For more than 20 years, Esri and Microsoft have partnered to deliver innovative technology that empowers customers with location-based insight. This long-standing relationship has enhanced product integrations via ArcGIS for Microsoft, which brings ArcGIS capabilities and data directly into the secure and familiar Microsoft environment.
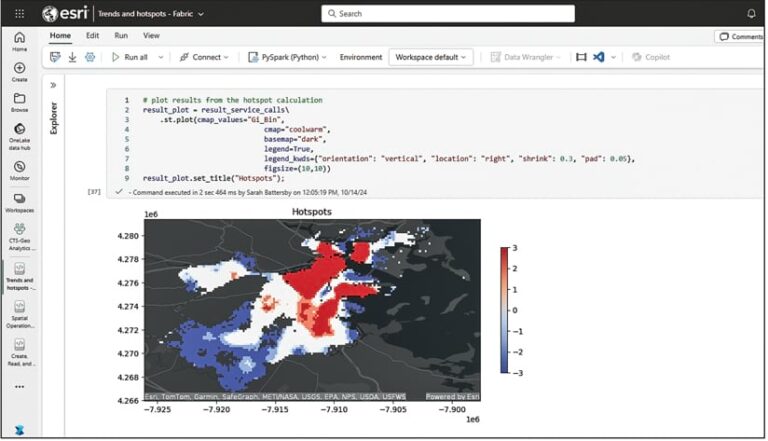
New to the suite of integrations available for Microsoft users is ArcGIS GeoAnalytics for Microsoft Fabric. Releasing this spring, GeoAnalytics for Fabric allows data scientists and data engineers to conduct spatial data integration, transformation, enrichment, and analysis at scale using Apache Spark, a distributed computing framework for processing large amounts of data.
Users can seamlessly access Esri’s advanced spatial analytics tools within Microsoft Fabric to detect patterns, perform predictive analytics, or produce business intelligence-ready data for exploration and strategy development. This results in powerful spatial insight that can easily be shared across organizational tools such as Microsoft Fabric, Microsoft 365, Microsoft Power BI, and Esri’s ArcGIS environment.
Together, Microsoft and Esri Offer Unmatched Value
ArcGIS for Microsoft seamlessly integrates ArcGIS capabilities and data with Microsoft productivity apps, intelligence services, and data platforms. It allows users to access and leverage geospatial information within Microsoft products such as Microsoft 365, Microsoft Fabric, and Microsoft Power Platform. This lets users across an organization—from data analysts performing complex spatial analyses to executives using spatial insight to make operational decisions—easily share location data and collaborate on important projects.
With ArcGIS for Microsoft, data analysts and data scientists can visualize and analyze data at scale and gain a deeper understanding of spatial relationships and underlying patterns. Users can uncover hidden trends and correlations that might not be apparent in traditional data analysis, leading to more informed and effective decision-making.
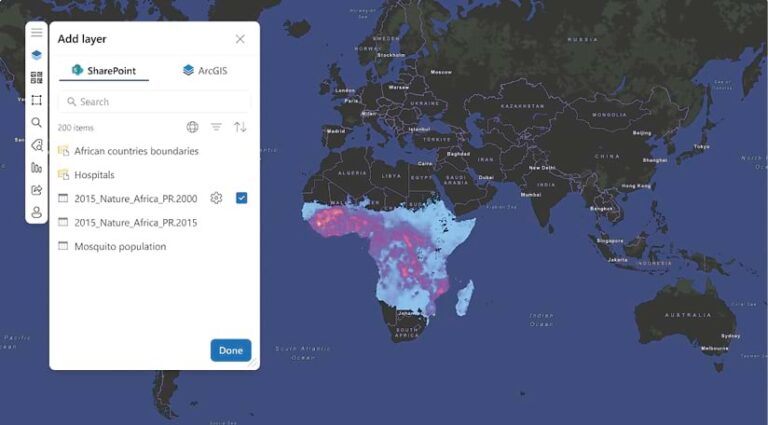
Because teams can work with ArcGIS geospatial data and apps directly in the Microsoft environment instead of switching between platforms, users are more productive and can collaborate more easily and efficiently. Additionally, sensitive information remains protected with Esri and Microsoft’s robust identity and access management solutions, as well as role enforcement. These safeguards—which comply with data privacy regulations and organizational policies—ensure that only authorized users can access an organization’s ArcGIS data.
One notable integration is that ArcGIS capabilities work in Microsoft’s Power Automate, an end-to-end cloud automation platform that helps users automate business processes through self-service configuration, without significant or costly involvement from IT. This integration can handle complex geospatial tasks, reducing manual effort and the potential for errors. And for developers, ArcGIS Maps SDK for .NET offers tools to build robust geospatial and location intelligence apps for both desktop and mobile platforms. This SDK enables developers to create custom apps that work seamlessly with existing Microsoft tools, enhancing the functionality and usability of geospatial data.
Add the Geospatial Perspective to Data Analysis
One of the most exciting new releases in the Microsoft-Esri ecosystem is ArcGIS GeoAnalytics for Microsoft Fabric. This new Spark-native library is packed with geospatial analytics tools to help users discover where things are occurring, how they relate, and which actions to pursue. It integrates directly into Fabric’s data science and data engineering workloads, allowing users to work with geospatial data—from integration and transformation to enrichment and analysis—within Microsoft Fabric’s Spark-based notebooks.
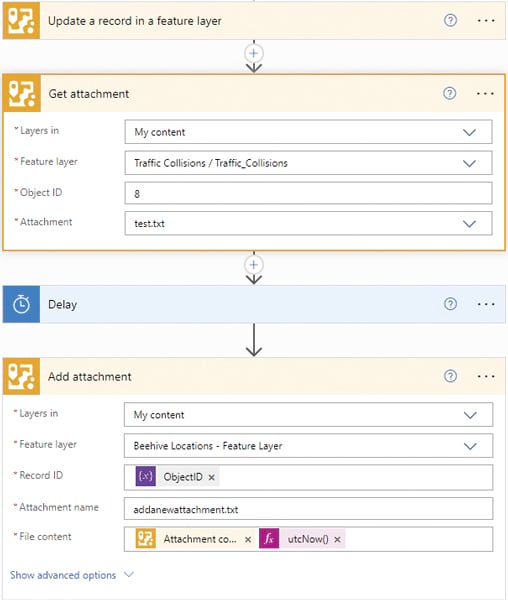
With GeoAnalytics for Fabric, users can do the following:
- Automate spatial data engineering and transformation: This allows users to streamline the process of managing and transforming geospatial data so they can increase efficiency and accuracy in their projects.
- Enrich data with location context: Users can enhance individual data points and big data analytic workflows by bringing in contextual datasets.
- Analyze events geographically: By incorporating geospatial analytics into Microsoft Fabric, users can discern patterns and trends in their data to gain a better understanding of where—and why—events are occurring.
- Visualize spatial relationships: Users can explore how different locations influence and relate to each other.
- Identify strategic locations: Organizations can improve their operations by finding the most strategic locations with ideal situational characteristics.
- Integrate with Microsoft Power BI: Users can deliver the results of their analyses in Microsoft Power BI or take their exploration further by leveraging the powerful interactive mapping capabilities of ArcGIS Online and ArcGIS Enterprise.
A Continued Commitment to Innovation
The ArcGIS for Microsoft team continues to enhance integrations between the two platforms and develop new products to provide Microsoft users with the spatial capabilities of ArcGIS technology. This ongoing commitment to innovation and integration ensures that organizations can harness the full power of geospatial data to drive business outcomes.