Indoor positioning adds location awareness to your indoor GIS. It enables real-time indoor navigation for visitors and building occupants to improve efficiency and reduce frustration of finding places and points of interest. It also supports facilities and IT workers in reducing services times, helping them navigate to work order locations and assets in complex campuses. Indoor positioning unlocks other capabilities like location sharing and providing insights related to occupancy patterns and trends in your indoor environment.
An Indoor Positioning System (IPS) is needed to get the familiar “blue dot” on an indoor map. The blue dot in common outdoor navigation apps is powered by Global Positioning System (GPS) which requires an unobstructed view of the sky hence it does not work inside buildings.
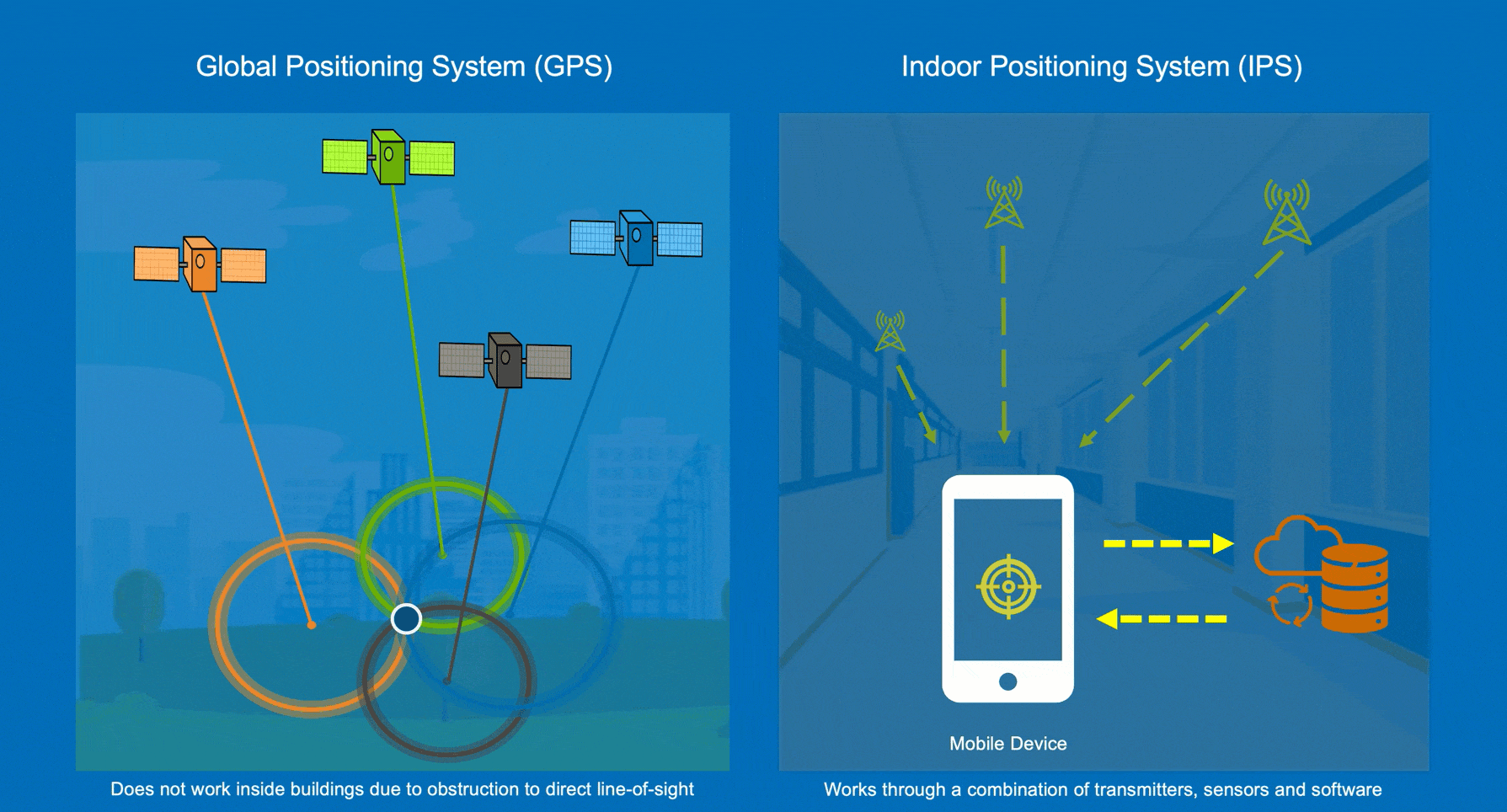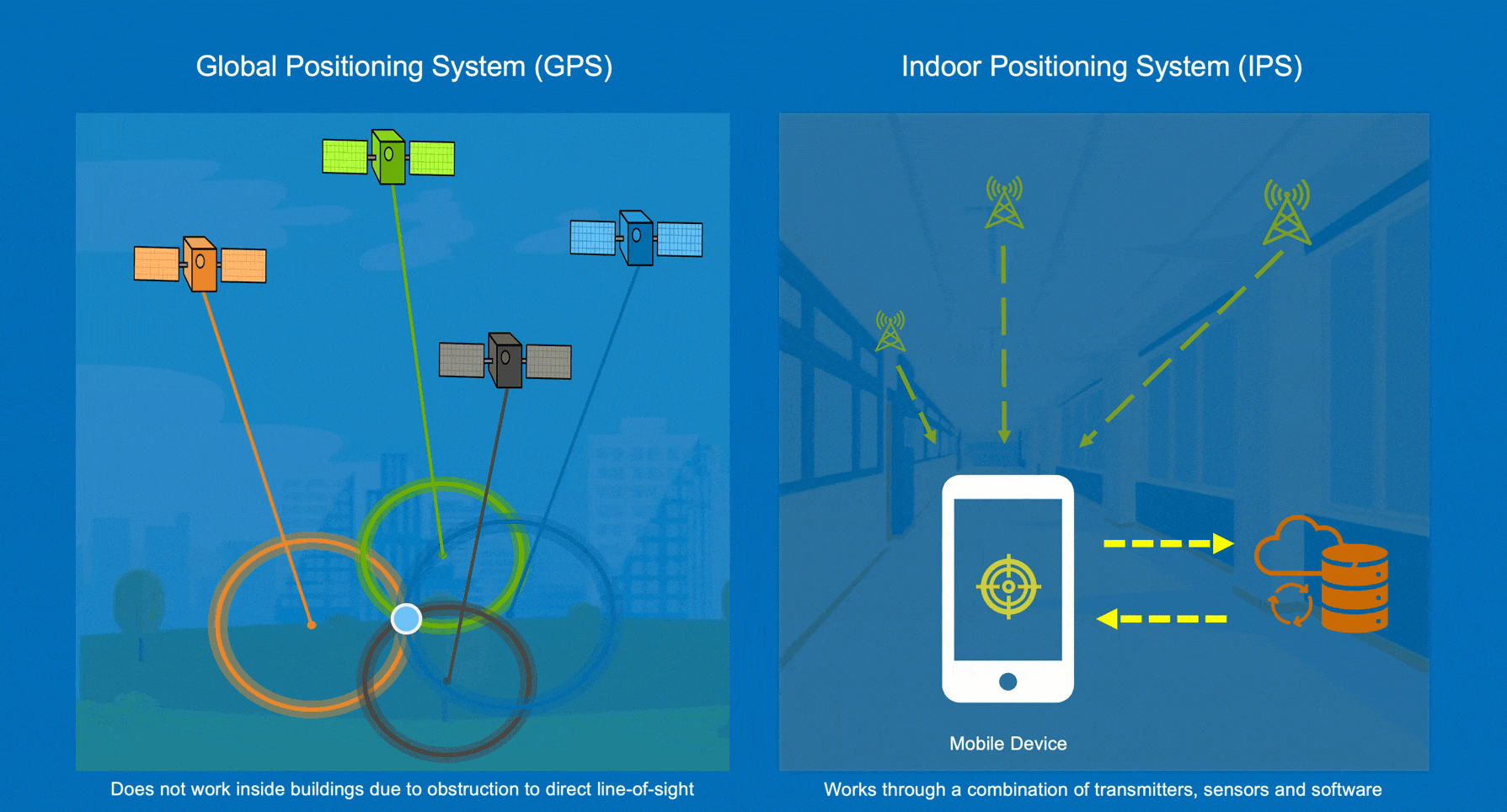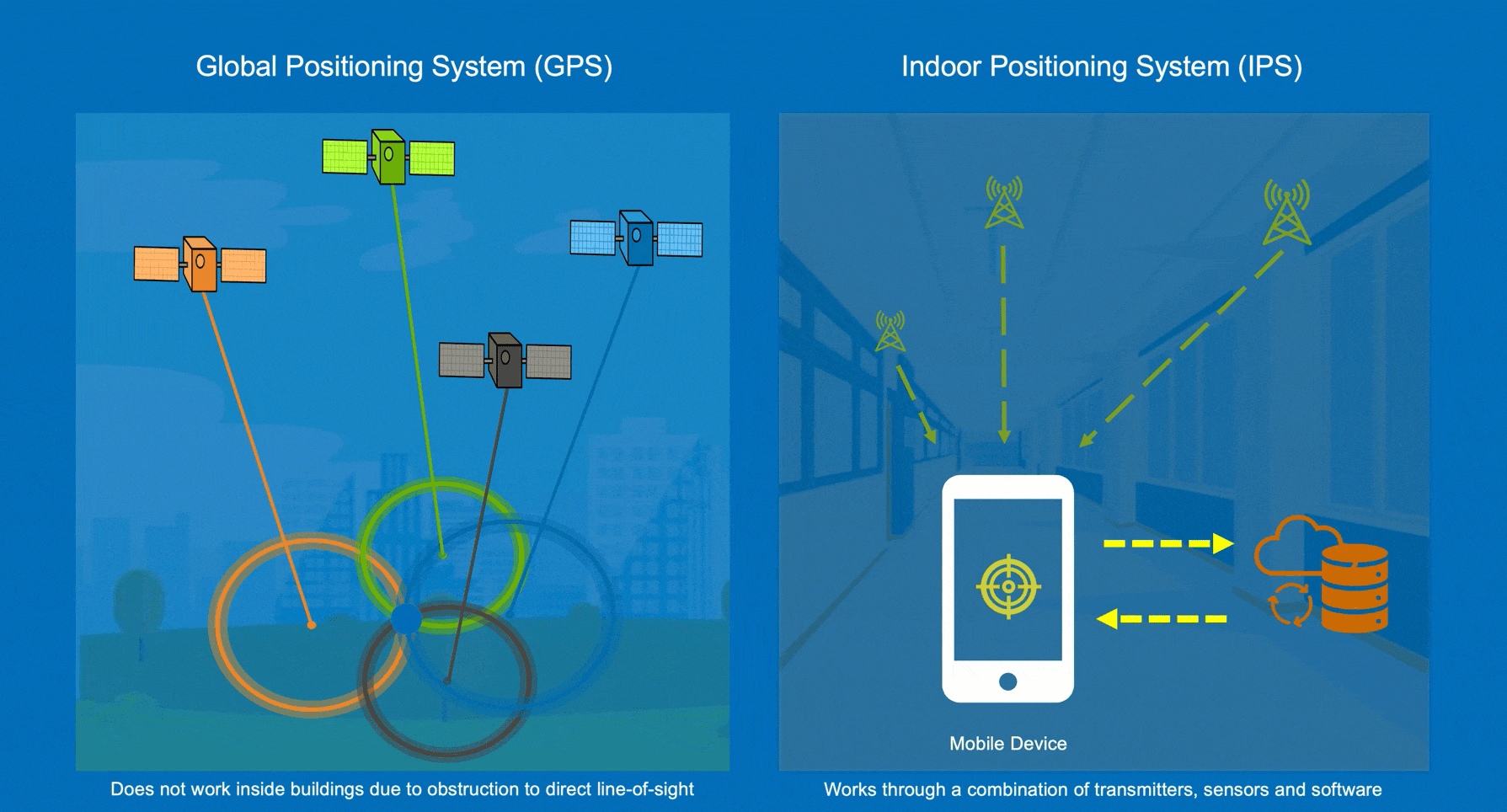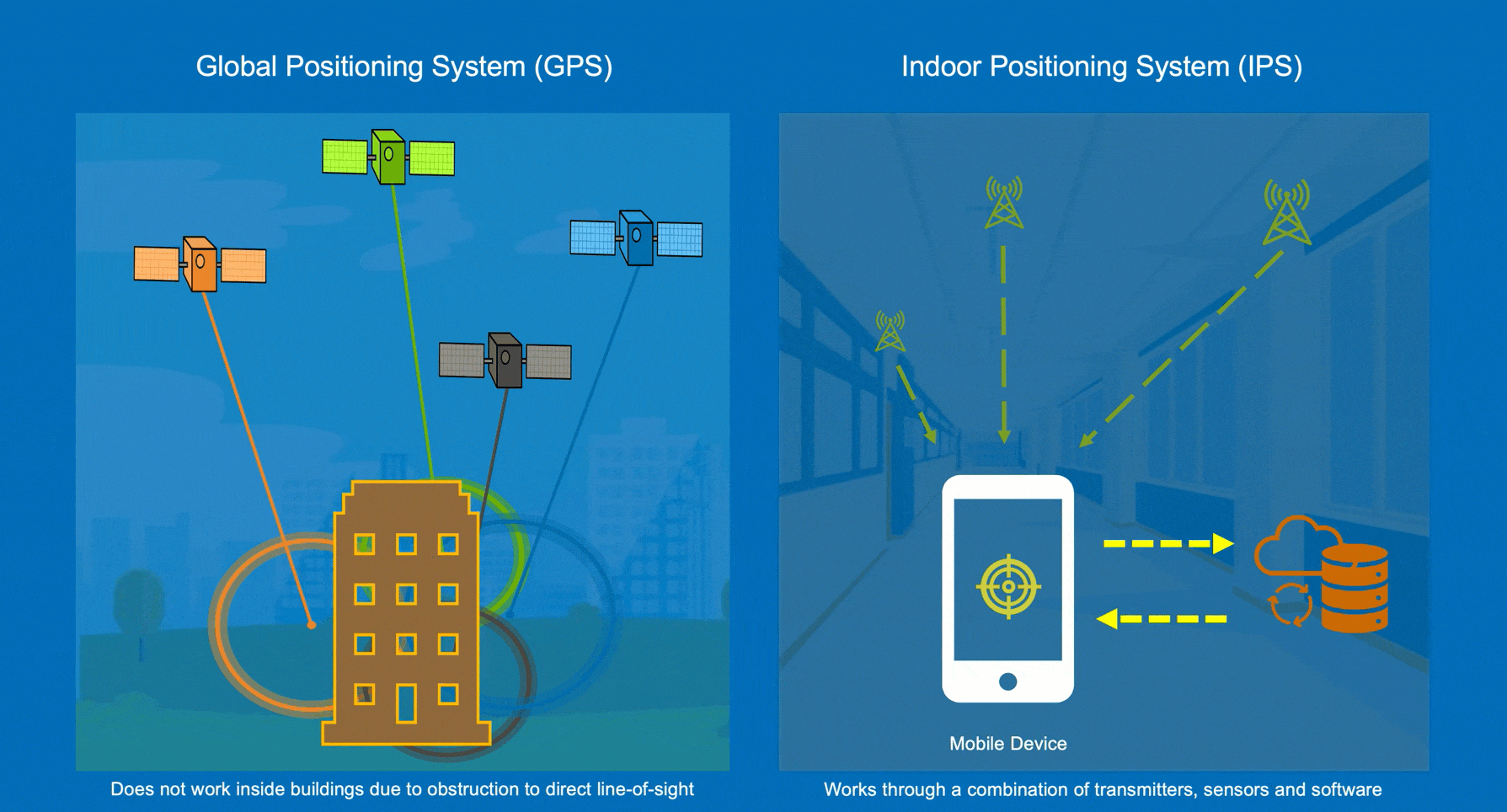
An increasing number of options for enabling IPS are available and your choice depends on various factors including existing hardware infrastructure like Bluetooth beacons and WiFi access points, accuracy requirements, and mobile device types amongst others.
ArcGIS Indoors mobile apps provide support for ArcGIS IPS, which uses Bluetooth beacons for positioning and works on both iOS and Android devices. ArcGIS IPS can also support WiFi-based positioning on Android devices, if the device is configured to allow WiFi sensor probing. WiFi positioning uses wireless access point (WAP) signal strengths to trilaterate the user’s location.
WiFi-based positioning on iOS is provided by Apple’s IPS and is supported by the ArcGIS Indoors mobile app for iOS.
Configure Apple IPS for ArcGIS Indoors
In this blog, we will discuss how to set up Apple IPS. Apple requires floor plan data in Indoor Mapping Data Format (IMDF) which can be created using floor plan data from ArcGIS Indoors. Safe Software provides an FME (Feature Manipulation Engine) workbench that converts an Indoors model geodatabase to IMDF using the ArcGIS Data Interoperability Extension. The following steps are required to convert data to IMDF and configure Apple Indoor Positioning:
- Sign up for Apple Indoor Maps Program through Apple Business Register
- Prepare indoor data for IMDF
- Run the FME workbench to convert indoor data to IMDF using the ArcGIS Data Interoperability Extension
- Validate IMDF in Apple’s IMDF Sandbox
- Submit IMDF to Apple for verification and approval
- Perform indoor surveys using Apple Indoor Survey app
- Test indoor positioning to assess accuracy and overall performance
After completing the above, you can make the IPS available for use in mobile apps such as Indoors Mobile.
Prerequisites
In order to complete the steps detailed in the blog, you should be familiar with the following:
- ArcGIS Pro
- ArcGIS Data Interoperability Extension
- The ArcGIS Indoors Information Model
- Creating a mobile map package (MMPK) for Indoors Mobile
Prepare indoor data for IMDF
Apple has certain data requirements for floor plans and will validate the IMDF file to ensure that requirements are met. Completing the following data configuration in ArcGIS Pro before running the Data Interoperability workbench can help ensure a more seamless validation process once you upload the IMDF file to Apple.
- Run the Generate Unit Openings geoprocessing tool to create simple line features that represent the entryways to units.
- Run the Repair Geometry geoprocessing tool on the floor plan layers (Facilities, Levels, Units, and Details). Choose OGC for the Validation Method parameter. This repairs self-intersections, duplicate vertices, unclosed polygons, and other geometry issues.
- Run Indoors validation checks and resolve flagged issues, such as duplicate IDs, overlapping units, and gaps between units on a level.
- Ensure that the USE_TYPE field is populated for Units features to make them easily identifiable. At a minimum, ensure that stairs, elevators, and walkways (such as hallways and atriums) are identifiable based on their USE_TYPE field value.
- Ensure that units are completely covered by the level with which they are associated. You can make minor changes to comply with this rule in the IMDF Sandbox.
Run the Indoors to IMDF workbench
Once you have validated and cleaned up your floor plan data, you can convert the Indoors model to an IMDF file to use for Apple indoor positioning. To convert the Indoors model to IMDF, use the ArcGIS Data Interoperability extension to run the ArcGIS Indoors Model to IMDF workbenches, available for download on FME Hub.
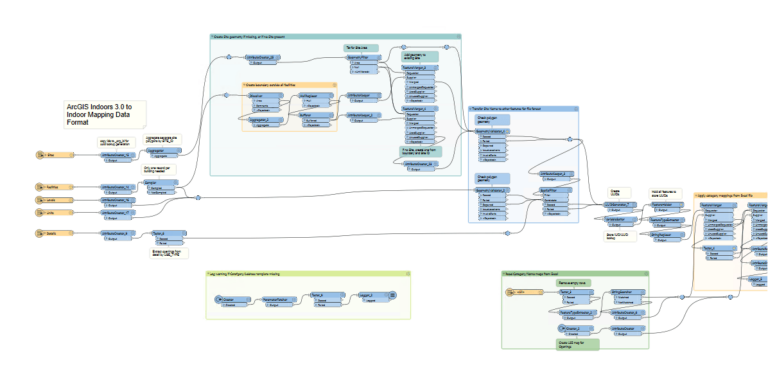
After downloading the workbenches from FME Hub, complete the following steps to convert your floor plan data to IMDF:
- Run the Make Indoors To IMDF Mapping Table workbench using the Data Interoperability extension. The workbench will create a Category_Address_Map XLSX spreadhseet.
- After running the Make Indoors To IMDF Mapping Table workbench, update the Category_Address_Map spreadsheet based on your data. At a minimum, update the following:
- On the Sites sheet, update the location information (Address, Locality, State, County, Postal Code) from the default values to the correct values for your venue.
- On the Units_Use sheet, update the IMDF_Category use types. At a minimum, define the use types that correspond to Walkways, Stairs, and Elevators to avoid errors when submitting the IMDF to Apple. Additional categorization can aid in visualization when reviewing the IMDF in the IMDF Sandbox and conducting a survey of your buildings.
- Run the Indoors To IMDF workbench using the Data Interoperability extension. This tool uses the spreadsheet from the first workbench as input.
At the end of this process, you will have a zip file that includes a GeoJSON for each of the following: Footprint, Venue, Openings, Units. This is the IMDF file that you will use to configure Apple Indoor Positioning.
Inspect the output in the Apple IMDF Sandbox
Once you have created the IMDF, you can upload it to the Apple IMDF Sandbox for initial validation. You can fix some types of errors, like units that extend beyond levels, in the IMDF Sandbox, while for other types of errors, such as self-intersection, you must make modifications in the indoor data and re-run the workbenches.
In addition to validation errors, the IMDF Sandbox provides a list of warnings. These are not necessarily data problems but should be inspected to ensure that the floor plan data is accurate. For example, a donut-shaped level in a building due to a central courtyard.
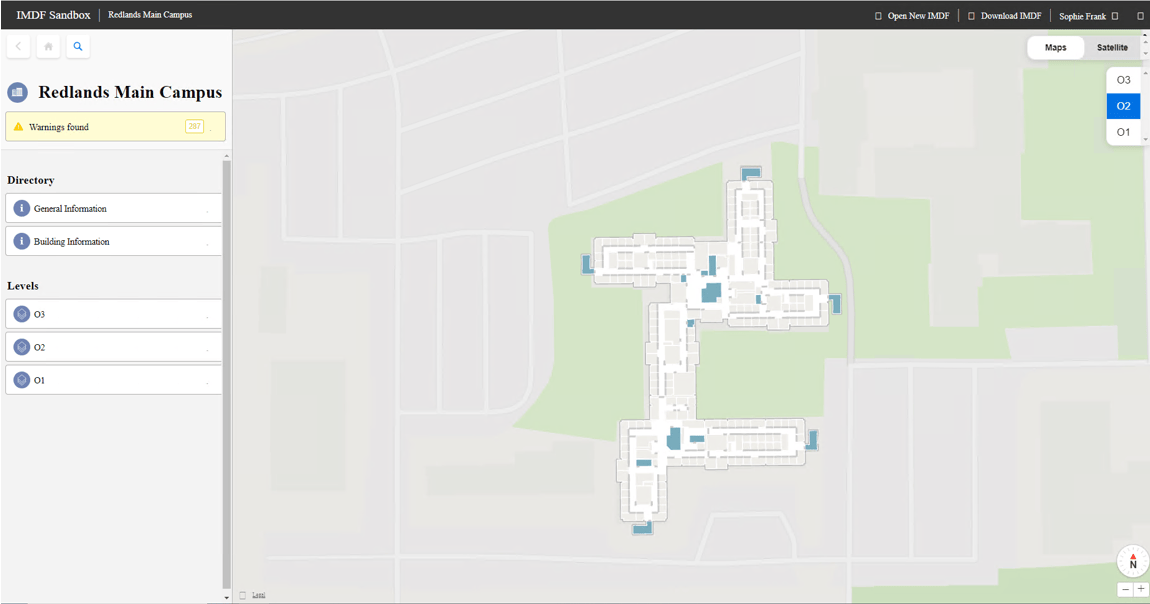
Once you have an IMDF that is error free and have confirmed that the warnings are acceptable data conditions, you can download your updated IMDF file.
Submit IMDF to Apple for verification and approval
Once you have registered with Apple Indoor Maps, you must create a venue associated to the address of your building and submit it for approval. After Apple approves the venue, you can upload the IMDF for further validation.
Apple validates the IMDF and provide a list of all the data conditions flagged as errors or warnings. If there are any errors you must fix them in your data before proceeding to the next step.
After Apple has validated and accepted the IMDF it goes through a georeferencing process. This involves a second set of validations for data positioning and accuracy. At the end of georeferencing, Apple provides a detailed list of any data conditions flagged as errors or warnings.
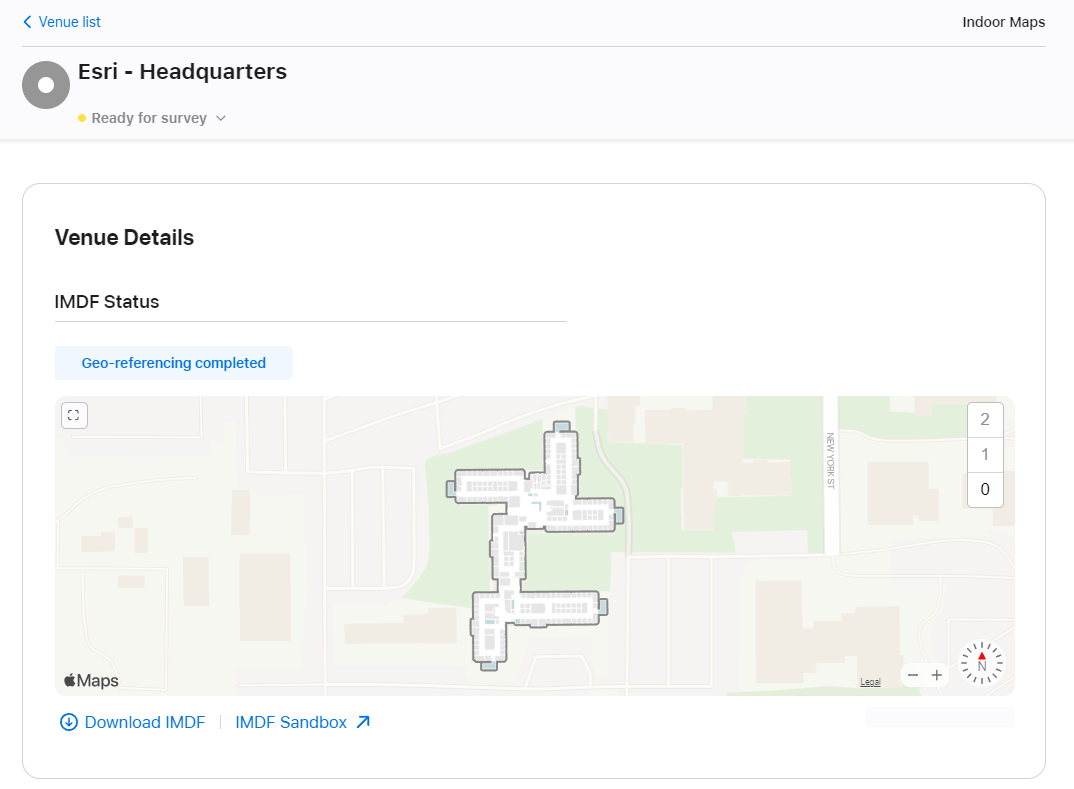
Once Apple has georeferenced the IMDF file, you can survey your building and configure indoor positioning.
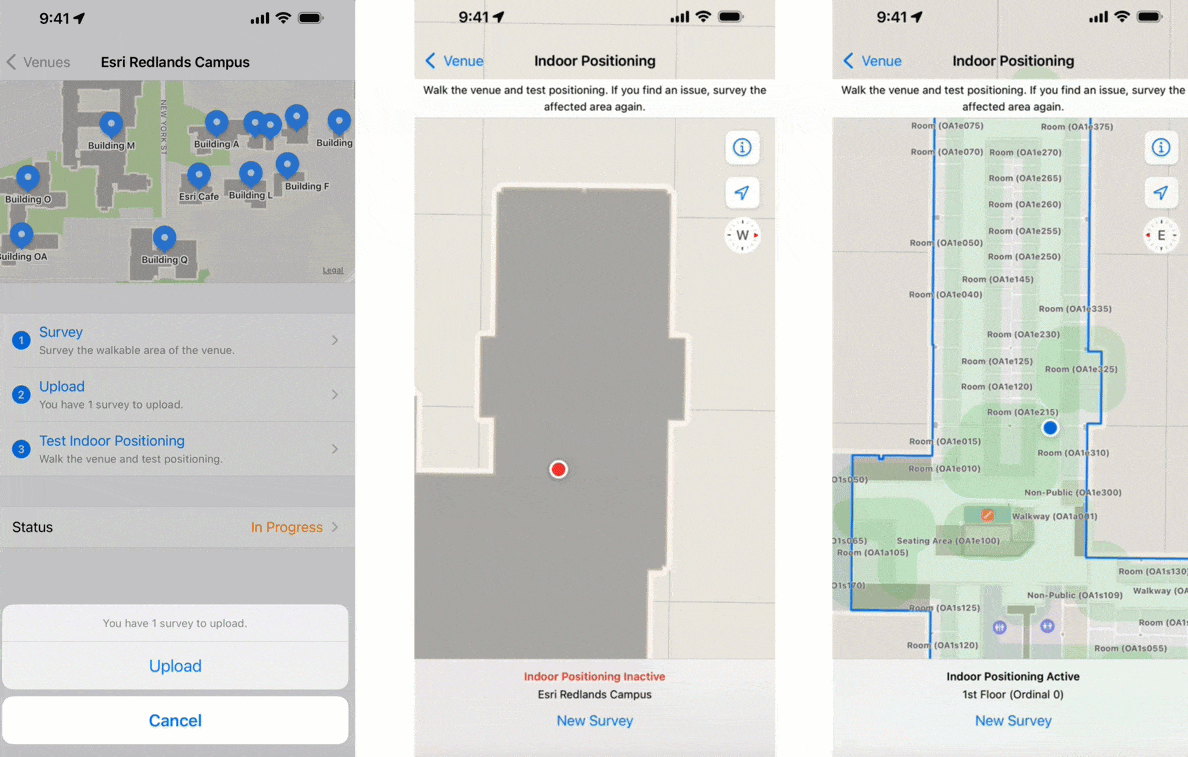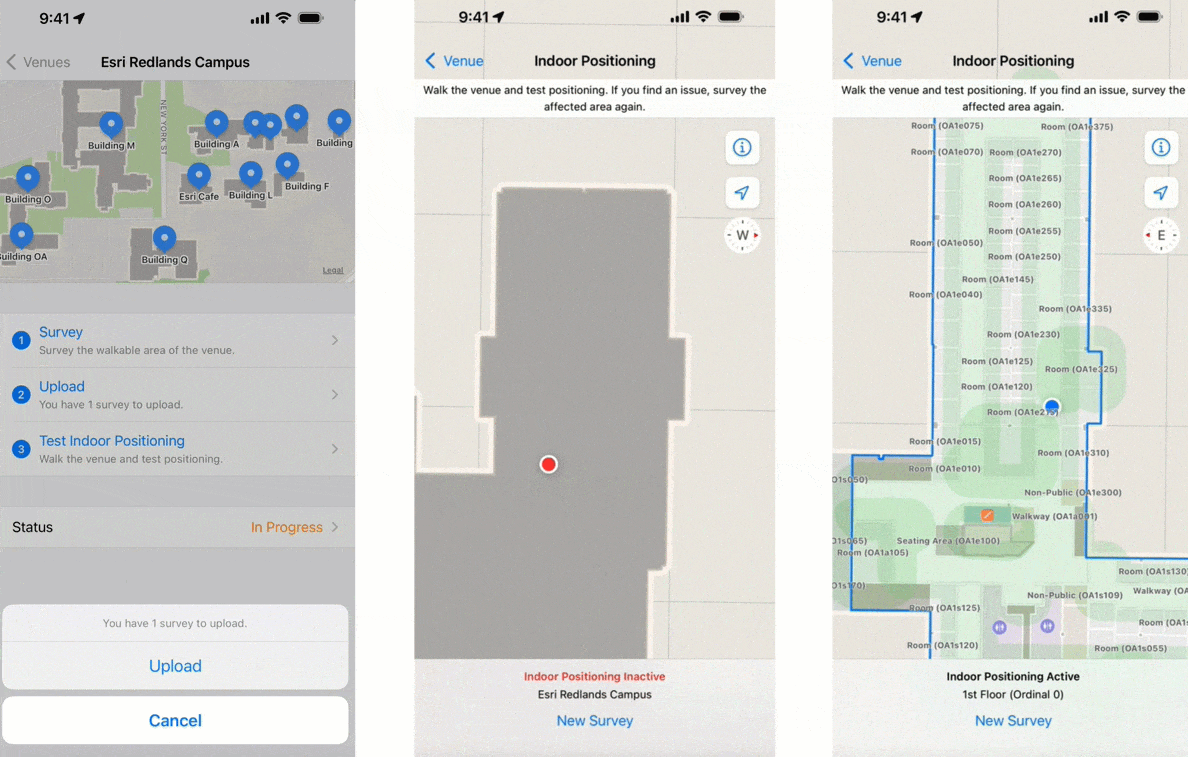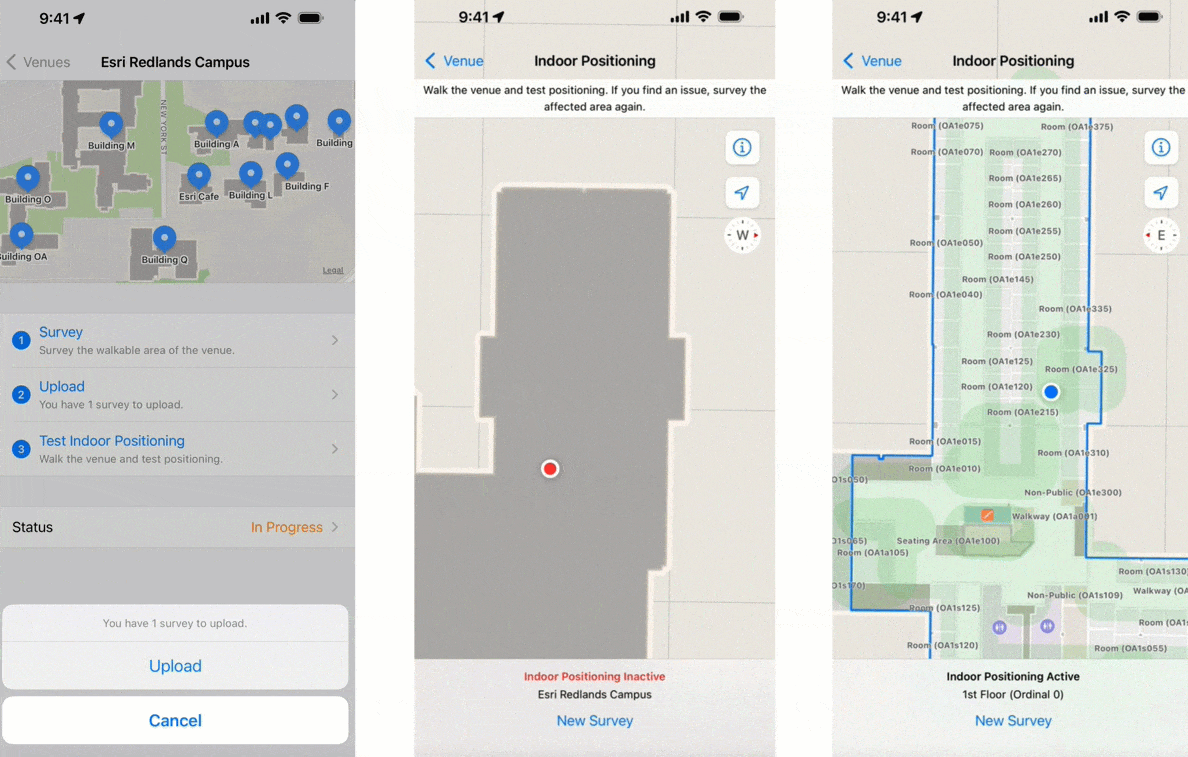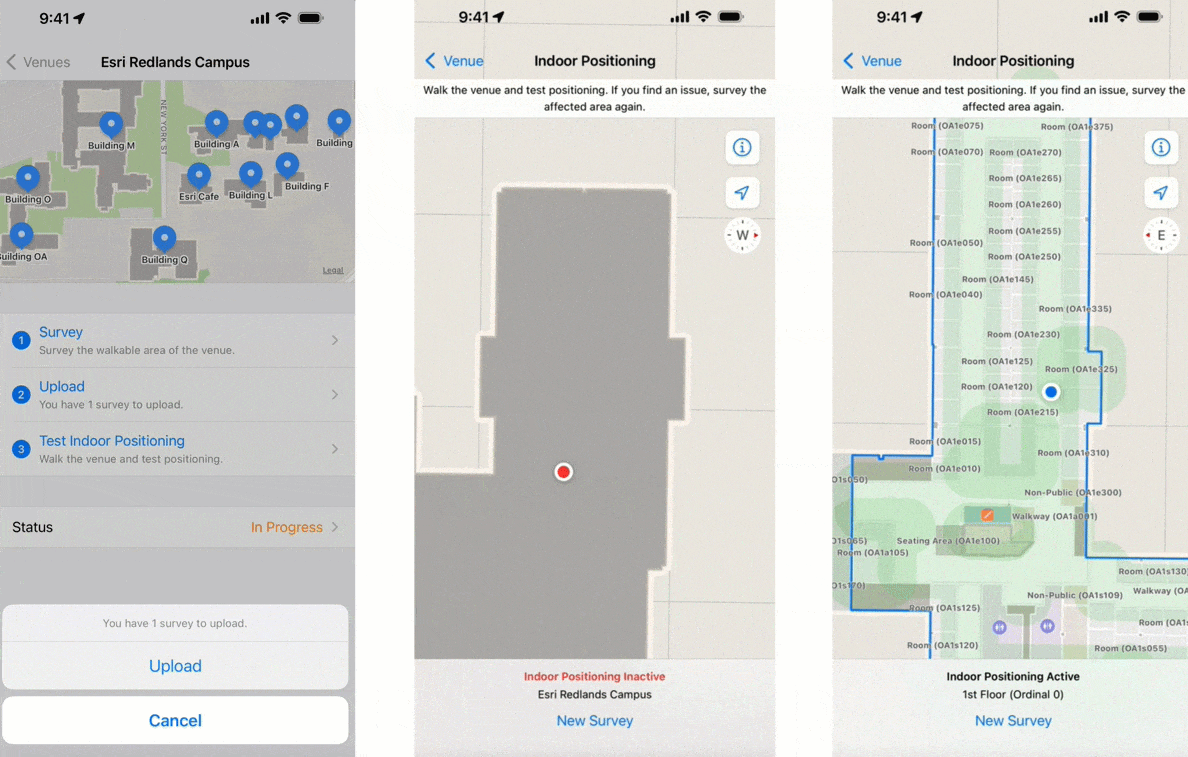
Perform indoor surveys
Just like GPS requires an unobstructed view of the sky to locate satellites, IPS must know the fixed location WiFi access points inside your buildings. Conducting an indoor survey using the Indoor Survey app from Apple collects this information.
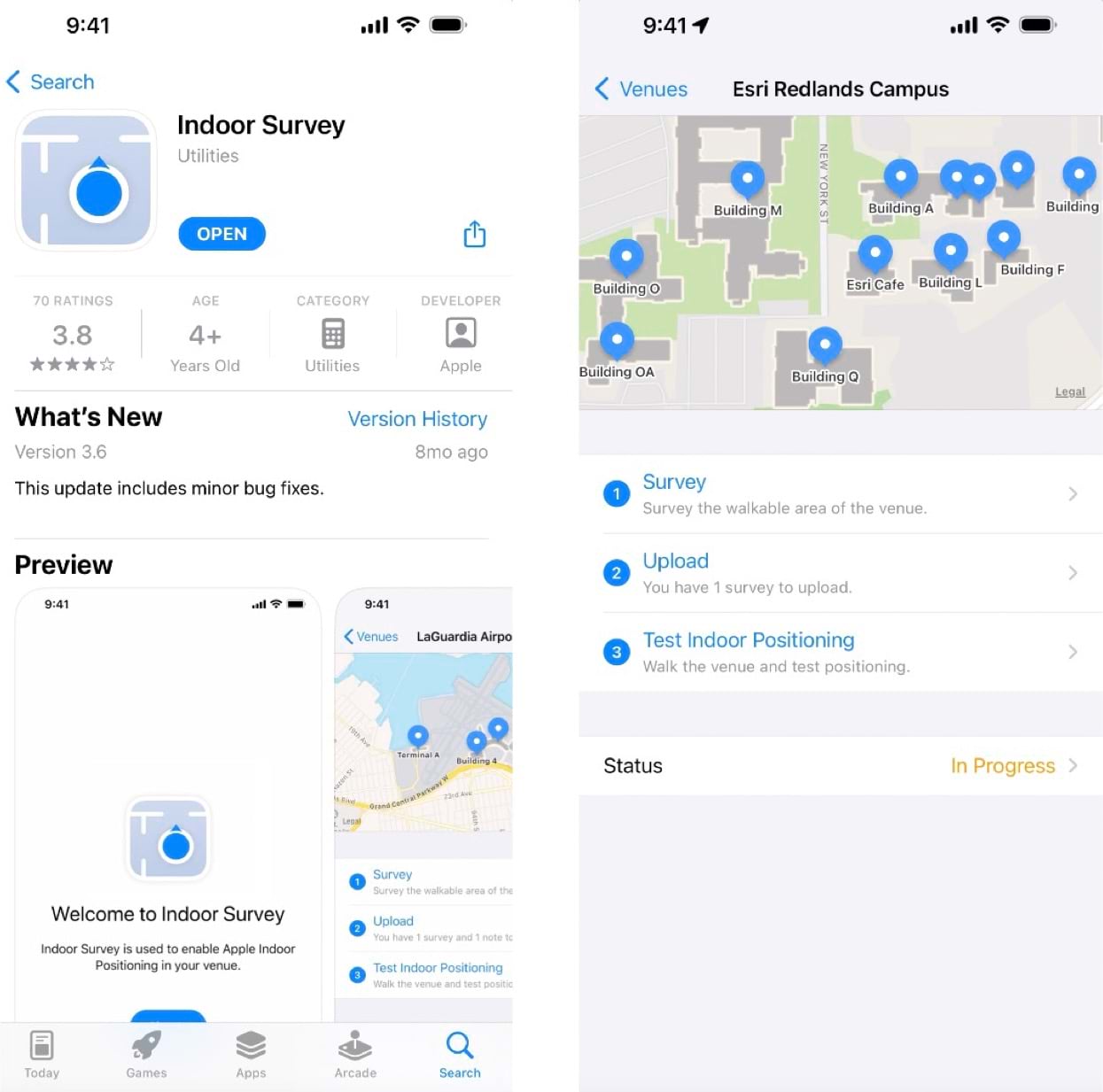
At its simplest, an indoor survey requires walking through hallways in your building and tapping on the indoor map to record your location at regular intervals in the Indoor Survey app. There are several strategies to follow if you require indoor positioning inside large rooms or open areas. Apple provides examples of sample surveys and answers to common questions.
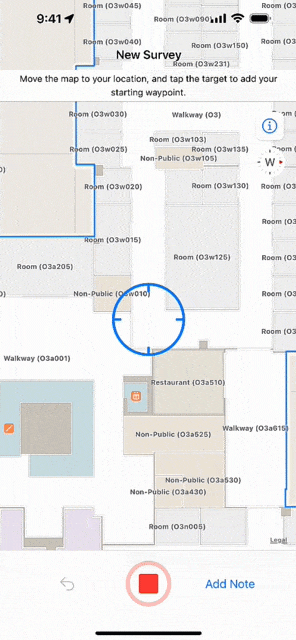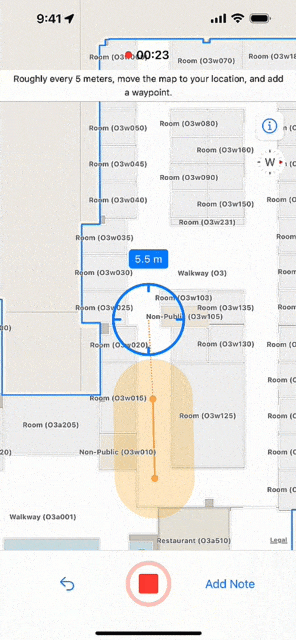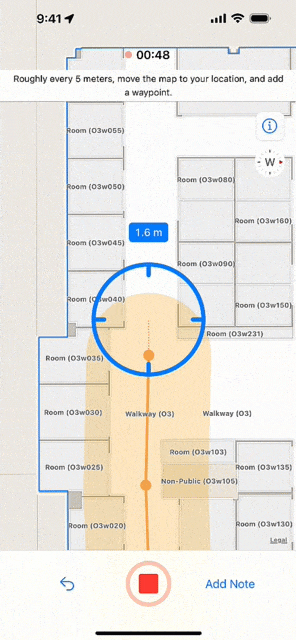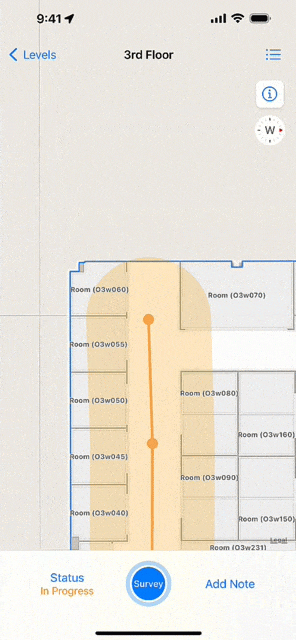
You should upload the survey once it is complete and test the indoor positioning. While testing, the app displays a red dot to indicate areas in which indoor positioning is not available. Surveyed areas that are processed appear with a green shade and the blue dot should be visible and follow you as you walk around.
Best practices when conducting a survey
Before conducting an Apple IPS survey, it is benefitial to understand the distribution of WiFi access points in the building, in order to efficiently plan survey paths. WiFi access points are mounted in way where they are not easily visible. In some cases, there may be only a few of them in a large area. You can work with your IT department to get additional access points installed if necessary.
- Use the same iPhone model to conduct all the surveys
- Hold the phone steady
- Avoid metal cases as they can interfere with magnetic fields
- Use a fully charged phone and avoid Low Battery mode
- Do not charge the phone while conducting the survey
- Walk in the center of hallways and stay 1 m away from walls
- Avoid dropping too many anchor points
- Complete a survey for an entire floor at a time
- Start and end a survey at the same place
- Walk around the perimeter when surveying large open areas
- Avoid surveying in crowded areas
Use Apple IPS in Indoors
Once you are satisfied with the indoor positioning results from your survey, you can make the indoor positioning live so it is available for use in ArcGIS Indoors mobile app for iOS. Location awareness unlocks many capabilities in the Indoors mobile app, including automatically detecting the floor you are on, searching for nearby amenities like first aid kits, travel time, and estimated time of arrival when navigating indoors amongst others. You can also choose to share your location with a selected group of colleagues so they can easily find you.
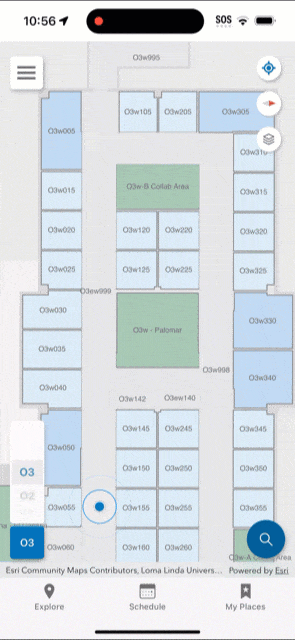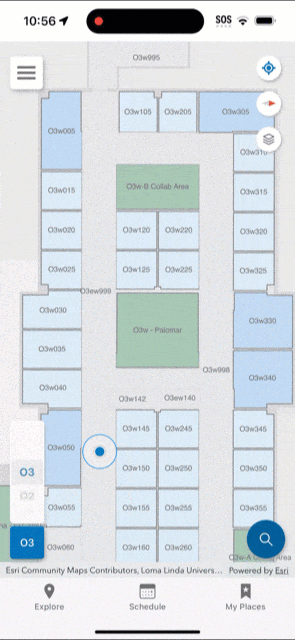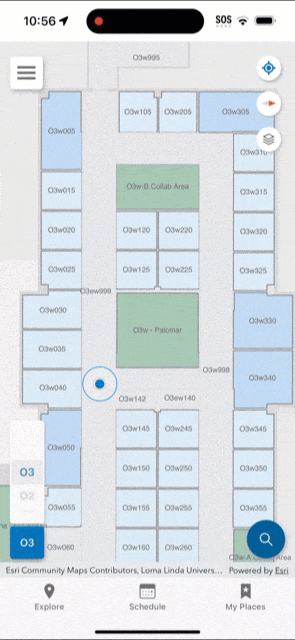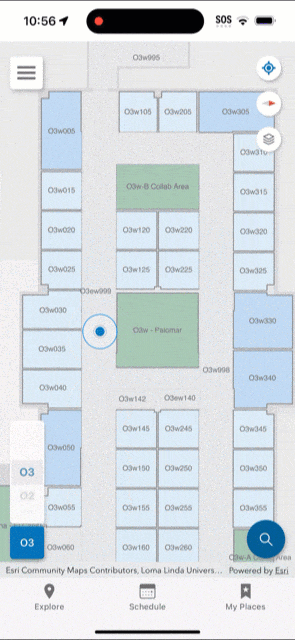
As your floor plan layouts change, you may need to periodically re-export the Indoors model to IMDF, upload to Apple, and conduct a new survey. Additionally, as your wireless network changes (for example, wireless access points move or are added) you may need to re-survey your buildings to keep the indoor positioning accurate in your organizational apps.

Article Discussion: