The 3D Analyst extension offers new and improved capabilities in ArcGIS Pro 3.4. We’ve added new toolsets, enhancements, and bug fixes to improve the ArcGIS 3D Analyst user experience. Here’s a rundown of what’s new in 3D Analyst.
ArcGIS Pro 3.4 was released in November, 2024.
For a complete summary of all the changes that have been made for this release, have a look at the What’s New in ArcGIS Pro 3.4 blog post.
New Capabilities to ArcGIS 3D Analyst
- The Delete Breakline tool was added to the interactive TIN Editor.
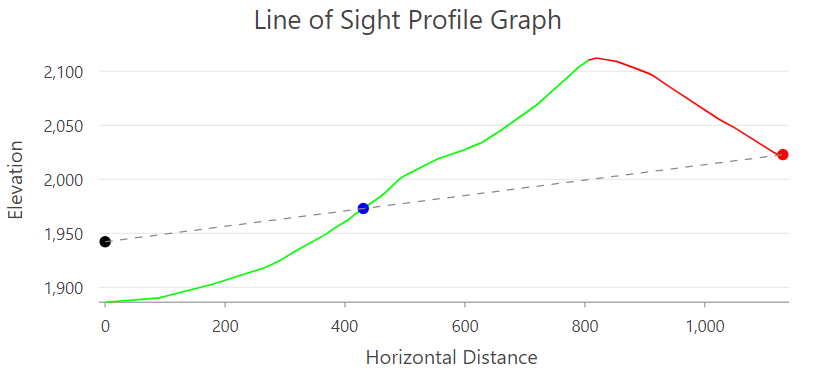
- A line of sight profile graph can be made from the feature output of the Line Of Sight geoprocessing tool.
- Profile graphs include the following items:
- Cursor tracking to mimic the cursor location in a graph at corresponding positions along the profiled lines.
- Chaining of features to treat multiple input lines as individual profiles. For example, you can combine multiple connecting roads, streams, or trails into single logical profiles in the graph.
- The option to use m-values from input polyline vertices for y-axis values as well as z-axis values.
Lidar and LAS datasets
- A new workflow topic explains how to extract building shells from aerial lidar.
- A notification appears when a LAS dataset with a missing or outdated display pyramid is added to a map or scene.
New geoprocessing tool
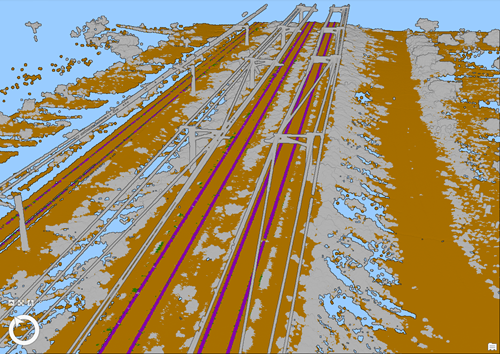
- Extract Rails From Point Cloud—Extracts rail track lines and center lines from classified railroad tracks in a LAS dataset, point cloud scene layer package, or I3S point cloud layer. The example below is of data courtesy of Esri India.
- Mesh To LAS—Converts an integrated mesh into a LAS format point cloud. Only with a basic license do you require the 3D Analyst extension.
Geoprocessing tool enhancements
- Classify LAS By Height—Offers improved performance and the functionality to classify areas at subfile granularity.
- Line Of Sight—New output attributes facilitate the creation of a line-of-sight profile graph.
- Classify LAS Ground—The new Recover Ridges ground detection option improves results for ridge areas that were not successfully classified using standard ground detection methods.
- Change LAS Class Codes—All class codes can be modified at once. For example, you can undo all existing classifications and classify a point cloud from the beginning.
- Interpolate Shape—Improved results are obtained with lidar-based surfaces across data voids such as rivers, lakes, and reservoirs.
- Skyline—The new Vertical Offset parameter enables the specification of vertical offsets to observer positions.
- Train Point Cloud Classification Model—The new Loss Function parameter allows for the use of focal loss. This improves results in the presence of unbalanced classes.

Article Discussion: