Bulgaria creates GIS for managing protected areas
In August 2013, the Bulgarian Ministry of Environment and Water (MEW) began using a unified GIS for the sustainable and transparent management of more the than 37,400 square kilometers of the country that are protected by Natura 2000.
What Is Natura 2000?
Created to ensure the long-term survival of Europe’s most valuable and threatened species and habitats, Natura 2000, the centerpiece of the European Union’s (EU) nature and biodiversity policy, is based on a broader concept of conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. It is a policy that holds that people and wildlife can coexist in harmony. Therefore, the EU-wide network of protected areas is not limited to nature reserves.
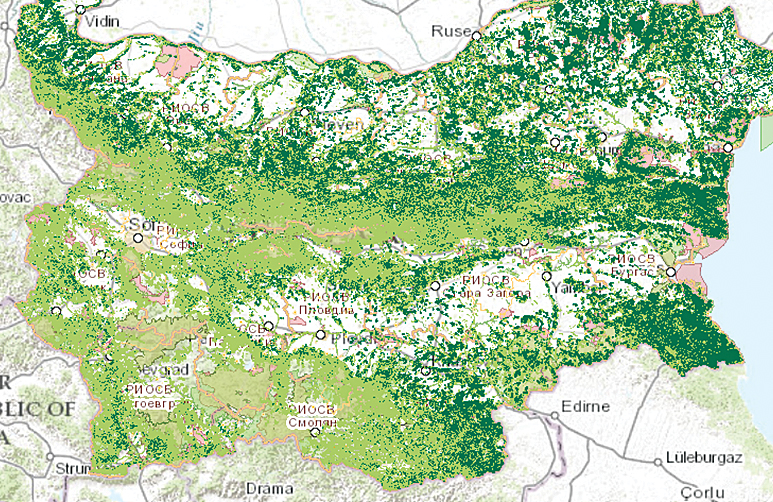
Natura 2000 is also a testimony to the commitment of all EU member states to work for biodiversity conservation. It is based on two key EU agreements related to the environmental preservation and biodiversity—the Birds Directive and the Habitats Directive. These two directives are also incorporated into Bulgarian law through the Biodiversity Act. Bulgaria has some of the largest Natura 2000 areas in Europe. Nearly 34 percent of its territory is part of this network.
The GIS for Natura, the first-of-its-kind GIS, centralizes scattered and inconsistent information about protected areas, assessments of compatibility, related registers, and documents. Besides powerful back-office GIS functionality, which supports preservation, planning, and management of the ecological network, the system also includes a public web application.
The unified GIS makes management of these protected areas more effective, transparent, and verifiable. Vesela Savova, project manager in MEW, noted that, “Moreover, we made a big step towards meeting the requirements of a number of EU directives in this field.”
Conserving Biodiversity
The ministry’s priorities include the development of management plans for protected areas, control of compliance regimes in those areas, assessments of the compatibility of investment projects, maintenance of public registers, and reporting to the European Commission based on a number of directives.
In carrying out these responsibilities, MEW faces many challenges. Different parts of the ministry collect data in different ways. The resultant data is heterogeneous, sometimes inconsistent, and often redundant. It also varies in precision, coordinate system, and format.
Lack of a single database for Bulgaria’s portion of the Natura 2000 ecological network hinders the work of experts and coordination between different administrative units, business, and nongovermental organizations (NGOs). It also hampers implementation of the ministry’s commitments to the European Commission, including the INSPIRE Directive.
MEW launched a project called the Development and Deployment of the Unified Information System for the Protected Areas of Natura 2000 Ecological Network to meet these challenges. It was funded under the European Operational Programme Environment. After a tender procedure, Esri Bulgaria Ltd. was selected to develop and implement the system as leading party in the Consortium NATURA-GIS.
From Scattered to Unified
To achieve the project’s objectives, Esri Bulgaria’s team initially made a business analysis of MEW’s processes regarding management of protected areas and assessment of investment project compatibility. It also studied and analyzed all data available from different administrative units and the coordination between those units.
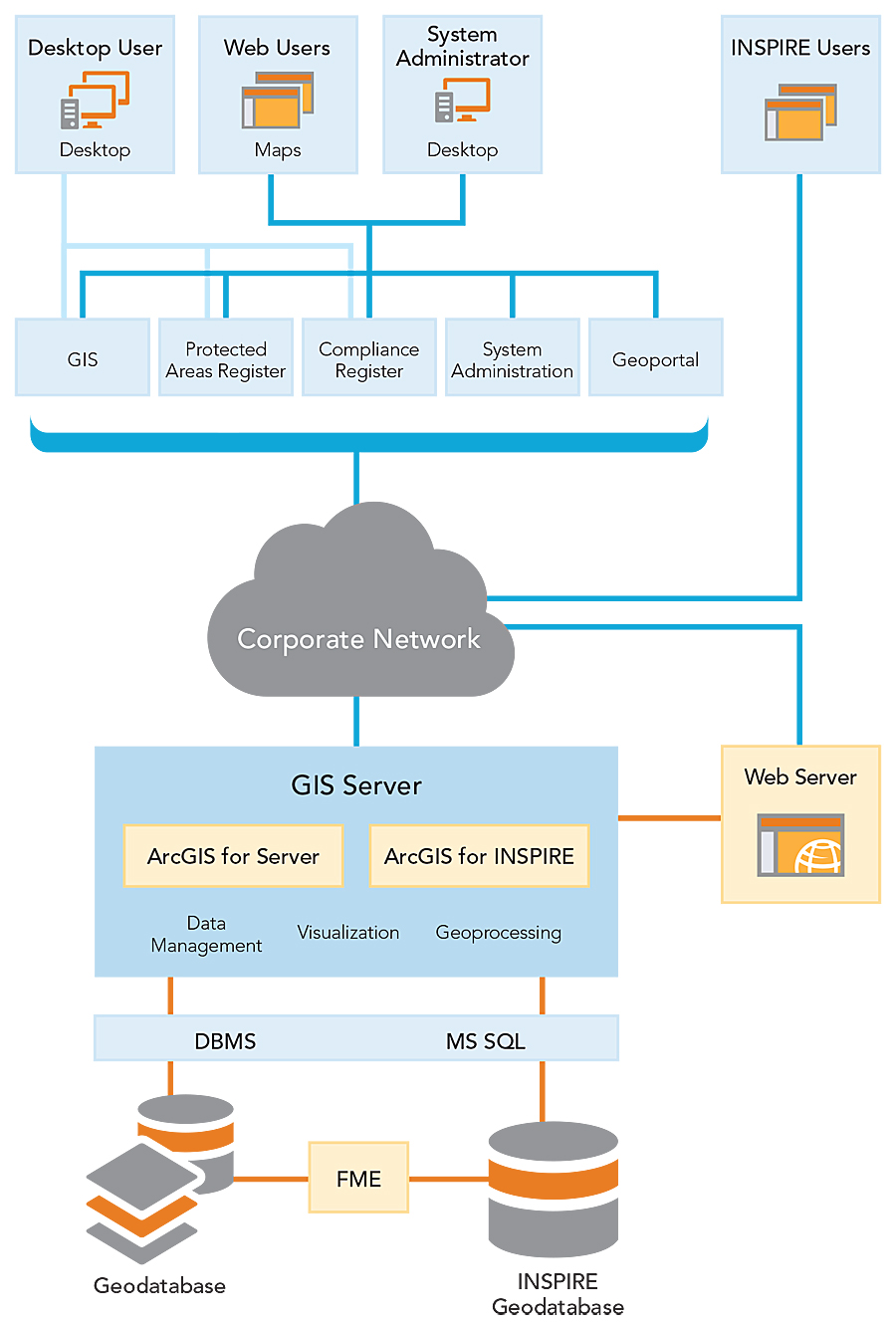
Based on this analysis, Esri Bulgaria designed a GIS for the protected areas. The GIS creates and maintains a single centralized database and powerful functionality, via desktop and the web, that uses Esri software: ArcGIS for Server, ArcGIS for Desktop, ArcGIS for INSPIRE, FME, and various extensions. Terabytes of data were processed, validated, verified, and integrated into the system. A total of 988 layers were incorporated into the geodatabase. A specific geodatabase with harmonized data was built and published via a special geoportal based on Esri Geoportal Server to meet the EU INSPIRE Directive.
The four functional modules—the GIS, the Register of Protected Areas, the Register of Procedures for Compatibility Assessment, and the Web Application—were developed as part of the system to meet MEWS identified needs.
GIS Module
The GIS module provides rich GIS functionality and enables MEW’s experts to identify protected habitats, species, and objects on a dynamic web map, as well as edit the associated spatial and attribute data, perform analyses, and review relevant documents. To meet the needs of different system users, the module provides a set of thematic maps that include, among others, a topographic map, an orthophoto map, and a hydrographic map.
Register of Protected Areas Module
The Register of Protected Areas module provides rich capabilities for entering, editing, maintaining, querying, analyzing, and managing data for protected areas. In this module, users can generate, edit, and export standardized Natura 2000 forms pursuant to EU legislation. The module also provides rich capabilities for working with metadata.
Register of Procedures for Compatibility Assessment
By using the Register of Procedures for Compatibility Assessment, users are able to enter, store, analyze, and manage all the information and documentation related to these procedures. Users can enter the location of compatibility assessments and perform various geospatial and statistical analyses with them and then export the results in the multiple formats supported by the system.
Web Application
The web application provides public access to current information about the spatial scope, location, and functional status of protected areas and various documents associated with them. Users can search protected areas by terms such as name, ID, and type and filter the results by different criteria. This ensures transparency in the conduct of the administrative procedures.
Integration with Other Information Systems
In accordance with identified needs, the GIS for protected areas was integrated with other ministry information systems, including the Register of protected areas in the Executive Environment Agency, the Biodiversity information system, and the information system for permits issuing and water management. In addition, the geodatabase Register of Procedures for Compatibility Assessment liaise with the public Register of Procedures for the Environmental Impact Assessment of the Executive Environment Agency.
IT Project of the Year
Computerworld Bulgaria awarded the Ministry of Environment and Water the IT Project of the Year in the category National IT Projects Implemented in Government Administration for the GIS for Natura 2000.
When Mihail Mihailov, director of Protected Areas, Department of MEW, accepted the award, he said, “The award proves that when the ministry took the decision to build GIS for Natura 2000, it was on the right track.”
“GIS for Natura 2000 solves strategic national objectives for protection of nature areas and puts Bulgaria in the forefront of countries that have successfully implemented the recommendations of the EU’s environment directives,” said Evgenia Karadjova, CEO of Esri Bulgaria.
For more information, contact Vesela Savova, project manager, Ministry of Environment and Water; Anastasia Chotrova, GIS expert, Esri Bulgaria; or Yanko Govedarov, team lead, Esri Bulgaria.

