We are thrilled to introduce ArcGIS Flight, a mobile application that revolutionizes the way drone flights are planned and executed for reality mapping and inspection within the ArcGIS system. Drone operators can seamlessly access their GIS content during flight planning, providing valuable context and situational awareness. The app offers different flight modes tailored to specific asset capture needs, whether it’s mapping larger areas or inspecting vertical structures. Flight execution is fully automated and repeatable, ensuring consistent high-quality imagery. Post-flight, the app enables in-field quality control and easy integration of imagery into ArcGIS for processing and analysis, including for 3D mesh generation using ArcGIS Reality software. With ArcGIS Flight, you can:
- Choose from various flight modes to suit different asset types.
- Plan flights with 2D or 3D GIS context.
- Automatically perform aircraft checks and execute flights.
- Utilize the Terrain Follow feature to maintain safety and consistent image resolution.
- Conduct on-site image quality control.
- Record video and geospatial video logs.
- Seamlessly integrate captured imagery into ArcGIS for further processing and analysis.
What’s New
ArcGIS Flight is set to replace both Site Scan Flight and Site Scan Flight LE, marking a significant upgrade in our offerings. This application streamlines the process of drone mission planning and data capture.
New enhancements:
– Unified login experience: ArcGIS and Site Scan accounts can now both be used to log in.
– Ability for users with an ArcGIS Mobile Worker, Creator, Professional and Professional Plus user type to use the app
– Multiple mission import.
– Refined settings experience.
– Improved RTK functionalities including the ability to add new network RTK providers.
– Support for Freefly’s Pilot Pro controller.
– Automatic mission upload after importing (Requires Site Scan Operator license)
– Quick Mission upload (Requires Site Scan Operator license)
Basic ArcGIS Flight Workflow Example
For those unfamiliar with ArcGIS Flight or drones in general, this workflow will demonstrate the capabilities of the app with a straightforward example of gathering drone imagery.
- Download the ArcGIS Flight application from the app store and launch the application.
- Sign in using one of the previously mentioned licensed user types.
- Create or select a project
- Connect your drone to the tablet running ArcGIS Flight and select the drone you want to fly with from the dropdown menu at the top right.
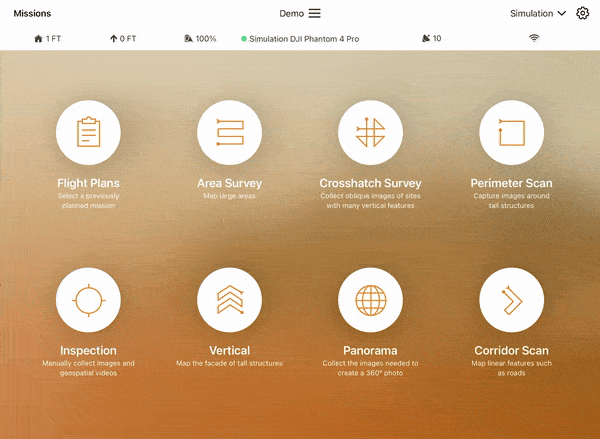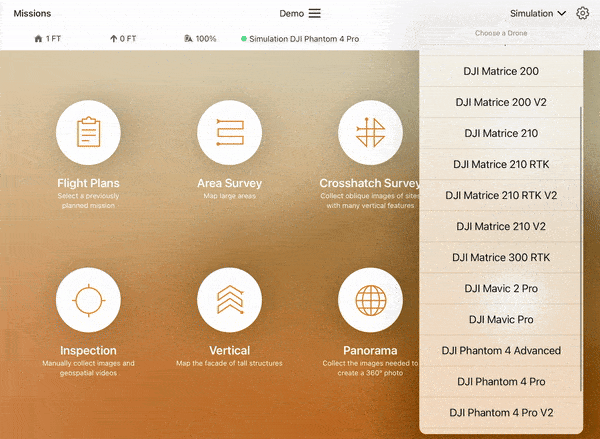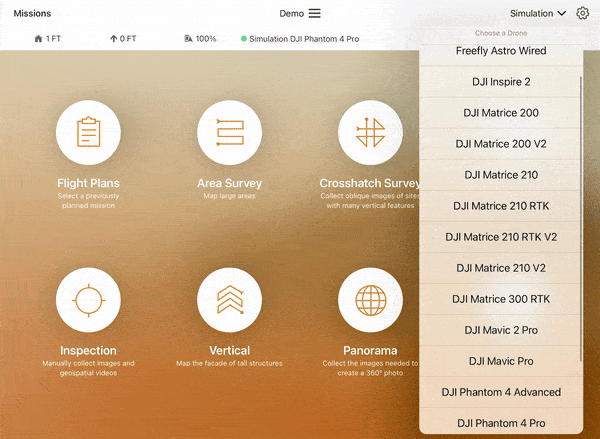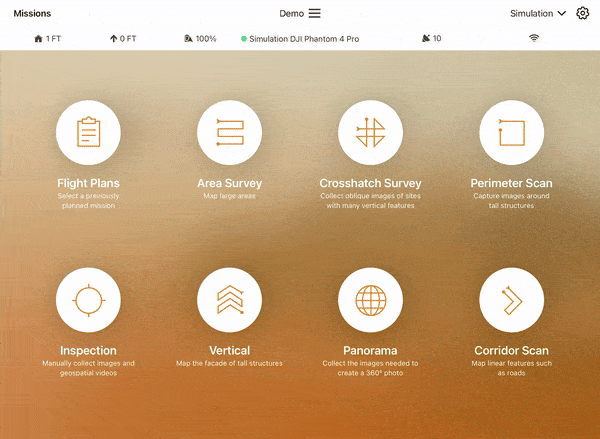
5. Select the Area Survey flight plan. This flight plan is the most accessible to beginners for understanding drone behavior during autonomous flight.
6. Add a descriptive title to your mission in the Mission Name box. Effective titles typically include information on the geographic area, purpose, client, or timeframe of your mission (e.g. Wetland_Monitoring_ClientName_June2024).
7. Specify the geographic area closest to your site by typing in the Mission Location dialog box and select NEXT.
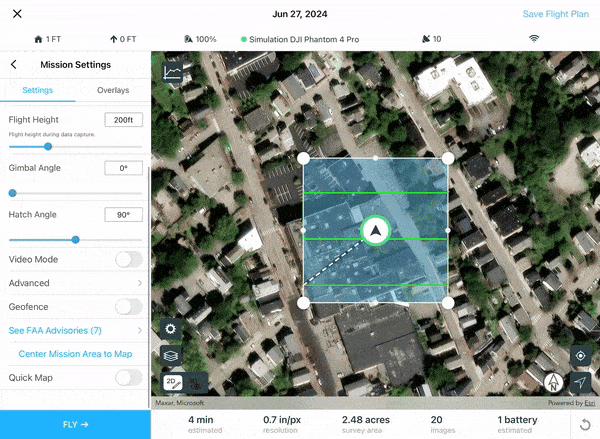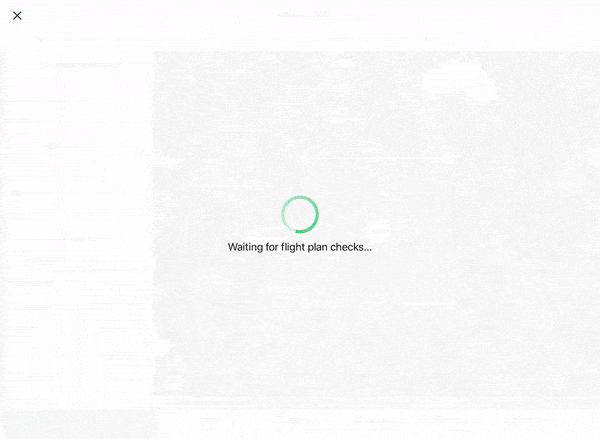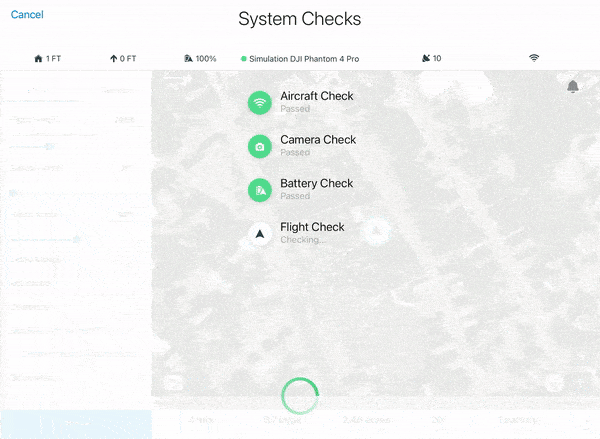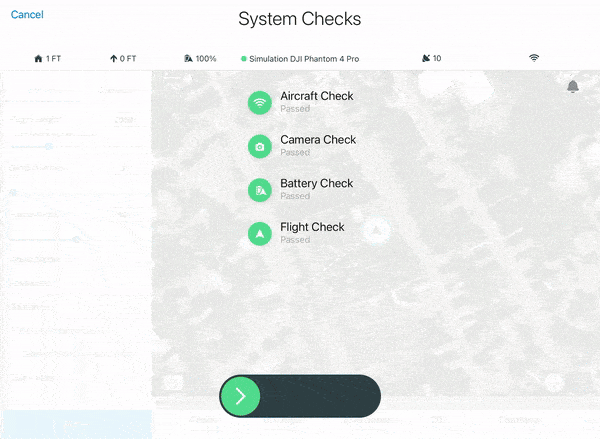
8. Use the Mission Settings tab to customize the parameters governing your drone flight (flight height, video mode). Drag and move any of the vertices of the flight polygon to change the shape of the mission area.
9. When ready for takeoff, select FLY. This will automatically conduct checks on your drone camera system and battery levels to ensure safe flight throughout the entirety of your mission. If all checks have been passed, swipe the green arrow to the right to initiate launch.
10. You can now watch in real time as your drone follows the flight path specified, collecting aerial imagery to generate orthomosaics, point clouds, and 3D meshes. The main map area indicates the real-world location of your drone, and the video feed in the corner shows a live stream of your drone’s point of view.
11. Upon completion of your mission, your drone will return to above the takeoff point and automatically descend to conduct a safe landing.
12. To collect the imagery gathered during flight, select the Get Images button on the mission completion window.
13. Images can be imported from the drone to the tablet using a WiFi connection with the Wireless Import option, or directly by removing the drone’s SD card from the drone and copying the images off the card with the Memory Card Import option.
14. Choose your desired method and select Import. Import progress for each image collected will be visible in the lower window. When imported, the images will appear in the upper map window in their real-world location.
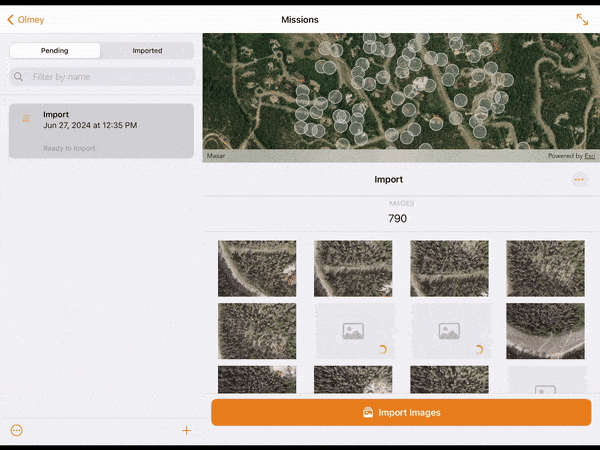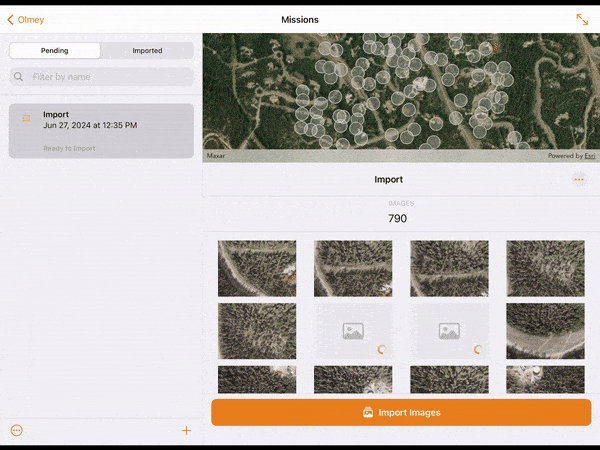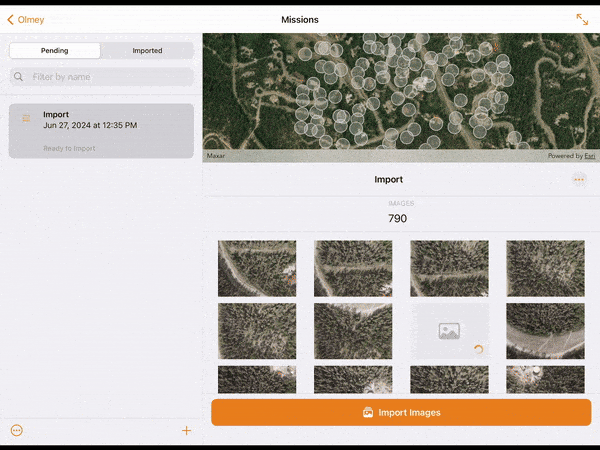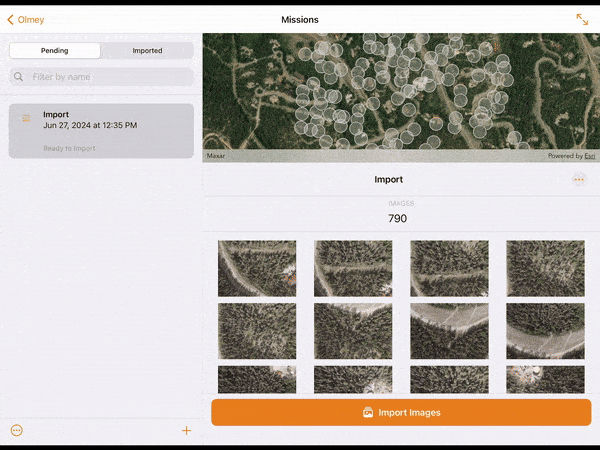
15. If you are signed in with a Site Scan account, images imported on to the device can be uploaded to Site Scan by selecting Upload Images.
Congratulations! You have planned and executed a simple drone mission over a chosen area using ArcGIS Flight. Drone flights collect high-fidelity imagery over large areas in a minimally invasive manner that is valuable across a variety of sectors including AEC, Mining, Transportation, Utilities and Natural Resources and Government. For more information on ArcGIS Flight, stay connected with the team by joining our ArcGIS Flight Esri Community Page.


I don’t see a lot of difference yet -save the background color- but downloading from SDcard is more easy. Thanks Team!!
Will ArcGIS Flight be compatible with DJI’s remote controllers such as for Mavic 3 Enterprise oder DJI Mini?