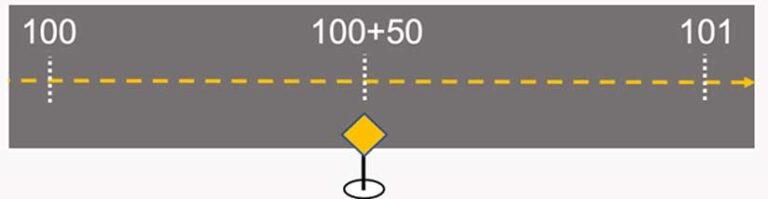
Linear referencing is a geographic approach for storing and describing the location of physical features in terms of measurements from a fixed point along a road, pipeline, or railroad. For example, the location of a yield sign along a highway can be described as “50 feet past mile marker 100.” Linear referencing is used to describe and locate assets by their distance from a fixed location.
Measurement values are stored as numeric values (doubles) in the m-value component of a linear geometry. M-values do not have a well-defined unit of measure but are often calibrated in US survey feet or meters.
Linear referencing is commonly used to describe location in the engineering, construction, and management of infrastructure that is tied to linear features. With the newly added support for linear referencing in ArcGIS Field Maps, mobile workers can locate—and even capture—measurements when inspecting assets along roads, railways, or pipelines.
Find Measure
Field Maps includes the Find Measure feature action, which supports the discovery of measurement values (m-values) along a selected linear feature. After selecting a measured linear feature, the Find Measure action appears. Tapping it will present the closest m-value perpendicular to the mobile worker’s current location. A search dialog box will appear. Simply tapping OK will place a pin at the interpolated, measured location. However, you can type an alternate measurement if you want to search for a location farther away from you.
Discover, validate, and capture measurements from any m-value-aware linear feature. The pin’s location can be used with the Compass or Directions tool for navigation, or the pin’s location can be used with Collect Here to capture a new feature. New features will store the measurement value if the layer is m-value aware.
Using Linear Referencing in Field Maps
The Find Measure action can be used with any measured line feature. The measured line feature does not need to participate in ArcGIS Roads and Highways or ArcGIS Pipeline Referencing, but features managed by those products will also work with this action.
Field Maps presents interpolated measurements the same way they are stored (numeric values without units). They are presented in the subtitle of the panel where details of the selected feature are shown. For display purposes only, measurement values are rounded to three decimal places.
Searching for measurement values will use all decimal values entered in the Find Measure dialog box. If the line feature geometry includes z-values, elevation will be used to interpolate the nearest perpendicular measure to your current location.
It is possible to label measurement values and even store measurement values in stationing notation using ArcGIS Arcade expressions. Copy and paste code from the Esri/arcade-expressions GitHub repository (https://bit.ly/3wXIwdj) to label features using stationing notation. You can apply the same expression to store the station value as an attribute of a point feature.
To find measurement values within a feature, they must adhere to these monotonic rules:
- All measurement values must be ascending or descending in value.
- Measurement values need to be strictly ascending or descending within a part, but duplicate m-values can exist at the ends of parts.
- Invalid routes will display an alert message, and details will be added into the Field Maps troubleshooting log.
What’s Next
The Find Measure feature action introduces support for linear referencing capabilities in Field Maps. Several enhancements, such as support for stationing notation and m-value editing of linear features, are under consideration. Esri wants to grow the linear referencing capabilities in ArcGIS Field Maps based on user feedback. Submit your ideas to Esri Community, or contact Esri directly through your account manager or by sending an email to ArcGISFieldMaps@esri.com.



