Kaukauna Utilities is a community-minded, environmentally responsible electric and water utility that serves 16,000 customers in the Kaukauna, Wisconsin, area. A few years ago, leaders at the utility decided to update its GIS to improve workflows, increase efficiency, aid with capital budget planning, and address the increasing complexity of the electric system. With help from Esri partner POWER Engineers, Kaukauna Utilities implemented ArcGIS Utility Network, which has helped enrich process improvements at the utility ever since.
According to Kaukauna Utilities’ engineering and operations director Dave Pahl, the upgrade to Utility Network was a “key requirement to the success of many other systems at Kaukauna Utilities.” By leveraging the network topology and integrations, he anticipated “efficiencies in distribution design, system operations, and outage management—all of which provide more reliable service to customers.”
From Manual to Automated
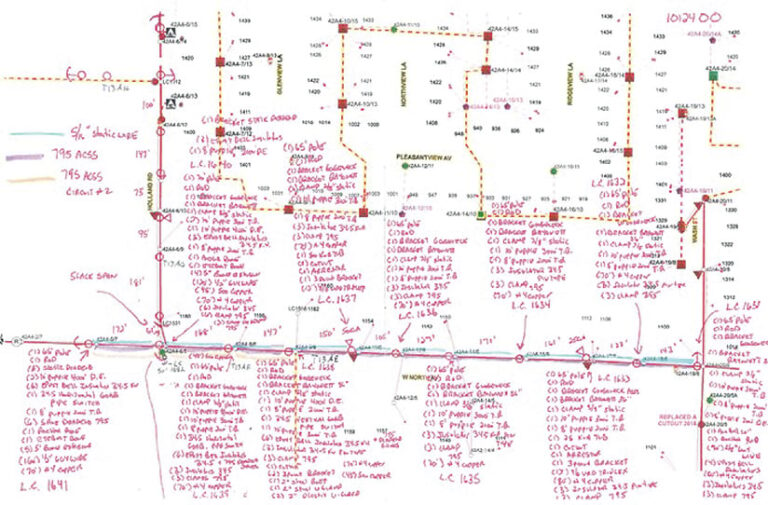
Kaukauna Utilities’ capital budget planning relies heavily on an engineering analysis of Kaukauna’s electric system. The utility uses WindMil software from Esri partner Milsoft Utility Solutions to generate comprehensive visual renderings of its electric grid.
The analysis model was difficult to maintain, however, because it required staff to make updates manually. It was a labor-intensive process and left the data open to errors. As a result, staff only updated the analysis model once a year at budget time, and they weren’t very confident in the model’s accuracy.
To streamline the process of creating and updating its engineering analysis of the electric grid with WindMil, Kaukauna Utilities needed to migrate from the geometric network it was using for network modeling to ArcGIS Utility Network. POWER Engineers specializes in integrating various technologies for utilities and other industries, so Kaukauna Utilities turned to POWER to get help implementing a solution that would automate feature extraction and keep the data accurate and up-to-date.

Saving Hours of Work
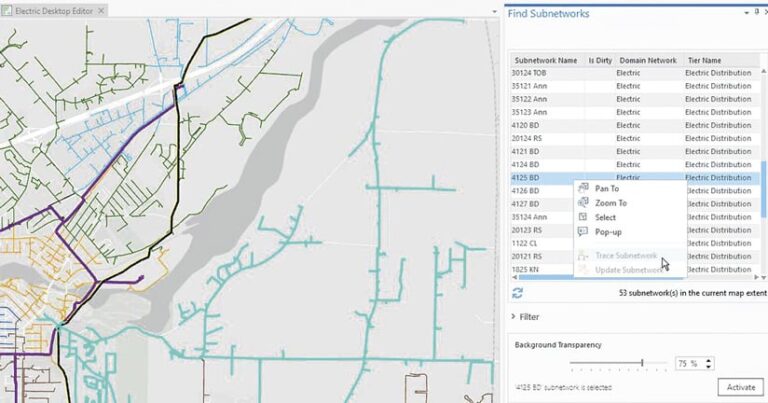
First, Kaukauna Utilities upgraded to ArcGIS Enterprise. It then established a plan to transition from the geometric network to Utility Network.
POWER developed the POWER Network Extractor tool to make it easier for utilities to extract GIS features and their associated network connections and then use this extracted data in third-party apps. The tool enabled Kaukauna Utilities to consume its GIS-based distribution, transmission, and subtransmission networks in the WindMil engineering analysis package.
POWER implemented numerous data quality rules and configured the POWER Network Extractor to run every night to catch all recent updates. The extract in WindMil not only supports the utility’s engineering analysis functions, but it also underpins the utility’s outage management system, provided by DataVoice.
“The extractor runs nightly to update Milsoft’s WindMil, [and] it’s coming through without any errors. It’s pretty amazing,” said Pahl. “POWER’s Network Extractor for Milsoft is one tool that has saved us hours of work.”
More Accurate, Higher-Quality Data
The built-in attribute rules of ArcGIS Utility Network naturally enforce much higher data quality, so Kaukauna Utilities now has more accurate data about its electric system.
Updating the analysis and outage management system models every day has proved to be a significant process improvement. It has dramatically advanced information currency at the utility, boosting employee morale and confidence in the data. By not having to input all the data manually, engineering staff save many hours of work and avoid preventable errors. The utility has a high-quality system analysis model that’s ready for its engineers to use without delay.
The solution also supports Kaukauna Utilities’ other operational software, including its customer information system. This new functionality is helping the utility differentiate between types of customers and improve the system’s accuracy. Now, customers are more consistently associated with the correct service.
Realizing Efficiencies All Around
Implementing Utility Network laid the groundwork for Kaukauna Utilities to make similar improvements in other areas of its business as well, including its water and fiber networks. Mobile staff now leverage ArcGIS Field Maps, for example, to view and collect data on the utility’s electric and water grid. And designers at the utility employ Utility Network to incorporate their electric network designs into WindMil and DataVoice.
“The choice to upgrade to Esri’s ArcGIS Utility Network was based on the realization that future integrations of systems depend on a solid connectivity model, which this network provides,” said Pahl. “Kaukauna Utilities is realizing efficiencies not only in mapping but also [in] engineering and operations.”

