Data quality plays an important role in any organization that has adopted and is using GIS technology. When data meets agreed-on standards for quality, its positive impacts are realized in multiple ways. For executive leadership, good data quality means minimizing risk in decision making by avoiding the use of faulty or incomplete information. This, in turn, keeps the organization’s reputation intact among its customers and stakeholders. For GIS managers, good data quality means decreased operational costs because the time spent fixing poor-quality data is now directed toward higher-value tasks, such as modeling and analysis. Most important, for data consumers, quality data means that they can finally realize the efficiencies and benefits of leveraging good data in their daily work.
Since its release in 1999, many organizations have implemented and managed their quality control processes with ArcGIS Data Reviewer for Desktop. This extension serves as an efficient replacement to traditional QC processes that are executed manually or through custom-built applications. With the ArcGIS 10.1 release, Esri has extended the QC capabilities to additional application platforms (web, mobile) through the new ArcGIS Data Reviewer for Server extension.
ArcGIS Data Reviewer for Server enables opportunities for expanding collaboration throughout the data quality process by providing the following:
- Web services to support the identification of data errors through automated and visual QC methods
- Ways to easily incorporate data quality feedback as an additional function to new or existing web applications
- Capabilities to track and measure data quality in new ways and across multiple reporting platforms
Below are some ways these new capabilities allow QC workflows to be deployed in a more flexible manner by leveraging multiple platforms.
Automated Quality Control
ArcGIS Data Reviewer provides the ability to implement data quality business rules as a series of configurable data validation checks. With the 10.1 release of ArcGIS for Server, organizations can validate their data via web services using those same business rules. These services offload and automate the time-consuming task of data validation to an organization’s intranet or cloud-hosted server infrastructure.
Also, the web services can be scheduled to validate data every time the organization carries out its routine data maintenance operations. Errors detected during these scheduled validations are automatically stored in a central location, which serves as a guide to what needs to be fixed. Using ArcGIS Data Reviewer for Desktop, users can easily navigate to these errors, correct them, and update the correction status to ensure no error was missed.
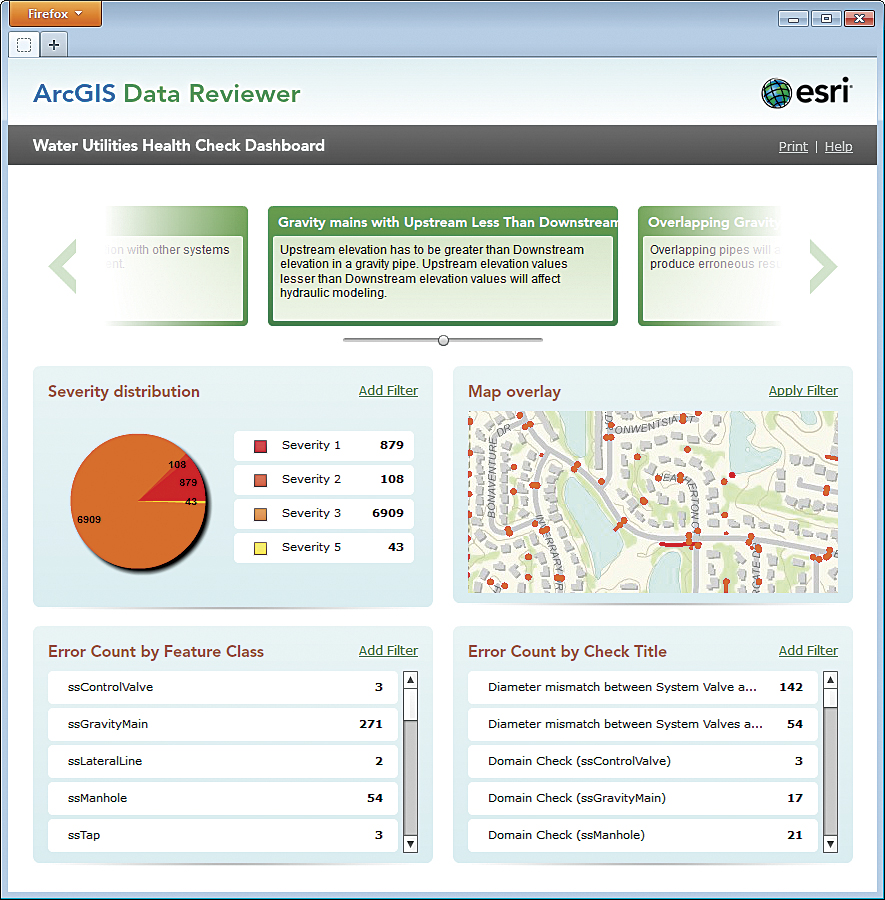
Error results can be summarized using the preconfigured reporting tools or visualized through a web client using ArcGIS Data Reviewer for Server reporting services so managers can gain insight into the health of the organization’s data.
Visual Quality Control
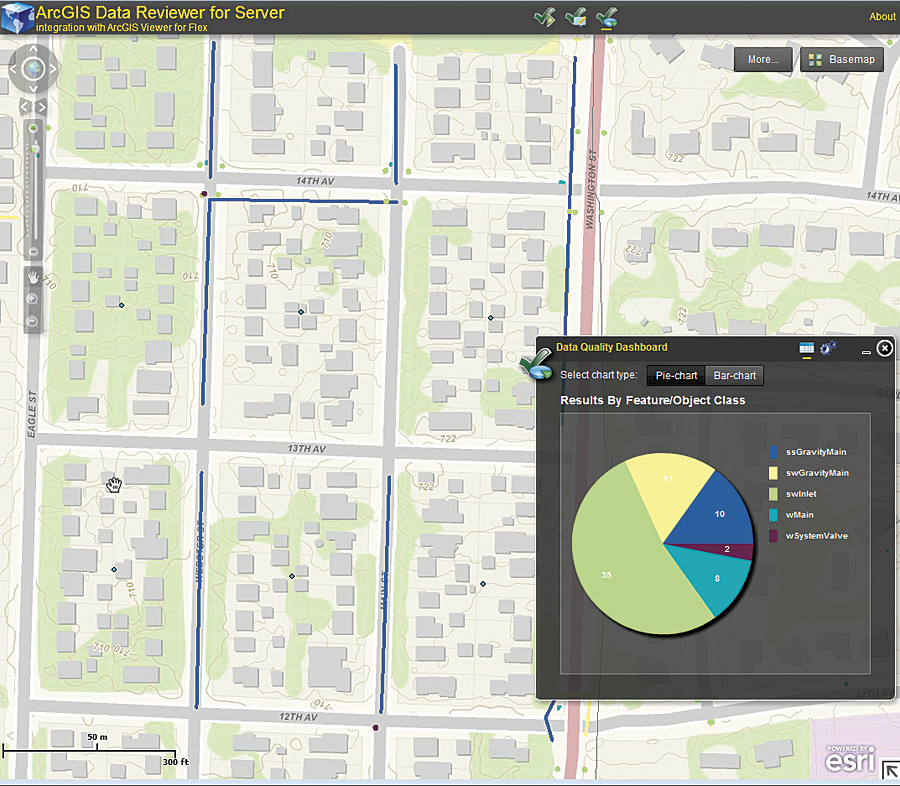
Another key capability of ArcGIS Data Reviewer is the ability to collect and manage error results obtained through nonautomated processes, such as visual review. With ArcGIS Data Reviewer for Server, feedback from a broad community of subject matter experts, stakeholders, and consumers of data can be incorporated as part of the QC process. Web application developers can easily include this feedback as a function of an existing (or new) web application, without the burden of implementing the entire QC workflow from scratch.
For example, ArcGIS Viewer for Flex can leverage the Report Feature widget (available from ArcGIS Resources) to enable a simple error reporting workflow for customer-facing web mapping applications. When customers discover an error, they can easily submit a report identifying its source and location. This report gets logged as part of the ArcGIS Data Reviewer error life cycle management process, where it can be reviewed and corrected.
Data Quality Reporting
Data quality reports help identify and communicate the extent to which data meets established standards of quality. Data producers can evaluate how well a dataset meets the criteria set forth in their production specification, while data consumers can evaluate whether a data product is suitable for its intended application. With ArcGIS Data Reviewer for Server, users can publish reports of error results detected using the automated or visual QC capabilities described above and monitor the health of data. These reporting capabilities can be integrated as a component of an organization’s overall business performance management system or as a stand-alone dashboard for reporting data quality.
By communicating data quality, stakeholders can track data compliance through time and are alerted when data does not meet the agreed-on standards.
For more information, visit esri.com/datareviewer.

