Do you have layers that occasionally need to be updated?
The workflow described in this article uses layer views to make updates quick and easy, and efficiently manage important feature layers.
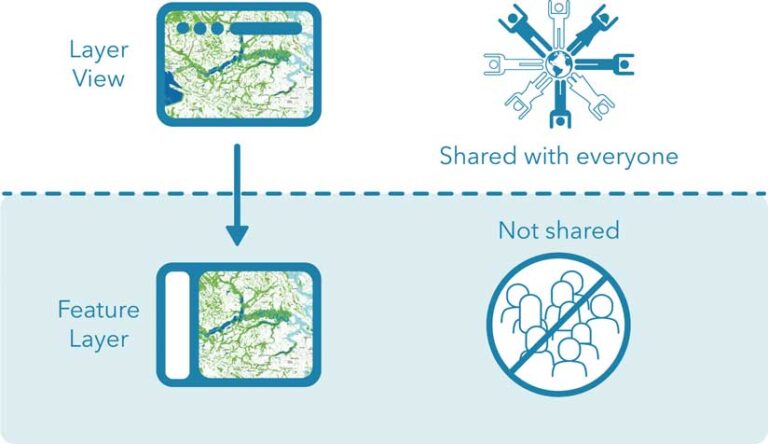
What Is a Layer View?
A hosted feature layer view looks and acts like a hosted feature layer but doesn’t have its own data. As the name implies, layer views are simply a second view of a hosted feature layer that lets you maintain a public-facing view while keeping its feature layer hidden.
This simple architecture—a shared layer view and a hidden feature layer—enables you to do updates out of sight of your users and make updates with minimal impact. ArcGIS Online provides a simple process for switching which feature layer a layer view uses. Layer swapping is a powerful technique that will make your work easier.
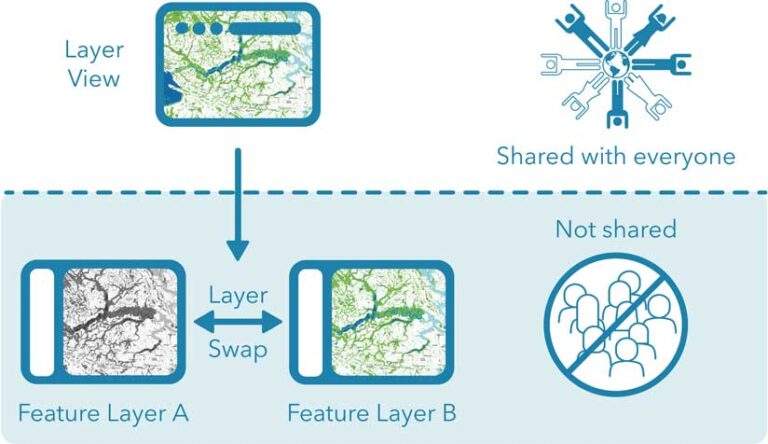
The Benefits of Layer Swapping
In addition to letting you perform seamless and instantaneous data updates, using layer swaps hides the lengthy publishing process, while giving you time to check the layer prior to changing a public-facing layer. If something in your updated layer doesn’t look right, you can quickly and easily swap back to the old layer. Symbology, pop-up configuration, and other properties can be saved in the layer view and will be maintained after the swap. Maintaining old feature layers leaves an archive of past versions.
Layer swap architecture is particularly useful when working with large layers. Updating a very large feature service can take some time—from minutes to hours—and a layer swap enables you to hide that layer while it publishes. This means you can take your time and check your work before sharing it with your users.
Performing a Layer Swap Is Quick and Easy
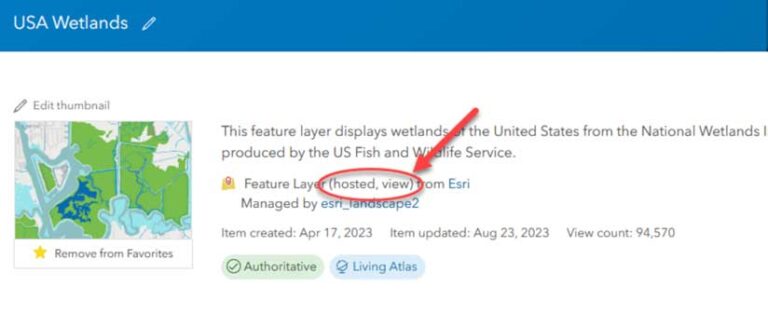
Start with a view layer. If you need help creating a view layer, read “Introducing the new create and update view layer experiences” to get started. Note that you must be the owner or administrator of a hosted feature layer to create and manage layer views from it.
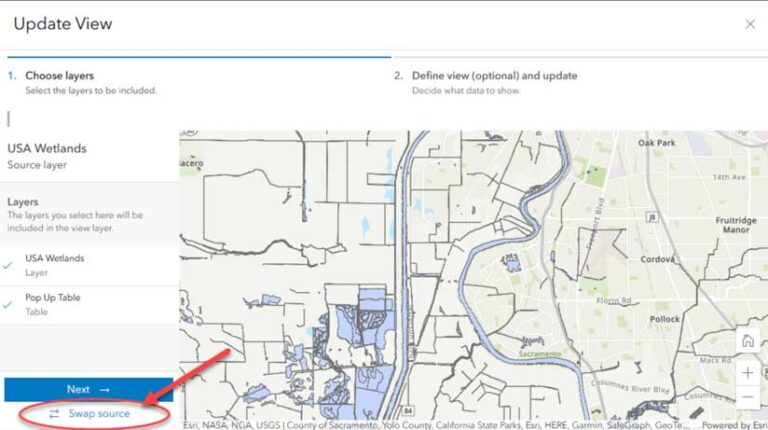
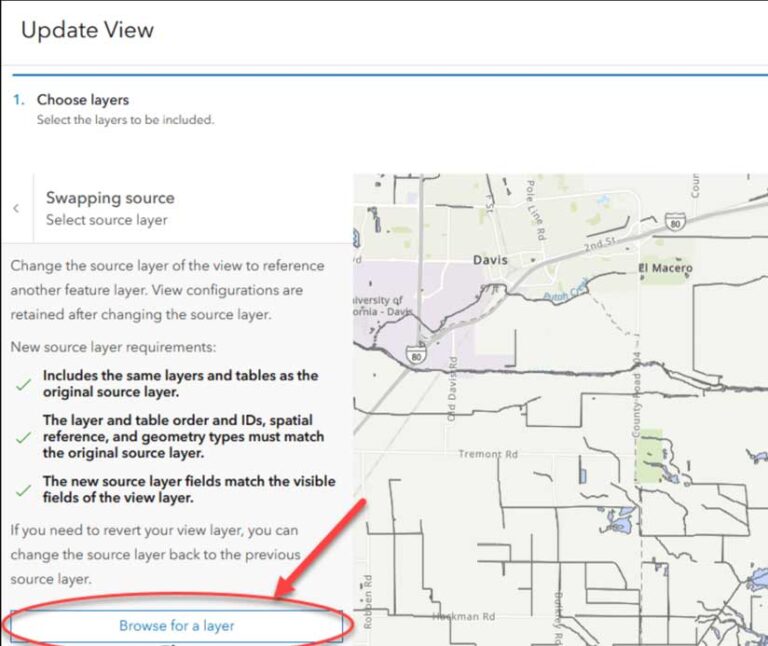
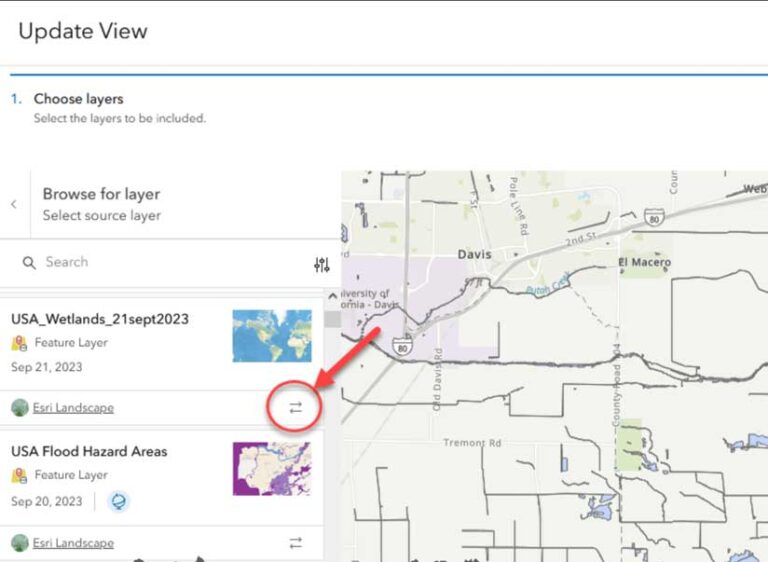
From the layer view’s item page, click the Settings tab and scroll down to the bottom of the window and click Update View. After the Update View window opens, click Swap source at the bottom of the window. After reviewing the source layer requirements, click Browse for a layer. Locate the replacement layer and click the arrows to swap layers. You can confirm that the layers swapped by looking at the source layer on the item page for the layer view.
Things to Know
While the layer swap is straightforward, there are a couple of things to keep in mind. The most important is that the schemas of the new and old feature layers should match. The new layer must include the same layers and tables as the original source. If you run into issues, make sure these things are the same in both layers:
- Coordinate system
- Spatial reference
- Geometry type
- Layer and table order must match
- Fields in the new attribute table must match the visible fields of the old layer
- Layer ID numbers must match
Use Layer Swaps in Your Work
Taking the time to set up a layer view will allow you to work behind the scenes and give your maps the professional edge that users expect from a top-quality product. Keep your data up-to-date with seamless transitions to give your users confidence that your layer will be there when they need it.

