The Boy Scouts of America Earn a Complete Geospatial Picture of Its Philmont Ranch
By John F. Olesak, Vice President, Integrated Intelligence, Northrop Grumman
Highlights
- Philmont GIS staff is building fly-through models so scouts can visualize their itineraries.
- ArcGIS Server 10 is at the core of the Commercial Joint Mapping Tool Kit Geospatial Appliance used by Philmont Ranch.
- The ArcGIS Server Image extension serves the geospatial data, and ArcGIS Desktop 10 manages the data and maps for those services.
Established in 1938, the Boy Scouts of America's Philmont Scout Ranch near Cimarron, New Mexico, encompasses 214 square miles (with access to another 190 square miles of adjacent national forest) of rugged mountain terrain that includes several peaks over 11,000 feet. Every year, thousands of Boy Scouts make the trek to the ranch for a two-week adventure excursion that includes hiking, horseback riding, rock climbing, mountain biking, and camping in and around the ranch's 55 campsites.
To commemorate the Boy Scouts' 100th anniversary, Esri Partner Northrop Grumman presented the iconic organization with high-resolution geospatial data of the ranch. This Philmont dataset will be used by the ranch's GIS and conservation staff, which has used ArcGIS for many years, to better manage the property and enhance the experience of the Boy Scouts that venture to the ranch each year.
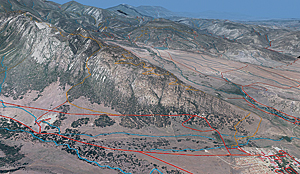
With imagery and GIS, scouts created this dramatic study of the Tooth of Time, the mountain ridge that is famously part of the Philmont Ranch.
The Philmont Scout Ranch was chosen for this project in part for its variety of topological characteristics, such as mountains, rangeland, and lakes and rivers, that provide diversity for the different types of data collected. Several of the Northrop Grumman employees working on the project are also former Boy Scouts or have ties to the Boy Scout community through troop leadership or parenting a scout. In addition to providing a common dataset for showcasing corporate capabilities, this project enabled the company to give something back to the organization during its centennial celebration.
The data was collected over several months in late 2009 and early 2010. The company's fleet of planes collected the data using advanced light detection and ranging (lidar) and electro-optical and infrared sensors to gather four-band imagery at one-foot (330 square miles) and six-inch (70 square miles) resolution and one-meter elevation postings (400 square miles).
Core of the Philmont Project
Besides giving the geospatial data to the ranch, the company donated a Commercial Joint Mapping Tool Kit (CJMTK) Geospatial Appliance (CGA). Though normally, the CGA would provide fast and easy access to maps built from National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) data products and commercial datasets, in this instance, it provides data collected for the Scouts and existing geospatial data (vector data) that Philmont had previously collected and used to manage the ranch.
At its core, the CGA utilizes ArcGIS Server 10, including the ArcGIS Server Image extension, to host the geospatial data as data services and utilizes ArcGIS Desktop 10 to manage the data and maps for those services. The CGA, with all the Philmont data, provides a central repository that can be easily accessed by staff throughout the ranch.
Philmont staff is currently building fly-through models of each of its preplanned itineraries (treks) to better illustrate the trip. The scouts will have a chance to see their trek as they go over logistics during their first day at the ranch. Other examples of how the data will be utilized include
- Managing land-use activities, such as forest typing for logging
- Erosion detection and control
- Better understanding of the current configuration of Philmont's land
- Aiding Philmont in understanding ways to expand its operation to bring more scouts to the ranch
- Helping build better maps for scouts to use on the property
A specific example of the ranch better protecting and preserving the natural resources is related to the impact of the 2002 Ponil Complex Fire. This wildfire consumed 90,000 acres, including approximately 30,000 acres on the Philmont Ranch alone. The forest fire was the largest on record in New Mexico's history, and suppression costs were estimated at $14 million. The imagery allows Philmont staff to check on reclamation projects already in place and identify areas that still need additional work.
About the Author
John F. Olesak is responsible for performance of programs in support of the Director of National Intelligence, NGA, the Defense Intelligence Agency, and the Department of Defense. He has more than 40 years of experience supporting, developing, and managing imagery and geospatial studies and analyses, systems engineering, integration and development programs, research and development activities, and data production programs.
For more information, contact Megan Mitchell, Northrop Grumman (e-mail: megan.mitchell@ngc.com).
See also "Processing the Philmont Geospatial Data."
Related Podcast
How Integrated Imagery and GIS Enhances Critical Decision Making
Lori Thompson, vice president of marketing and support services for ITT VIS, discusses how image processing integrated with GIS is used across different industries for better decision making. Listen to the podcast. [8:00 | 7 MB]