Drones are now everywhere – superbowl halftime shows, delivering packages, racing in the DRL (Drone Racing League), and now can be used to supplement your GIS program. With Drone2Map you’re able to take drone images from a flight, create actionable information with them, and share it with everyone who would need to see it. You can create 2D orthomosaics, digital surface models, 3D objects, point clouds, and an inspection viewer. Since Drone2Map is accessed by logging in with your ArcGIS Online organizational account, Drone2Map is connected to the rest of the ArcGIS Platform which allows you to view, edit, and update your outputs in other areas of the platform such as ArcGIS Pro and ArcGIS Online. Drone2Map allows users to quickly and accurately create actionable information from drone data. This blog post will describe how to get started and sample workflows of how water utilities can leverage Drone2Map.
Selecting the Right Template
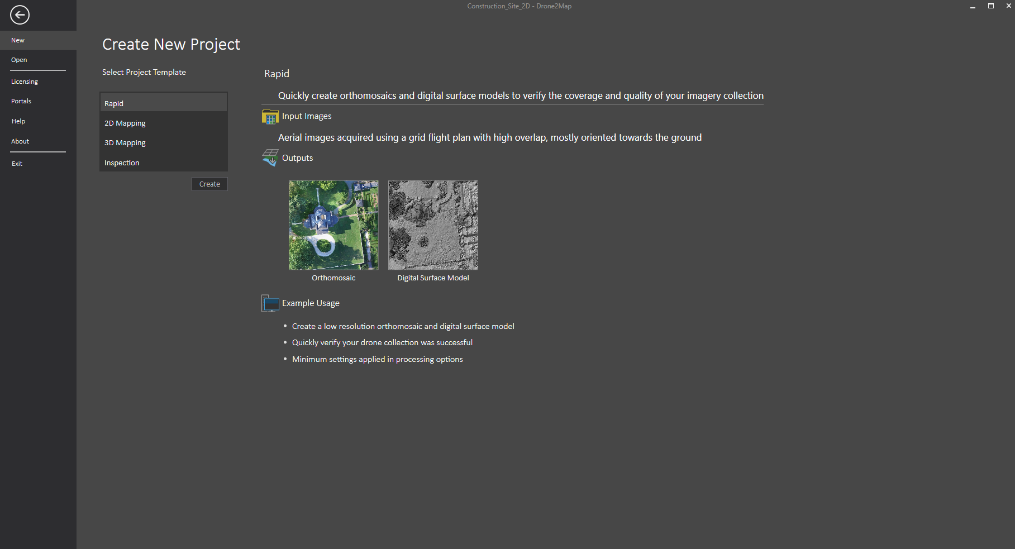
When Drone2Map is opened, you are presented with 4 different project templates. These templates will serve as your guide to get you the outputs you need.
- Rapid – Quickly create orthomosaics and digital surface models to verify the coverage and quality of your imagery collection.
- 2D – Create high resolution orthomosaics, digital surface models, and multispectral indices.
- 3D – Create detailed 3D colorized point clouds, 3D textured meshes, and 3D PDFs.
- Inspection Viewer – Process drone imagery and quickly inspect objects of interest.
Planning your Flight
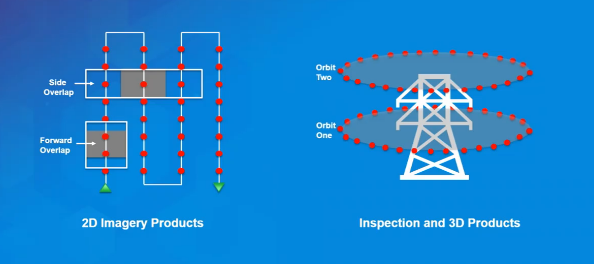
When getting started with Drone2Map it’s important to think about what kind of outputs you want. To create the best 3D output, you will need a different flight plan than creating the best 2D output.
|
2D Flight Plan |
3D/Inspection Flight Plan |
|
|
Workflow Examples
Inspecting Infrastructure
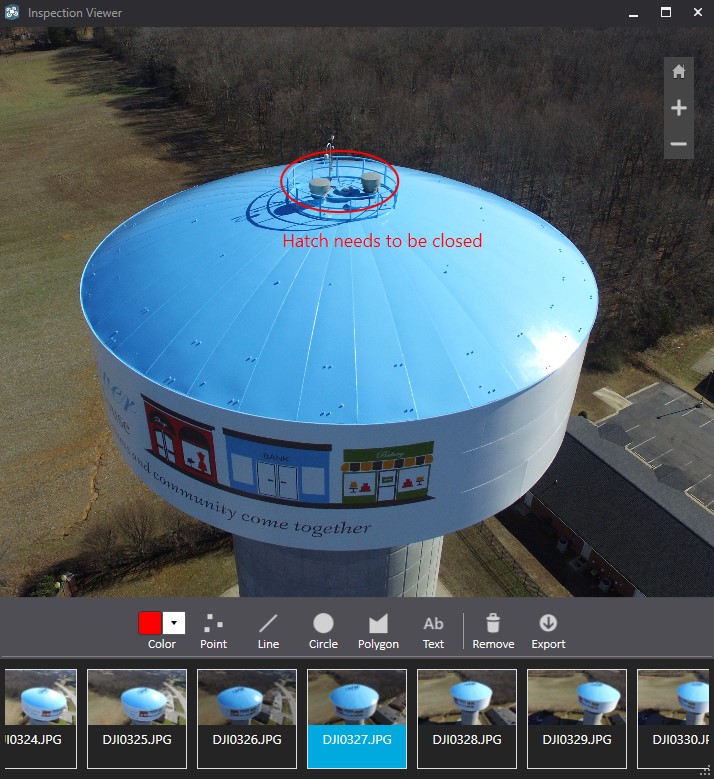
Many water utilities are using Drone2Map to inspect their tanks. Instead of sending a worker up a tower for a hatch inspection why not send a drone? A drone is a safer, easier, and more efficient way to inspect water tanks. Below I outline a quick process to inspect water tanks with a drone and Drone2Map.
- Flight Pattern – Since we’re looking for an inspection viewer we’ll want to use orbits and oblique camera angles.
- Collect Data – Using the flight pattern in step 1 collect the data with your drone.
- Process Data – Using the Inspection Template in Drone2Map the data can be processed right then and there in the field or can be brought back into the office to be processed.
- View Product – The Inspection Viewer in Drone2Map allows us to view each image we captured and annotate over each image. Therefore, we can draw and write on the image and share that with whoever would need to know.
Updating Basemaps
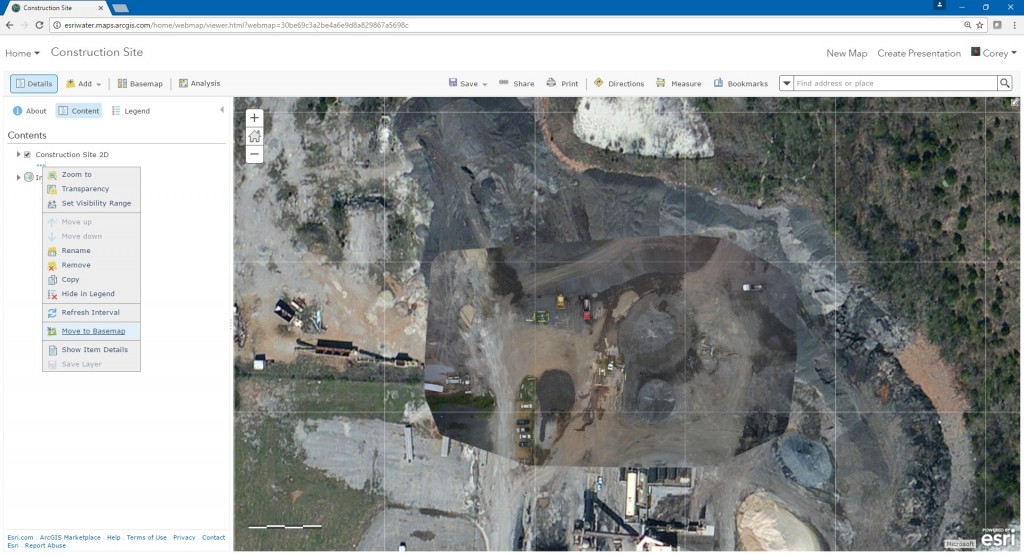
Water utilities are also leveraging Drone2Map to update their basemaps. Instead of using inaccurate outdated basemaps utilities can update their basemaps whenever they see fit and therefore have a current view of their service area. Below I outline a quick process to update basemaps with a drone and Drone2Map.
- Flight Pattern – Since we’re looking for an orthomosaic, which is a 2D output, we’ll want to use the grid flight pattern with side and forward overlap.
- Collect Data – Using the flight pattern in step 1 collect the data with your drone.
- Process Data in Field – Using the Rapid Template quickly process the data in the field to ensure you captured the appropriate data. If you did not repeat step 2.
- Process Data in the Office – Use the 2D Mapping Template to process the data.
- Share Products to ArcGIS Online – Click Tile Layer on the Share ribbon to share your orthomosaic to ArcGIS Online.
- Update Basemaps – Add the hosted tile layer to the web maps you consume. Once the tile layer is in the web map click the More Options button and select “Move to Basemap”. This will add the tile layer you created in Drone2Map to the basemap.
- Track Progress of Projects
- Calculate Volume
- Update Basemaps for new Developments
- Inspect Canals
- Create 3D Renderings of Infrastructure
- Comparison Analysis
- Create Point Clouds
- Inspect Pipelines
- Create Elevation Models
- Collect Asset Data for Visible Features (hydrants, inlets, etc.)
And many more…
Drone2Map provides utilities a safe, efficient, and easy way to inspect assets, update basemaps, and do much more. Please share your drone use cases.
Commenting is not enabled for this article.