ArcGIS 10.5 provides new capabilities that enhance analytical and problem-solving and makes it easier to connect to and integrate many types of enterprise data with ArcGIS. The most significant change with the ArcGIS 10.5 release is ArcGIS Enterprise. ArcGIS Enterprise is the new name of the ArcGIS for Server product family that includes ArcGIS Server, Portal for ArcGIS, ArcGIS Data Store, and ArcGIS Web Adaptor.
The first step when getting started with ArcGIS Enterprise is to create a base ArcGIS Enterprise deployment. A base deployment is the configuration of the four software components—ArcGIS Server, Portal for ArcGIS, ArcGIS Data Store, and ArcGIS Web Adaptor—that is a functional Web GIS that resides in your infrastructure. The base deployment can be configured with all components on a single machine or with components distributed across multiple machines in a multitier configuration. ArcGIS Enterprise can always be deployed with high availability.
Server Roles
From the single ArcGIS Server software component, you can license the specific server capabilities that your organization needs through server roles. At ArcGIS 10.5, there are five server roles: ArcGIS GIS Server, ArcGIS Image Server, ArcGIS GeoEvent Server, ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server, and Esri Business Analyst Server. The five server roles of ArcGIS Enterprise provide an off-the-shelf solution that feels completely custom. Each server role added to the base ArcGIS Enterprise deployment can be scaled independently. ArcGIS Enterprise can be deployed on any infrastructure that meets the minimum system requirements so it can be architected to align with any organization’s technology road map.
ArcGIS GIS Server
This role captures everything ArcGIS for Server was in prior software releases. It provides the same service types and has the same analytical capabilities. ArcGIS GIS Server is offered in Basic, Standard, and Advanced editions and at the Workgroup level. Users will still be able to extend and customize the functionality of ArcGIS GIS Server through Esri-built extensions or through custom written server object extensions and interceptors. It powers Web GIS behind a firewall, but it can also be used in dedicated server sites to support specific functions for an organization, such as mapping and visualization and maintaining workload separation for optimal system performance.
ArcGIS Image Server
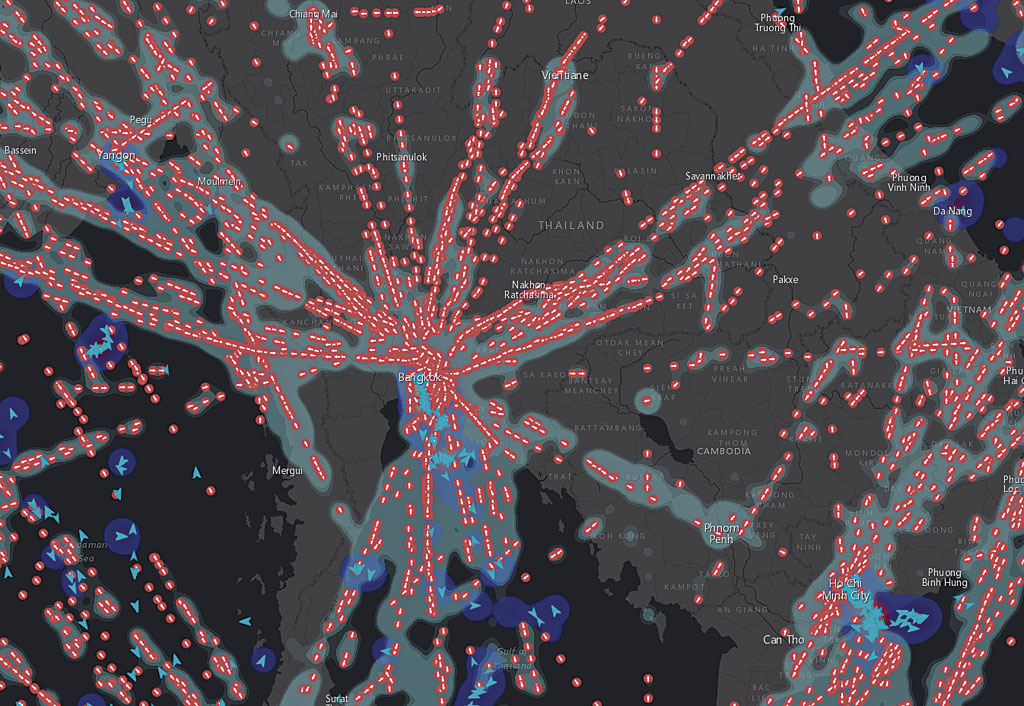
At ArcGIS 10.5, ArcGIS Image Extension for Server has been replaced by ArcGIS Image Server. It provides everything ArcGIS Image Extension for Server offered but also introduces Raster Analytics. By harnessing the power of distributed and parallelized computing, Raster Analytics can produce pervasive, full-resolution raster/imagery output in a fraction of the time previously required. Users can run simple raster analysis tools or can chain together analytical functions to create raster models to answer even the most complex questions. Whether the data resides in a data center or the cloud, Image Server has many options for connecting to existing raster and imagery libraries.
ArcGIS GeoEvent Server
Replacing ArcGIS GeoEvent Extension for Server, which was available in previous releases, ArcGIS GeoEvent Server serves the same purpose and has the same analytical horsepower. ArcGIS GeoEvent Server is designed to handle high-volume, high-velocity real-time and streaming data. It provides solutions through on-the-fly analysis and dynamic aggregation of large datasets, which makes data visualization simple. When connected to the base ArcGIS Enterprise deployment, ArcGIS GeoEvent Server can archive data to the spatiotemporal data store for further data analyses.
ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server
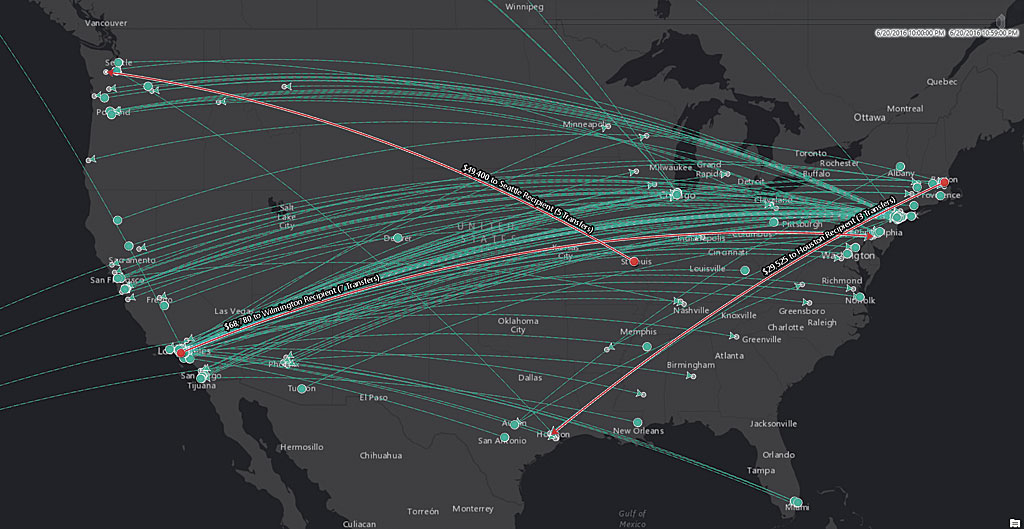
ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server makes its debut at the 10.5 release. It is designed to handle the analysis of massive datasets. GeoAnalytics tools are a subset of Esri geoprocessing tools that use distributed and parallelized computing to run space-time analyses on extremely large datasets. These tools can be executed using the Portal for ArcGIS map viewer, ArcGIS Pro, the ArcGIS Server REST API, or from the new ArcGIS API for Python. ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server can connect to data from the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), Hive, local file shares, and data from within ArcGIS Enterprise, including using the archived spatiotemporal output from ArcGIS GeoEvent Server as input. Because ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server uses the base ArcGIS Enterprise deployment to write and store analytical output, it is easy to use and share the resultant layers and data.
Esri Business Analyst Server
Esri Business Analyst Server is an Esri solution package that has been turned into a server role. Unlike the other server roles, Esri Business Analyst Server includes a bundle of specialized tools, data, and apps. Esri Business Analyst Server content is specially curated and proprietary to Esri. It allows users to target specific markets and enrich the data analysis process. Custom tools and applications make analyzing, generating, and exploring business intelligence data easy. Full integration with the base ArcGIS Enterprise deployment means that all business intelligence data remains safely behind the firewall.
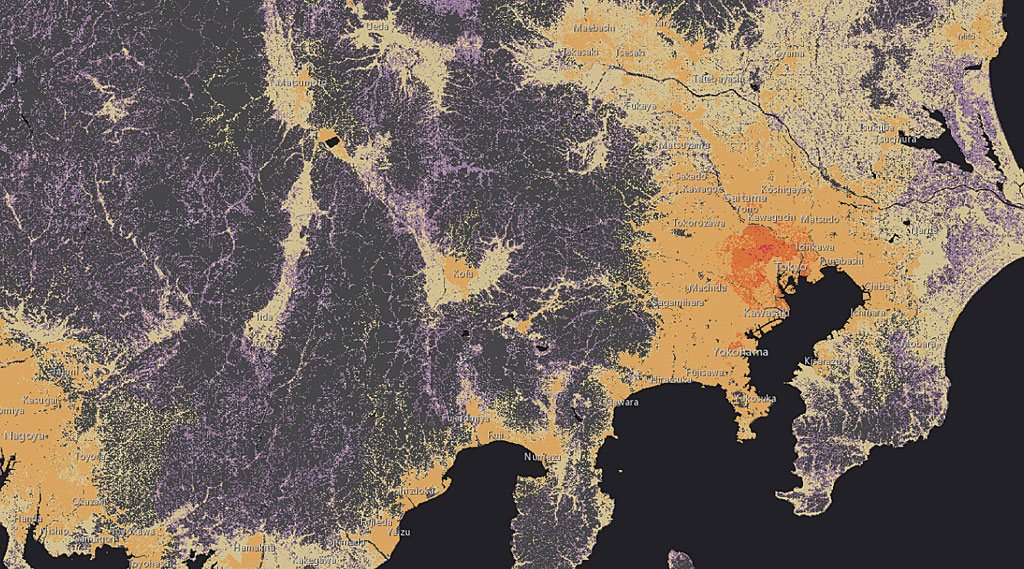
In addition to the server roles, ArcGIS Enterprise differs from its predecessor ArcGIS for Server by delivering Esri-curated Living Atlas of the World content behind the firewall. Using the base ArcGIS Enterprise deployment, an administrator can configure Portal for ArcGIS to include Living Atlas content, which includes imagery, demographics and lifestyle data, historical maps, and basemaps. An administrator can decide which Living Atlas resources to make available to the organization to align with the organization’s business priorities.
Extending Collaborative Capabilities
ArcGIS 10.5 is designed for full integration with Web GIS. Web GIS provides a centralized location for an organization to share data, analyses, and information. Esri offers two paths to Web GIS: ArcGIS Enterprise and ArcGIS Online. The choice will depend on whether an organization wants to manage the infrastructure behind its Web GIS.
If everything should be kept behind an organization’s firewall and software installations and deployments are handled in-house, then ArcGIS Enterprise is the choice. If it makes more sense for the organization to have Esri manage the scaling, updating, and overhead of its Web GIS, then ArcGIS Online is the choice.
With the release of ArcGIS 10.5, the collaborative capacity of Web GIS has been expanded. New with ArcGIS 10.5 is the concept of distributed Web GIS, in which content is shared between multiple, independent Web GIS implementations. The first wave of distributed Web GIS—portal to portal collaboration—is unveiled at ArcGIS 10.5. portal to portal collaboration uses the Portal for ArcGIS component to share content between two or more ArcGIS Enterprise deployments.
In addition to greater collaborative capabilities in Web GIS, the apps offered by ArcGIS 10.5 give better connectivity between the office and the field so an organization can gain new information from its data.
Interactive Data Discovery and Exploration
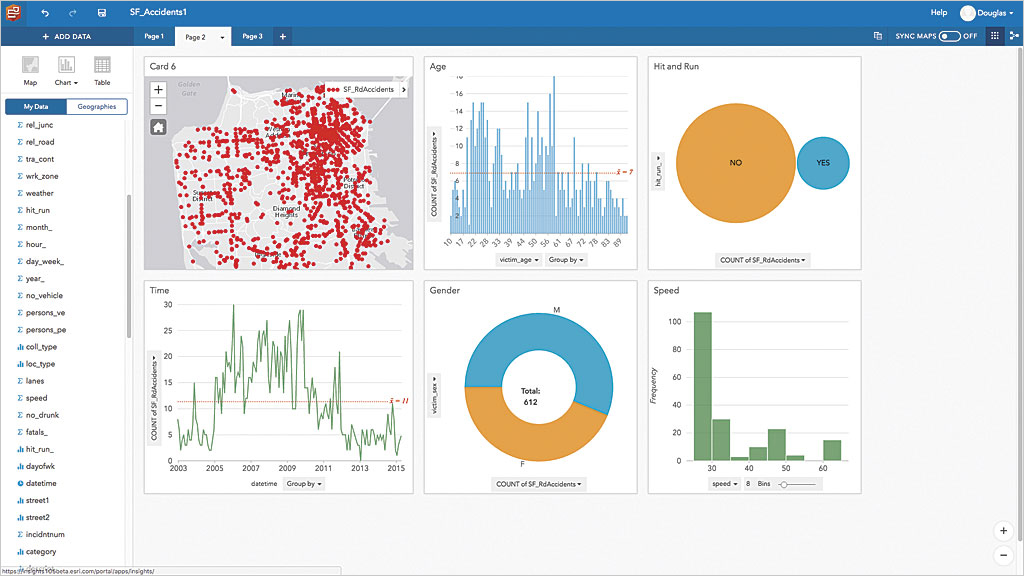
Insights for ArcGIS, debuting with ArcGIS 10.5, is an innovative web-based app that provides interactive discovery and exploration of both spatial and nonspatial data. Insights can incorporate data from enterprise databases, such as SQL Server and SAP HANA; geodatabases; Microsoft Excel spreadsheets; and any data that can be brought into ArcGIS as a feature layer.
Insights uses a smart, graphical user interface (UI) that analyzes data as it is added and recommends appropriate data exploration tools and visualizations. Insights projects are managed in workbooks that include data connections, iterative analysis, visualizations, workflows, and the information produced by analysis. Workbooks contain pages for collecting related content. On a page, data is visualized on cards as maps, charts, and tables.
Cards are the primary way to interact with Insights for ArcGIS. Analysis happens dynamically. The connected nature of the card interface provides on-the-fly synchronization between data views. Create, update, and compare maps, charts, and tables; draw buffers; aggregate numeric data across any geography; apply spatial tools; and slice and summarize data by any field—all using cards.
The app automatically tracks and diagrams workflow steps. This makes analysis workflows repeatable and verifiable. Integration with ArcGIS Enterprise lets Insights workbooks be shared and viewed across the organization.
Tools for Developers Too
ArcGIS is code free by design. Everything from running analyses to creating web apps can be accomplished without writing a single line of code. However, ArcGIS 10.5 has many GIS tools for developers, programmers, and data scientists. It introduces ArcGIS API for Python, which provides new options for scripting and automating analysis and administrative tasks within the ArcGIS platform. It is especially useful when applied to ArcGIS Online or ArcGIS Enterprise. ArcGIS API for Python integrates well with Jupyter Notebooks and the SciPy stack and includes modules that allow display and modification of maps directly from Jupyter Notebooks.

