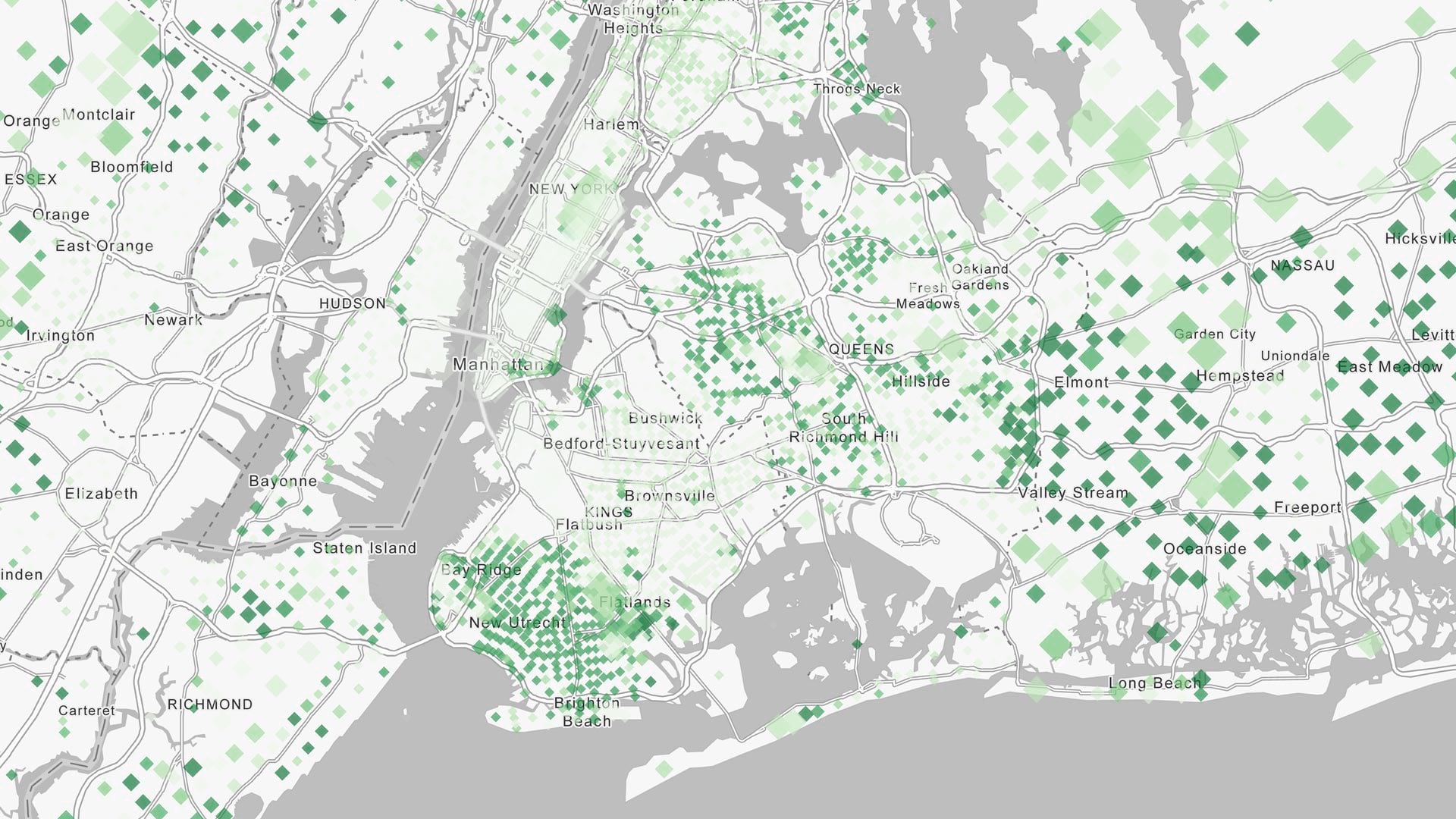
As organizations require ever more storage for their data, data storage technologies need to adapt to provide adequate data retention and processing. Cloud data warehouses do this, making data such as point-of-sale information, telemetry data from sensors, and sales leads generated by websites easier to access and process. For Esri users, ArcGIS Pro 2.9 (and later) and ArcGIS Enterprise 10.9.1 (and later) offer support for connecting to cloud data warehouses and publishing that data.
The Advantages of Cloud Data Warehouses
Anyone who works with constant streams of data—whether cataloging sales transactions for a grocery store chain or tracking data produced by delivery truck fleets—needs a data storage solution that can keep up with enormous intakes of structured data.
Traditional databases may run into challenges when serving this data to a wide audience. If the data is stored on premises, an existing deployment would likely need to be scaled up, which comes with considerable cost. If a dataset is used as a source for an app that’s available worldwide, making the data accessible at that scale becomes a significant challenge.
Cloud data warehouses offer several advantages over other forms of structured data storage, including the following:
- Lower total cost of ownership: Cloud data warehouses reside on infrastructure that is maintained by a data center. This off-loads the costs of setting up and maintaining the hardware and networking requirements.
- Improved speed and performance: As opposed to traditional structured data solutions, cloud data warehouses are systematically engineered with data access in mind. Multiple servers are implemented for optimal load balancing, which results in greater efficiency when retrieving data.
- Better data access and integration: A common benefit of working in the cloud is the ability to make services and data available across multiple regions. This is an important capability of cloud data warehouses because they service the data constantly around the globe.
- Scalability and elasticity: Consistent with other cloud-based services, cloud data warehouses can scale indefinitely to meet users’ needs.
How to Access Data Stored in a Cloud Data Warehouse
The ability to connect to and use data from cloud data warehouses was implemented in ArcGIS Pro 2.9 and ArcGIS Enterprise 10.9.1 on Windows, Linux, and Kubernetes. The software supports connections to three cloud data warehouses: Google BigQuery, Snowflake, and Amazon Redshift.
Adding this data to ArcGIS Pro is like adding data from any other database. One of the main challenges of working with cloud data warehouses, however, is access. There is a cost associated with accessing data stored in cloud data warehouses, which is something developers need to keep in mind when building web maps or apps that rely on this data.
To balance cost and access, data publishers can publish data from cloud data warehouses to ArcGIS Enterprise as map services. There are three ways to do this, based on how frequently users need to retrieve the data stored in cloud data warehouses:
- Accessing data directly: Retrieving data stored within a cloud data warehouse is a great way for data publishers to experiment with how structured and semistructured data may behave with other workflows. When they publish a map image layer, it references the data warehouse directly, querying data as needed to fulfill requests. Due to the costs associated with retrieving the data, this workflow should only be considered for smaller datasets or when the most up-to-date data is required.
- Accessing data via a snapshot: When publishing data in a cloud data warehouse as a snapshot, the data that’s stored in the cloud data warehouse is copied to ArcGIS Data Store. When a map image layer needs to retrieve the data, it references a location on ArcGIS Data Store rather than in the cloud data warehouse. This configuration allows organizations to avoid the costs associated with accessing the data directly in the cloud data warehouse. Bear in mind, however, that updates made at the cloud data warehouse level are not automatically applied to the snapshot. To ensure that updates carry through, data publishers need to conduct on-demand updates within the ArcGIS Enterprise portal.
- Accessing data via a materialized view: This method of accessing data in a cloud data warehouse supports query layers within ArcGIS Pro. In a materialized view, requests to retrieve data are still made directly to the cloud data warehouse but not against the data itself. Instead, the requests are made to an appropriate cached query in the cloud data warehouse. This is a middle-of-the-road option for data publishers who need the most up-to-date data on a clearly defined subset of the total dataset. Apps that require faster query performance, as opposed to faster drawing performance, should employ materialized views over snapshots.
Keeping Up with the Evolution of Big Data
As much of the world moves toward wider adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) technology and Web 3.0, the amount of data being produced will only continue to scale up. Cloud data warehouses are a widely adopted standard for users who work with an immense amount of structured data.
ArcGIS Pro 2.9 (and later) and ArcGIS Enterprise 10.9.1 (and later) offer several ways to access data in cloud data warehouses, allowing users to more easily—and cost-effectively—explore, visualize, and share large volumes of structured data. To learn more about how Esri supports connecting to cloud data warehouses, read the following blog posts on ArcGIS Blog: