As a GIS Pro, you already appreciate the power of date and time data for analyzing and tracking patterns over time. Whether you’re exploring population dynamics, weather events, or wildlife locations, you’re no stranger to the challenges of managing dates, times, and time zones. But, we’ve got your back with some new field types and web map settings that make managing temporal data easier.
In this article, we’ll take a look at some of the latest tools available to help you make the most of your temporal data. Get ready to level up!
We’ll break this into 4 parts:
- Level Up Tip #1: Choose the Right Fields
- Level Up Tip #2: Set the Web Map Time Zone
- Level Up Tip #3: Preserve the Time Zone of the Data
- Level Up Tip #4: Adjust for Daylight Savings Time

Level Up Tip #1: Choose the Right Fields for Your Data
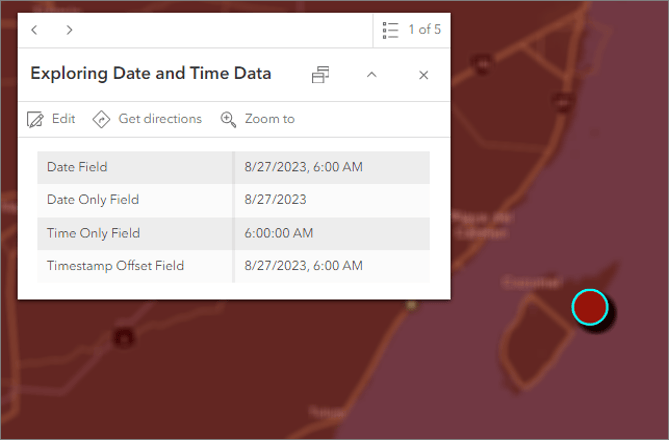
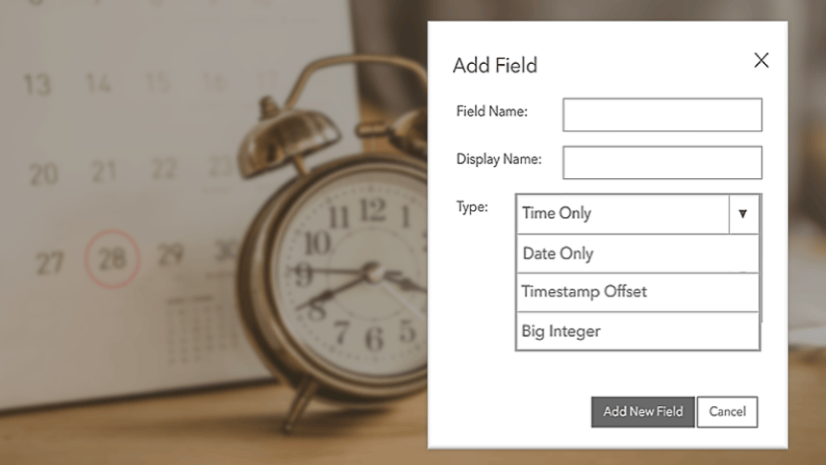
Previously, ArcGIS only had one field type for storing date and time information; a Date field type that combines both date and time values. In the original (OG) field, each date value has an associated time value, and vice versa. However, we recently introduced new field types that provide more flexibility. Let me break it down for you:
- The Date field is best when both date and time are important.
- The Date only field is ideal for tracking events, recording historical data, and conducting date-based queries where the time of the event is irrelevant.
- The Time only field stores only time values, without a date. It’s great for storing information like business hours or transit schedules.
- The Timestamp offset field stores date and time values and the time zone (stored as an offset from UTC). This is really useful for records that occur across different time zones.
For more information on when to use the new field types, check out the article Time Is On Your Side with New Field Types in ArcGIS Online.
Level Up Tip #2: Set the Time Zone on your web map
In October 2023, we introduced support for setting the web map time zone. Setting the time zone for your map gives you more control over how date and time values are displayed. Date and time values displayed in popups, tables, and labels are usually adjusted to display according to the viewer’s device time zone. But you can change that. To configure the map time zone in Map Viewer, expand the Time section in the Map properties pane. Then select one of the following:
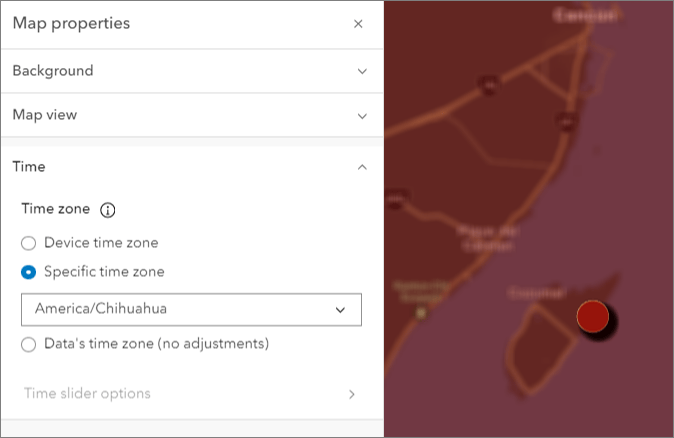
- Device time zone: Displays the date and time based on the viewer’s device time.
- Specific time zone: Choose a specific time zone from a drop-down menu.
- Data’s time zone: Displays the date and time data as-is, without any adjustments.
Setting the time zone helps ensure your date and time values are displayed consistently in the web map. For a deeper dive into web map time zones, check out Working with Time Zones in Map Viewer.
Level Up Tip #3: Preserve the Data’s Time Zone
Preserve the Time Zone for the Layer
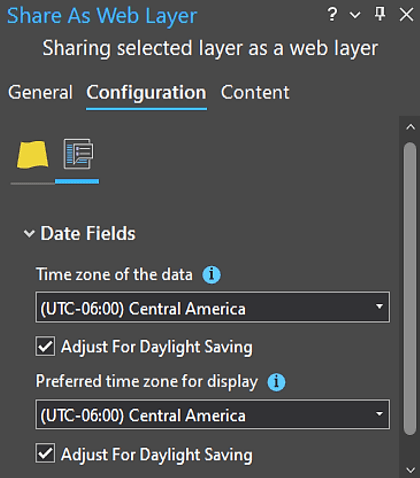
When you publish a layer with temporal information, from either ArcGIS Pro or from a file, you can set a time zone for the layer. This is handy when A) all of the data was collected in the same time zone, and B) you want to preserve the time zone information with the layer.
Note: If you don’t specify a time zone for your data, the time zone defaults to UTC. That can affect how the date and time values are displayed online. We’ll talk about that in more detail later.
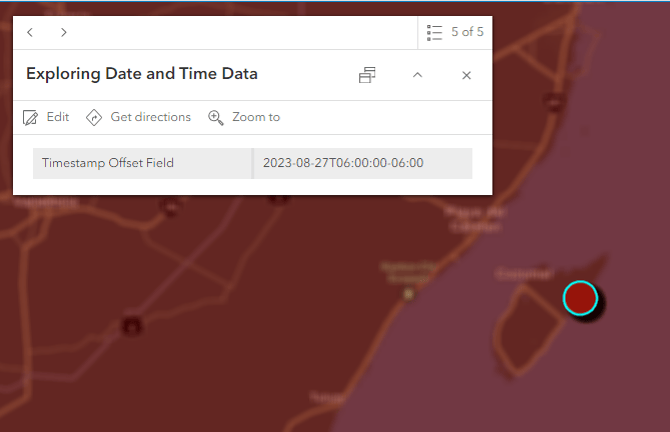
Preserve the Time Zone for each Feature
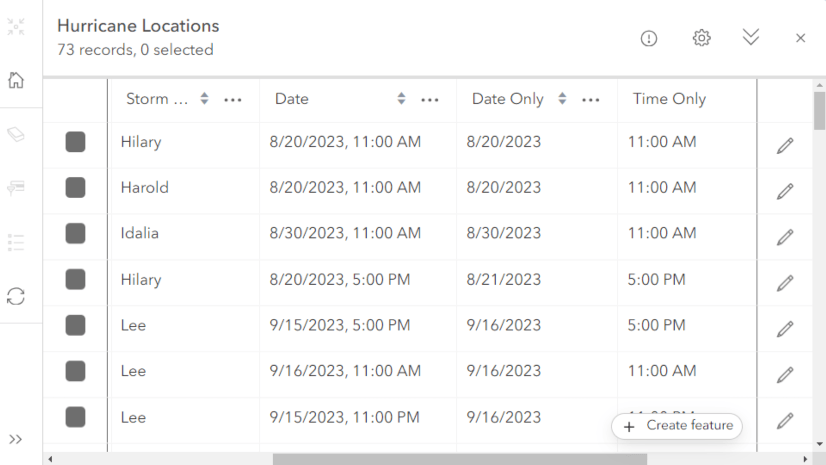
Selecting different time zones for different features is possible with the Timestamp offset field. This is especially useful when you’ve got a data with locations that span different time zones. Using a Timestamp offset field, editors can set the date, the time, and the time zone the feature was collected in, preserving time zone information for each feature in the layer. Pretty cool, huh?
In this field, the time zone is stored as an offset from UTC (in hours and minutes). For example, when the time zone is 6 hours behind UTC, let’s call that UTC-06:00, the timestamp offset would be stored as -06:00. Visit ArcGIS Online help for more information on Timestamp offset fields.
Level Up Tip #4: Adjust for Daylight Savings Time
When publishing a layer from ArcGIS Pro, you have the option to adjust for daylight savings time (DST). When its enabled, the date and time values are automatically adjusted, forward or back, based on when daylight savings time starts or ends in the region.

Exploring Strategies for Managing Date and Time Data
Example 1: Use the right field type
Imagine you have a dataset that uses the OG Date field type. You enter dates in this field, but no time. When you view the values, you notice that a time was added to the date. That’s because the Date field stores both date and time, always…so if you don’t enter a time value, a default time of 12:00 am (midnight) is automatically added.
Level Up Recommendation: When you’re working with dates that don’t require a time value, use the Date only field. Using the date only field eliminates the time component all together, making it easier to store and manage date-only data.
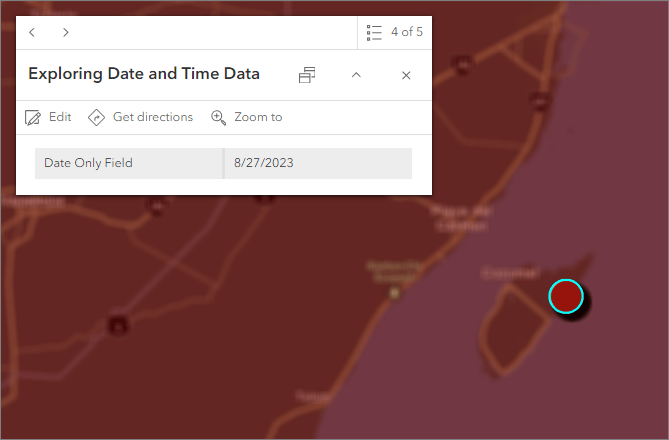
Example 2: Control the display of your data
We already touched on how time values are stored and displayed in ArcGIS- in UTC. Then, the display is adjusted based on the device time. Usually this provides an accurate, user-friendly experience. But that’s not always the case. Imagine you enter the following date:
1/1/2023 12:00 am
When viewed on a device in a time zone 1 hour behind yours, this value is displayed as:
12/31/2022 11:00 pm
The time, the date, and even the year changed, or rather, the way they display was adjusted. How can you prevent such adjustments? You’ve got options. Some possibliities include:
- Use a different field type, such as date only, which remains constant (no adjustments), or
- Set the time zone on the web map so that the values are consistent regardless of the device time.

Summary
In this article, we explored different strategies to help you level up your date and time data management in ArcGIS. You can leverage these options to choose an approach that’s right for your data depending on your goals. Mapping and editing date and time data can be tricky, but having the right tools can make it easier. We hope you’ll take advantage of tools including new field types, web map time zones, and publishing options that give you more control over how dates and times are displayed in ArcGIS Online.
More resources
ArcGIS Online Help has a wealth of information on working with date and time data. Be sure to join the conversation on Esri Community where you can ask questions, connect with other ArcGIS Users and share your own insights.



Commenting is not enabled for this article.