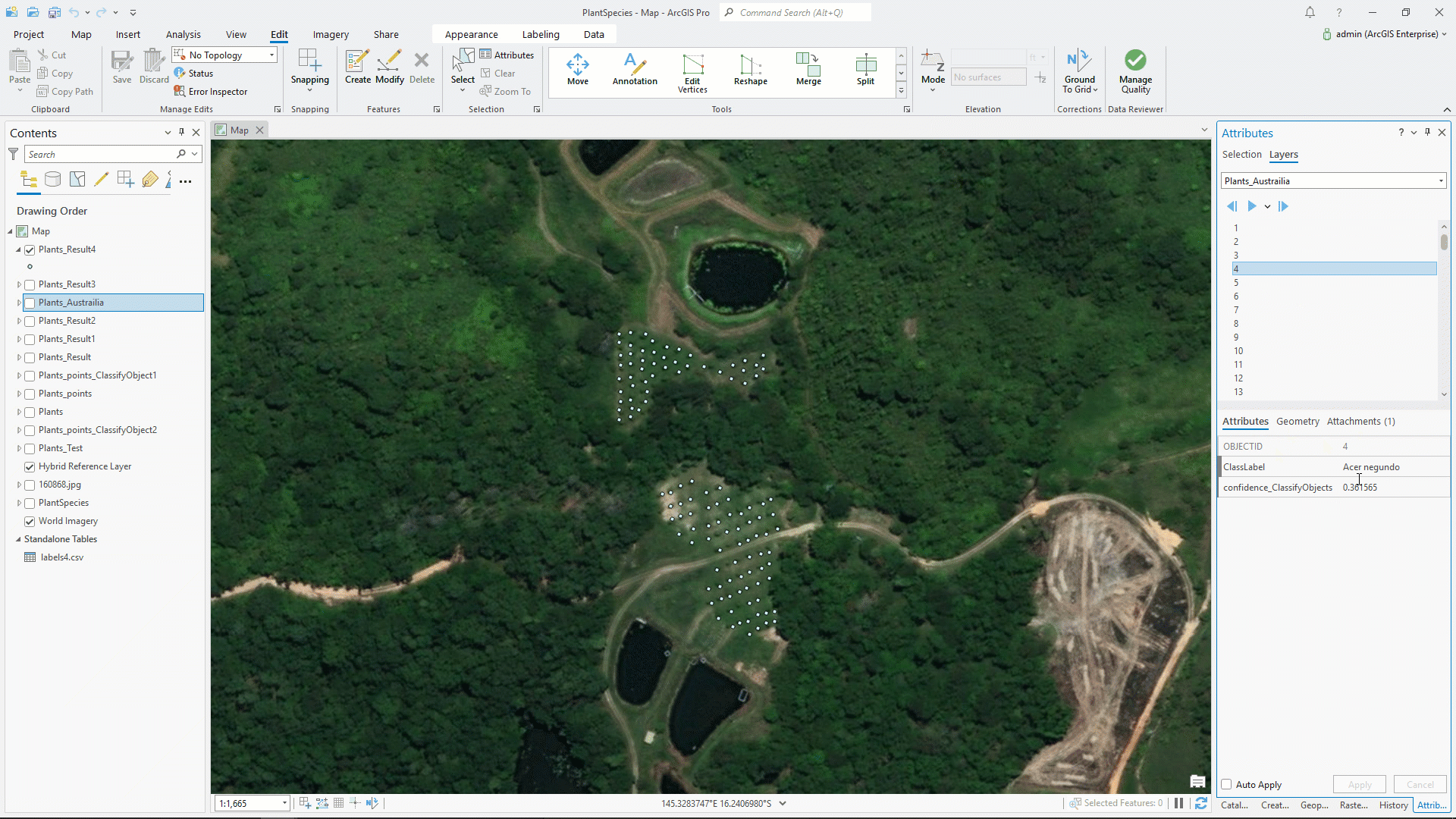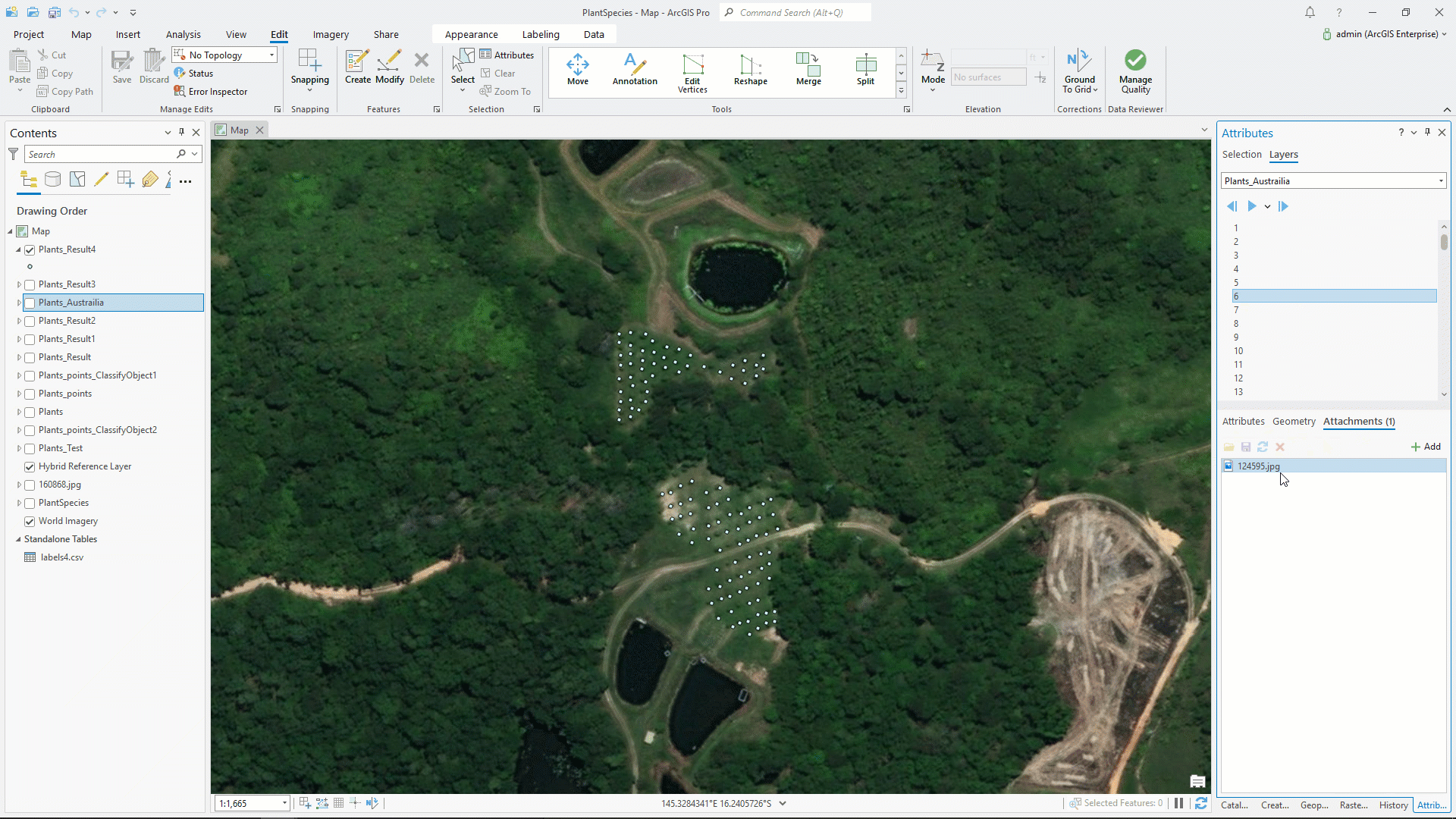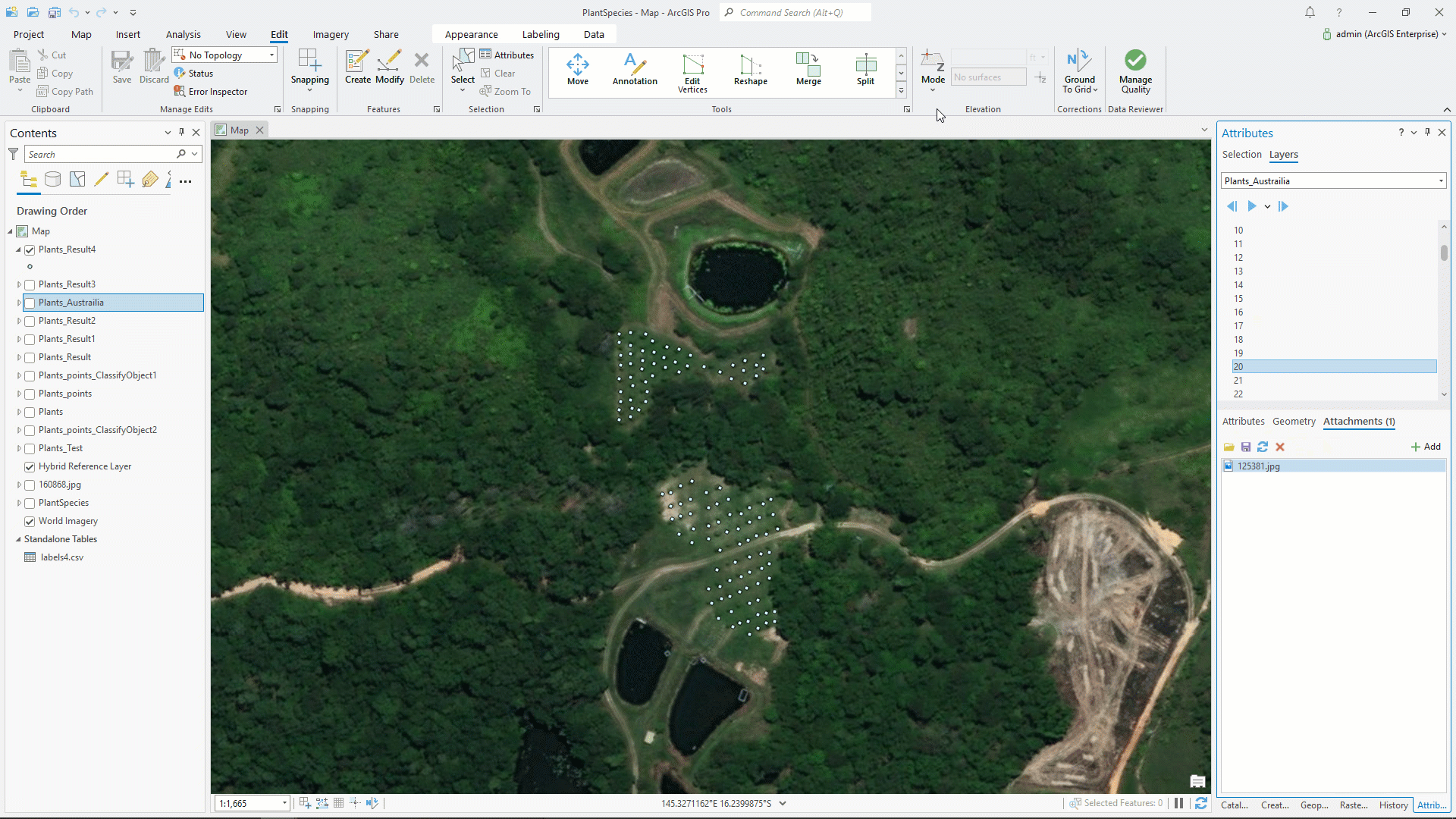
Image used in this Article Banner is taken from commons.wikimedia.org, Source URL: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kuopio_forest.jpg taken on 1/13/2022 and modified to 1920 by 1080 pixels to fit in this blog. This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic license.



Shouldn’t there be sample datasets to work with?
Is it possible to get the dataset for this example?